- Lithium Golf Cart Battery
- Forklift Lithium Battery
-
48V
- 48V 210Ah
- 48V 300Ah
- 48V 420Ah (949 x 349 x 569 mm)
- 48V 420Ah (950 x 421 x 450 mm)
- 48V 456Ah
- 48V 460Ah (830 x 630 x 590 mm)
- 48V 460Ah (950 x 421 x 450 mm)
- 48V 460Ah (800 x 630 x 600 mm)
- 48V 460Ah (820 x 660 x 470 mm)
- 48V 500Ah
- 48V 560Ah (810 x 630 x 600 mm)
- 48V 560Ah (950 x 592 x 450 mm)
- 48V 600Ah
- 48V 630Ah
-
48V
- 12V Lithium Battery
12V 150Ah Lithium RV Battery
Bluetooth App | BCI Group 31
LiFePO4 Lithium
Discharge Temperature -20°C ~ 65°C
Fast Charger 14.6V 50A
Solar MPPT Charging - 24V Lithium Battery
- 36V Lithium Battery
- 48V Lithium Battery
-
48V LiFePO4 Battery
- 48V 50Ah
- 48V 50Ah (for Golf Carts)
- 48V 60Ah (8D)
- 48V 100Ah (8D)
- 48V 100Ah
- 48V 100Ah (Discharge 100A for Golf Carts)
- 48V 100Ah (Discharge 150A for Golf Carts)
- 48V 100Ah (Discharge 200A for Golf Carts)
- 48V 150Ah (for Golf Carts)
- 48V 160Ah (Discharge 100A for Golf Carts)
- 48V 160Ah (Discharge 160A for Golf Carts)
-
48V LiFePO4 Battery
- 60V Lithium Battery
-
60V LiFePO4 Battery
- 60V 20Ah
- 60V 30Ah
- 60V 50Ah
- 60V 50Ah (Small Size / Side Terminal)
- 60V 100Ah (for Electric Motocycle, Electric Scooter, LSV, AGV)
- 60V 100Ah (for Forklift, AGV, Electric Scooter, Sweeper)
- 60V 150Ah (E-Motocycle / E-Scooter / E-Tricycle / Tour LSV)
- 60V 200Ah (for Forklift, AGV, Electric Scooter, Sweeper)
-
60V LiFePO4 Battery
- 72V~96V Lithium Battery
- Rack-mounted Lithium Battery
- E-Bike Battery
- All-in-One Home-ESS
- Wall-mount Battery ESS
-
Home-ESS Lithium Battery PowerWall
- 24V 100Ah 2.4kWh PW24100-S PowerWall
- 48V 50Ah 2.4kWh PW4850-S PowerWall
- 48V 50Ah 2.56kWh PW5150-S PowerWall
- 48V 100Ah 5.12kWh PW51100-F PowerWall (IP65)
- 48V 100Ah 5.12kWh PW51100-S PowerWall
- 48V 100Ah 5.12kWh PW51100-H PowerWall
- 48V 200Ah 10kWh PW51200-H PowerWall
- 48V 300Ah 15kWh PW51300-H PowerWall
PowerWall 51.2V 100Ah LiFePO4 Lithium Battery
Highly popular in Asia and Eastern Europe.
CE Certification | Home-ESS -
Home-ESS Lithium Battery PowerWall
- Portable Power Stations
What is the Relationship Between Voltage and Amp Hours in Batteries?
The relationship between voltage and amp hours (Ah) in batteries is crucial for understanding battery performance. Voltage represents the electrical potential that drives current, while amp hours indicate the battery’s capacity to deliver that current over time. Together, these factors help determine how long a battery can power a device.
What is Voltage and How Does it Affect Battery Performance?
Voltage, measured in volts (V), indicates the electrical potential difference between two points in a circuit. In batteries, voltage determines how much power can be delivered to a device. Higher voltage typically means more power output, which is essential for devices requiring significant energy.
| Voltage Level | Common Applications |
|---|---|
| 1.5 V | AA/AAA batteries |
| 3.7 V | Lithium-ion cells |
| 12 V | Car batteries |
| 24 V | Electric vehicles |
Understanding voltage is critical because it directly impacts how well a device operates. For instance, a device designed for 12V will not function correctly if supplied with only 6V.
How Does Amp Hours (Ah) Indicate Battery Capacity?
Amp hours (Ah) measure the total charge a battery can deliver over time. Specifically, it indicates how many amps a battery can provide for one hour before being depleted. For example:
- A 4Ah battery can supply 4 amps for 1 hour or 1 amp for 4 hours.
- A 6Ah battery can supply 6 amps for 1 hour or 1 amp for 6 hours.
This metric helps users understand how long a battery will last under specific loads, making it essential for applications requiring sustained power.
What is the Relationship Between Voltage and Amp Hours?
Voltage and amp hours are interconnected but serve different purposes:
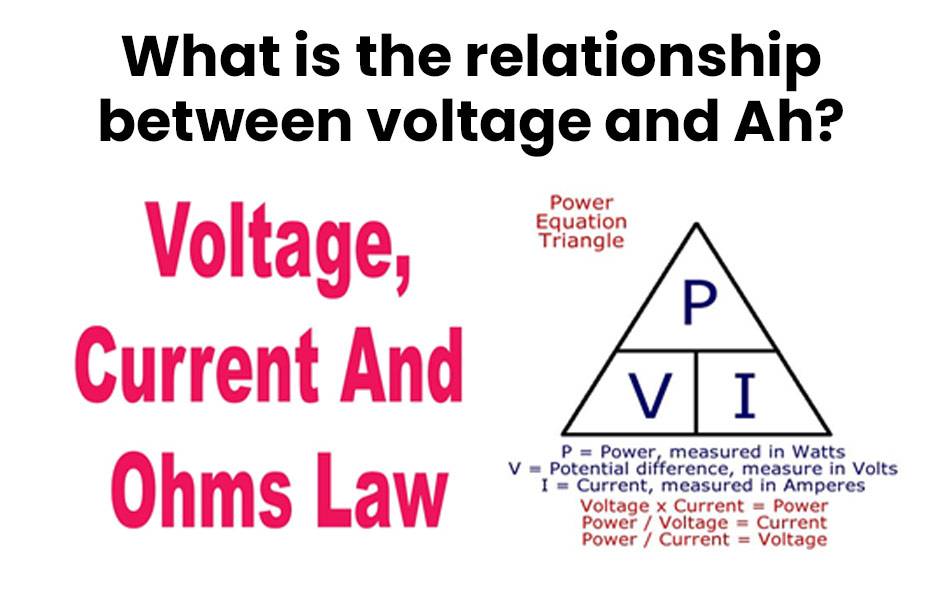
- Power Calculation: The total energy capacity of a battery can be calculated using the formula:
Power W =Voltage V ×Current A
This equation shows how both voltage and current (derived from Ah) contribute to overall power output.
- Energy Storage: The total energy stored in watt-hours (Wh) can be calculated as:
Wh=Voltage V ×Ah
This relationship highlights that both voltage and amp hours are crucial for determining how much energy a battery can store.
Why is Understanding Both Voltage and Ah Important for Battery Users?
Understanding both voltage and amp hours ensures optimal performance when selecting a battery:
- Voltage Compatibility: Devices require specific voltages to function correctly; using an incompatible voltage can damage equipment.
- Capacity Needs: Knowing amp hours helps determine how long devices will run before needing recharging, which is critical for planning usage.
Balancing these factors ensures that users select batteries that meet their specific power demands effectively.
How Do Different Applications Benefit from Specific Voltage and Ah Ratings?
Different applications have varying power requirements:
- Power Tools: Tools requiring sustained power benefit significantly from higher voltages (e.g., 18V or 24V) to generate sufficient torque.
- Long-Duration Applications: Devices like flashlights may benefit from higher amp hour ratings to ensure extended runtime without frequent recharging.
| Application | Recommended Voltage | Recommended Ah |
|---|---|---|
| Power Tools | 18V – 24V | 2Ah – 5Ah |
| Electric Vehicles | 48V – 72V | 20Ah – 100Ah |
| Portable Electronics | 5V – 12V | 1Ah – 10Ah |
Choosing the right combination based on application needs leads to better performance and efficiency.
Can You Have High Voltage with Low Ah or Vice Versa?
Yes, it’s possible to have high voltage with low amp hours or vice versa:
- High Voltage, Low Ah Example: A small device like a camera may operate at high voltage (e.g., 12V) but have low capacity (e.g., 1Ah).
- Low Voltage, High Ah Example: A deep-cycle battery used in solar applications might operate at lower voltages (e.g., 6V) but have high capacities (e.g., 200Ah).
This flexibility allows manufacturers to design batteries tailored to specific needs based on performance characteristics rather than strict adherence to one metric.
What Replacement Options Are Available for Lithium-Ion Batteries?
For those looking for alternatives or replacements, consider:
- Nickel-Metal Hydride (NiMH): Offers decent performance but generally has lower energy density than lithium-ion.
- Lead-Acid Batteries: More affordable but heavier and less efficient compared to lithium-ion options.
- Solid-State Batteries: Emerging technology with potential advantages in safety and energy density.
Redway Power has great solutions for enhancing performance with high-quality lithium-ion batteries tailored to specific needs.
Tips for Battery Wholesale Buyers
When sourcing batteries wholesale, consider these key points:
- Quality Assurance: Ensure manufacturers adhere to strict quality standards.
- Experience: Choose manufacturers with proven expertise in lithium battery production.
- OEM Capabilities: Look for manufacturers like Redway Power, known for their OEM services, ensuring they can meet specific design requirements.
To place an OEM order with a reliable manufacturer like Redway Power, follow these steps:
- Define your specifications clearly.
- Contact the manufacturer to discuss your needs.
- Review samples or prototypes before finalizing your order.
Redway Power Expert Views
“Understanding the distinction between voltage and amp hours is essential for selecting the right battery,” states an expert from Redway Power. “These parameters not only define how a battery performs but also influence its suitability across various applications.”
FAQ Section
- What does voltage represent in batteries?
Voltage represents the electrical potential that drives current through a circuit, indicating how much power a device can draw. - What do amp hours indicate?
Amp hours indicate the capacity of a battery, showing how long it can deliver power before needing recharging. - Can I use a battery with higher voltage than my device requires?
Using a higher voltage than specified can damage your device; always match the battery voltage to your device’s requirements.
- Voltage (V): Voltage, measured in volts (V), determines the strength of an electric charge. Higher voltage means more power output for devices requiring quick bursts of energy, like cameras or drills.
- Ah (Ampere-Hours): Ah measures a battery’s capacity to sustain its output before needing recharging. A higher Ah rating implies longer-lasting power for devices with lower power requirements, such as flashlights or remote controls.
It’s crucial to consider both voltage and Ah when choosing a battery for your device or project. Simply multiplying voltage by Ampere-hours doesn’t accurately measure total energy storage capacity, as batteries have different discharge rates and efficiencies.
Factors that Affect Voltage and Ah
Several factors influence the relationship between voltage and Ah in batteries. Understanding these factors is essential for optimizing battery performance. Let’s explore some key considerations:
- Temperature: Lower temperatures can reduce battery voltage and overall capacity, impacting performance.
- State of Charge: As a battery discharges, its voltage decreases gradually. Therefore, the state of charge affects both voltage and Ah.
- Battery Type: Different battery chemistries have varying characteristics, influencing voltage and Ah measurements.
- Load: The connected load affects battery performance, with higher loads often resulting in lower voltages and decreased capacity.
- Age and Usage Patterns: Over time, batteries naturally degrade, and frequent deep discharge cycles can further reduce capacity.
Considering these factors helps in selecting the most suitable battery for specific applications and ensuring optimal performance over time.
How to Calculate Voltage and Ah
Calculating voltage and Ah (ampere-hours) is essential for understanding battery capacity and performance. Let’s explore the simple steps involved:
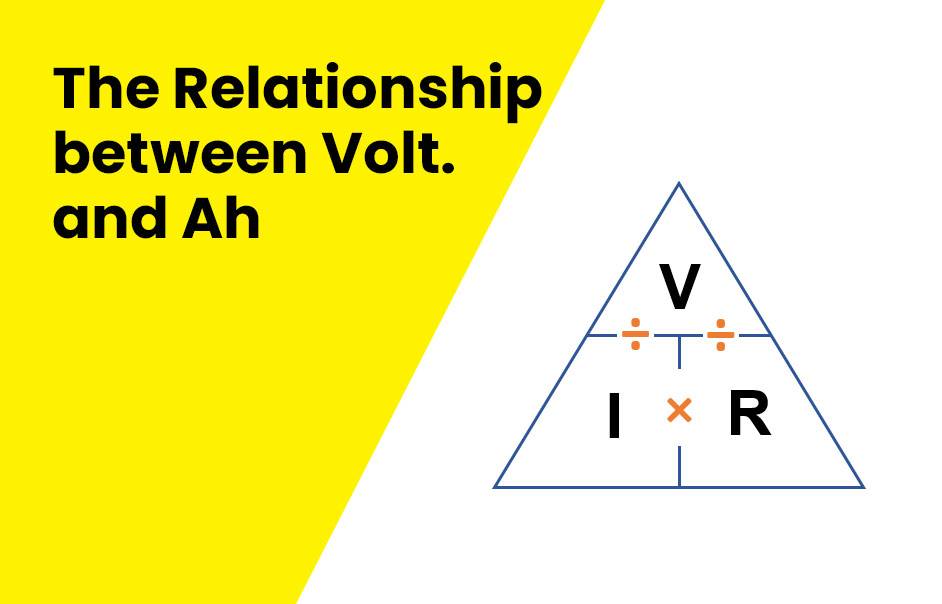
- Voltage Calculation: Measure the potential difference between two points in the circuit using a voltmeter. This measurement, expressed in volts (V), determines the battery’s voltage.
- Ah Calculation: Multiply the current (in amperes) by the time (in hours). This straightforward formula gives you the battery’s Ah rating, indicating its capacity.
Understanding how to calculate voltage and Ah helps us accurately assess a battery’s capabilities for various applications. Consideration of factors like temperature and discharge rate ensures informed decision-making when selecting batteries.
Applications of Voltage and Ah in Everyday Life
Voltage and Ah are integral to various aspects of our daily lives, from powering electronic devices to renewable energy storage. Let’s explore their practical applications:
- Powering electronic devices: Voltage determines the electrical current strength, while Ah indicates battery longevity for devices like smartphones and power tools.
- Electric vehicles: Higher voltage enables faster acceleration, and larger Ah extends the driving range in electric vehicles.
- Renewable energy storage: Batteries with high voltage and Ah capacity store excess energy from sources like solar panels for later use.
- Backup power supply: Batteries with adequate voltage and Ah provide backup power for critical systems during outages or emergencies.
- Portable lighting: Batteries power portable lighting solutions for outdoor activities, ensuring illumination on the go.
- Remote control toys: Battery-operated toys rely on voltage and capacity for efficient performance.
- Garden tools & Lawnmowers: Higher voltage batteries enhance the effectiveness of battery-powered garden tools like lawnmowers.
- Power banks: Power banks with sufficient voltage output keep mobile devices charged while on the move.
Understanding the role of voltage and Ah in everyday applications helps us make informed decisions about battery usage.
Choosing the Right Battery for Your Needs
Choosing the right battery involves considering several factors to ensure it meets your specific needs. Let’s explore these factors:
- Voltage Requirement: Identify the voltage needed for your device and ensure the battery’s voltage matches it for compatibility.
- Capacity Requirement: Assess your power consumption needs and opt for a battery with an adequate Ah rating, indicating its energy storage capacity.
- Application: Consider the intended use of the battery, whether for rechargeable or non-rechargeable applications, to ensure suitability.
- Size and Weight: Take into account any size or weight constraints to ensure the battery fits and doesn’t add unnecessary bulk.
- Operating Conditions: Evaluate environmental factors like temperature and humidity to choose a battery that can withstand the conditions it’ll be used in.
- Cost: Compare prices while considering other factors to find a battery that balances performance and affordability.
By considering these factors, you can select a battery that meets your requirements effectively and efficiently. Always refer to manufacturer guidelines for safety and performance recommendations.












