- Lithium Golf Cart Battery
- Forklift Lithium Battery
-
48V
- 48V 210Ah
- 48V 300Ah
- 48V 420Ah (949 x 349 x 569 mm)
- 48V 420Ah (950 x 421 x 450 mm)
- 48V 456Ah
- 48V 460Ah (830 x 630 x 590 mm)
- 48V 460Ah (950 x 421 x 450 mm)
- 48V 460Ah (800 x 630 x 600 mm)
- 48V 460Ah (820 x 660 x 470 mm)
- 48V 500Ah
- 48V 560Ah (810 x 630 x 600 mm)
- 48V 560Ah (950 x 592 x 450 mm)
- 48V 600Ah
- 48V 630Ah
-
48V
- 12V Lithium Battery
12V 150Ah Lithium RV Battery
Bluetooth App | BCI Group 31
LiFePO4 Lithium
Discharge Temperature -20°C ~ 65°C
Fast Charger 14.6V 50A
Solar MPPT Charging - 24V Lithium Battery
- 36V Lithium Battery
- 48V Lithium Battery
-
48V LiFePO4 Battery
- 48V 50Ah
- 48V 50Ah (for Golf Carts)
- 48V 60Ah (8D)
- 48V 100Ah (8D)
- 48V 100Ah
- 48V 100Ah (Discharge 100A for Golf Carts)
- 48V 100Ah (Discharge 150A for Golf Carts)
- 48V 100Ah (Discharge 200A for Golf Carts)
- 48V 150Ah (for Golf Carts)
- 48V 160Ah (Discharge 100A for Golf Carts)
- 48V 160Ah (Discharge 160A for Golf Carts)
-
48V LiFePO4 Battery
- 60V Lithium Battery
-
60V LiFePO4 Battery
- 60V 20Ah
- 60V 30Ah
- 60V 50Ah
- 60V 50Ah (Small Size / Side Terminal)
- 60V 100Ah (for Electric Motocycle, Electric Scooter, LSV, AGV)
- 60V 100Ah (for Forklift, AGV, Electric Scooter, Sweeper)
- 60V 150Ah (E-Motocycle / E-Scooter / E-Tricycle / Tour LSV)
- 60V 200Ah (for Forklift, AGV, Electric Scooter, Sweeper)
-
60V LiFePO4 Battery
- 72V~96V Lithium Battery
- Rack-mounted Lithium Battery
- E-Bike Battery
- All-in-One Home-ESS
- Wall-mount Battery ESS
-
Home-ESS Lithium Battery PowerWall
- 24V 100Ah 2.4kWh PW24100-S PowerWall
- 48V 50Ah 2.4kWh PW4850-S PowerWall
- 48V 50Ah 2.56kWh PW5150-S PowerWall
- 48V 100Ah 5.12kWh PW51100-F PowerWall (IP65)
- 48V 100Ah 5.12kWh PW51100-S PowerWall
- 48V 100Ah 5.12kWh PW51100-H PowerWall
- 48V 200Ah 10kWh PW51200-H PowerWall
- 48V 300Ah 15kWh PW51300-H PowerWall
PowerWall 51.2V 100Ah LiFePO4 Lithium Battery
Highly popular in Asia and Eastern Europe.
CE Certification | Home-ESS -
Home-ESS Lithium Battery PowerWall
- Portable Power Stations
Why are we not using sodium-ion batteries?

Why haven’t sodium-ion batteries taken the spotlight in battery technology despite their promising features? While lithium-ion batteries have long dominated, sodium-ion batteries have been quietly advancing. Let’s unravel the mysteries behind sodium-ion batteries, comparing them to lithium-ion counterparts, understanding their advantages and challenges, and exploring their current and future applications. Get ready for an illuminating journey into the world of sodium-ion batteries!
Comparison between sodium-ion and lithium-ion batteries
Sodium-ion batteries are gaining attention as potential alternatives to lithium-ion batteries. Let’s break down the key factors in comparing these two:
- Energy Density: Currently, lithium-ion batteries have higher energy density, storing more energy in a smaller package. Researchers are working on improving sodium-ion batteries to enhance their competitiveness.
- Cost: Sodium is abundant and cheaper than lithium, making sodium-ion batteries potentially more cost-effective. This affordability could lead to wider adoption across various industries.
- Safety: Sodium-ion technologies are generally considered safer than lithium-ion due to their inherent stability, addressing safety concerns associated with lithium-based systems.
- Performance: Lithium-ion batteries still outperform sodium-ion in terms of cycle life and charging speed. Ongoing research aims to improve sodium-based systems’ overall performance.
While lithium-ion batteries currently excel in certain aspects, it’s crucial to recognize sodium-ion batteries’ potential benefits in terms of cost-effectiveness and enhanced safety features.
Advantages of sodium-ion batteries
Sodium-ion batteries are emerging as promising alternatives to traditional lithium-ion counterparts. Let’s delve into their key advantages:
- Cost-Effectiveness and Abundance: Sodium-ion batteries leverage the abundance of sodium, a more cost-effective and environmentally friendly resource compared to limited lithium. This abundance positions sodium-ion batteries as sustainable solutions for various applications.
- Enhanced Safety Profile: Unlike lithium-ion batteries, sodium-ion technology significantly reduces the risk of fire or explosions. This makes sodium-ion batteries a safer choice for applications like electric vehicles and portable electronics, ensuring user safety.
- Higher Energy Density: Sodium-ion batteries offer higher energy density, allowing them to store more energy in a compact size. This translates to longer-lasting power for devices, extending battery life and minimizing the need for frequent recharging.
- Renewable Energy Storage: Sodium-ion technology holds promise for efficient renewable energy storage. As we shift towards cleaner energy sources, sodium-ion batteries could play a vital role in storing excess renewable energy and releasing it during high-demand periods.
In conclusion, the advantages of sodium-ion batteries make them an attractive option for various industries, contributing to a sustainable and energy-efficient future. Ongoing research to address production challenges will further solidify sodium-ion technology’s role in powering our transition to cleaner energy solutions.
Challenges in implementing sodium-ion technology
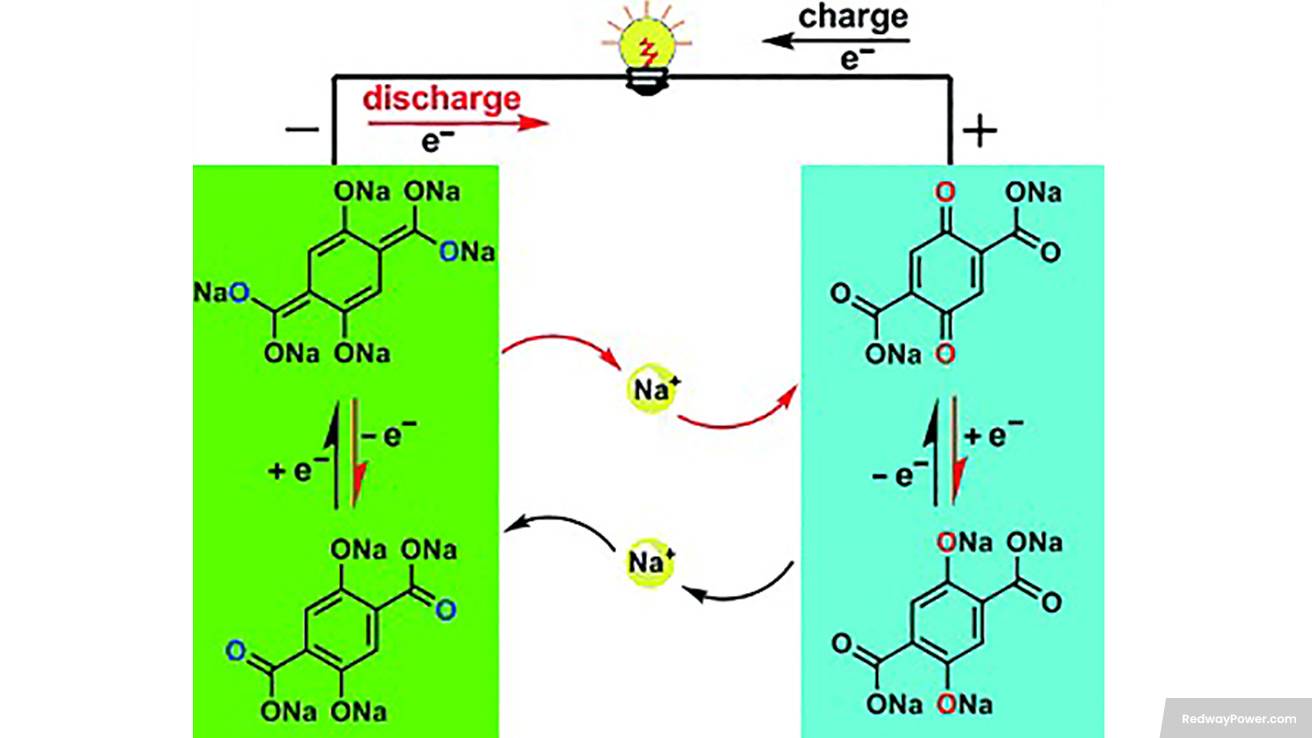
While sodium-ion batteries show promise, their widespread implementation faces significant challenges. Let’s explore these obstacles:
- Cost and Scalability: Despite the abundance of sodium, manufacturing efficient sodium-ion batteries at scale demands substantial investment. Overcoming cost barriers and achieving scalability remain crucial challenges.
- Energy Density Limitations: Sodium-ion batteries currently lag in energy density compared to lithium-ion counterparts. This limitation restricts their application in industries where high energy storage is essential.
- Cycle Life and Stability: Ensuring long cycle life and stability poses a challenge for sodium-ion batteries. The repeated charging and discharging process can lead to electrode degradation, impacting overall battery performance.
- Safety Concerns: Addressing safety concerns specific to sodium-ion batteries is vital. While both lithium-ion and sodium-ion batteries carry risks, understanding and mitigating sodium-related safety issues are essential for widespread acceptance.
- Material Availability and Stability: Despite abundant raw materials for sodium-based electrodes, developing stable electrolytes remains a technical hurdle. Stability in materials is crucial for consistent and reliable battery performance.
- Research Funding Needs: Adequate research funding is imperative for advancing sodium-ion technology. Collaborative efforts and continued financial support from governments, private institutions, and investors are necessary to tackle these challenges and drive innovation.
Tackling these hurdles requires interdisciplinary collaboration among researchers and sustained investments to enhance efficiency, stability, affordability, and overall performance of sodium-ion battery technologies.
Current use of sodium-ion batteries in various industries
While sodium-ion battery technology is in its early phases, several industries are already exploring its potential applications. Let’s delve into these sectors:
- Renewable Energy: Sodium-ion batteries show promise in storing electricity from renewable sources like solar and wind power. This could contribute to efficient energy distribution and storage in the renewable energy sector.
- Transportation: Sodium-ion batteries offer a potential alternative in the transportation industry, particularly for electric vehicles (EVs). With lower manufacturing costs, sodium-ion cells might make EVs more affordable, expanding accessibility to a broader consumer base.
- Grid-Scale Energy Storage: Sodium-ion batteries are emerging as efficient solutions for grid-scale energy storage. As reliance on intermittent renewable energy grows, these batteries can store excess energy during low-demand periods, stabilizing the electrical grid.
- Stationary Power Systems: Sodium-based technologies find application in stationary power systems, serving as backup power supply units for critical infrastructure and off-grid locations with limited access to reliable electricity.
While sodium-ion batteries currently have specific use cases compared to lithium-ion alternatives, ongoing research suggests advancements that may lead to broader adoption across industries. With continuous innovation and investment, sodium-based battery technology could play a pivotal role in achieving a greener future with enhanced energy storage capabilities.
Potential for future advancements and applications
Exploring the future potential of sodium-ion batteries reveals exciting possibilities. Despite current challenges, researchers are diligently addressing obstacles to harness these benefits:
- Electric Vehicles (EVs): Sodium-ion batteries could revolutionize the EV industry, offering a more affordable and accessible option. Their lower cost and abundant raw materials make them a promising solution for creating a greener and more economical transportation system.
- Renewable Energy: Sodium-ion batteries hold significant promise in the renewable energy sector. They could provide an economical alternative for storing excess power generated by wind and solar sources, contributing to a more sustainable and reliable energy grid.
- Off-Grid Solutions: Remote areas and developing regions with limited access to electricity grids can benefit from sodium-ion battery systems. As off-grid solutions, these batteries offer a clean and cost-effective energy source, replacing environmentally harmful alternatives like diesel generators.
In conclusion, while lithium-ion batteries currently dominate, ongoing research may soon position sodium-ion batteries as a viable alternative. With improved performance characteristics on the horizon, sodium-ion technology could redefine how we power our devices, emphasizing affordability without compromising efficiency. Stay tuned for the exciting advancements in this transformative field!

















