- Forklift Lithium Battery
-
48V
- 48V 210Ah
- 48V 300Ah
- 48V 420Ah (949 x 349 x 569 mm)
- 48V 420Ah (950 x 421 x 450 mm)
- 48V 456Ah
- 48V 460Ah (830 x 630 x 590 mm)
- 48V 460Ah (950 x 421 x 450 mm)
- 48V 460Ah (800 x 630 x 600 mm)
- 48V 460Ah (820 x 660 x 470 mm)
- 48V 500Ah
- 48V 560Ah (810 x 630 x 600 mm)
- 48V 560Ah (950 x 592 x 450 mm)
- 48V 600Ah
- 48V 630Ah
-
48V
- Lithium Golf Cart Battery
- 12V Lithium Battery
12V 150Ah Lithium RV Battery
Bluetooth App | BCI Group 31
LiFePO4 Lithium
Discharge Temperature -20°C ~ 65°C
Fast Charger 14.6V 50A
Solar MPPT Charging - 24V Lithium Battery
- 36V Lithium Battery
- 48V Lithium Battery
-
48V LiFePO4 Battery
- 48V 50Ah
- 48V 50Ah (for Golf Carts)
- 48V 60Ah (8D)
- 48V 100Ah (8D)
- 48V 100Ah
- 48V 100Ah (Discharge 100A for Golf Carts)
- 48V 100Ah (Discharge 150A for Golf Carts)
- 48V 100Ah (Discharge 200A for Golf Carts)
- 48V 150Ah (for Golf Carts)
- 48V 160Ah (Discharge 100A for Golf Carts)
- 48V 160Ah (Discharge 160A for Golf Carts)
-
48V LiFePO4 Battery
- 60V Lithium Battery
-
60V LiFePO4 Battery
- 60V 20Ah
- 60V 30Ah
- 60V 50Ah
- 60V 50Ah (Small Size / Side Terminal)
- 60V 100Ah (for Electric Motocycle, Electric Scooter, LSV, AGV)
- 60V 100Ah (for Forklift, AGV, Electric Scooter, Sweeper)
- 60V 150Ah (E-Motocycle / E-Scooter / E-Tricycle / Tour LSV)
- 60V 200Ah (for Forklift, AGV, Electric Scooter, Sweeper)
-
60V LiFePO4 Battery
- 72V~96V Lithium Battery
- Rack-mounted Lithium Battery
- E-Bike Battery
- All-in-One Home-ESS
- Wall-mount Battery ESS
-
Home-ESS Lithium Battery PowerWall
- 24V 100Ah 2.4kWh PW24100-S PowerWall
- 48V 50Ah 2.4kWh PW4850-S PowerWall
- 48V 50Ah 2.56kWh PW5150-S PowerWall
- 48V 100Ah 5.12kWh PW51100-F PowerWall (IP65)
- 48V 100Ah 5.12kWh PW51100-S PowerWall
- 48V 100Ah 5.12kWh PW51100-H PowerWall
- 48V 200Ah 10kWh PW51200-H PowerWall
- 48V 300Ah 15kWh PW51300-H PowerWall
PowerWall 51.2V 100Ah LiFePO4 Lithium Battery
Highly popular in Asia and Eastern Europe.
CE Certification | Home-ESS -
Home-ESS Lithium Battery PowerWall
- Portable Power Stations
What is the Bulk Charging Stage in Battery Charging?
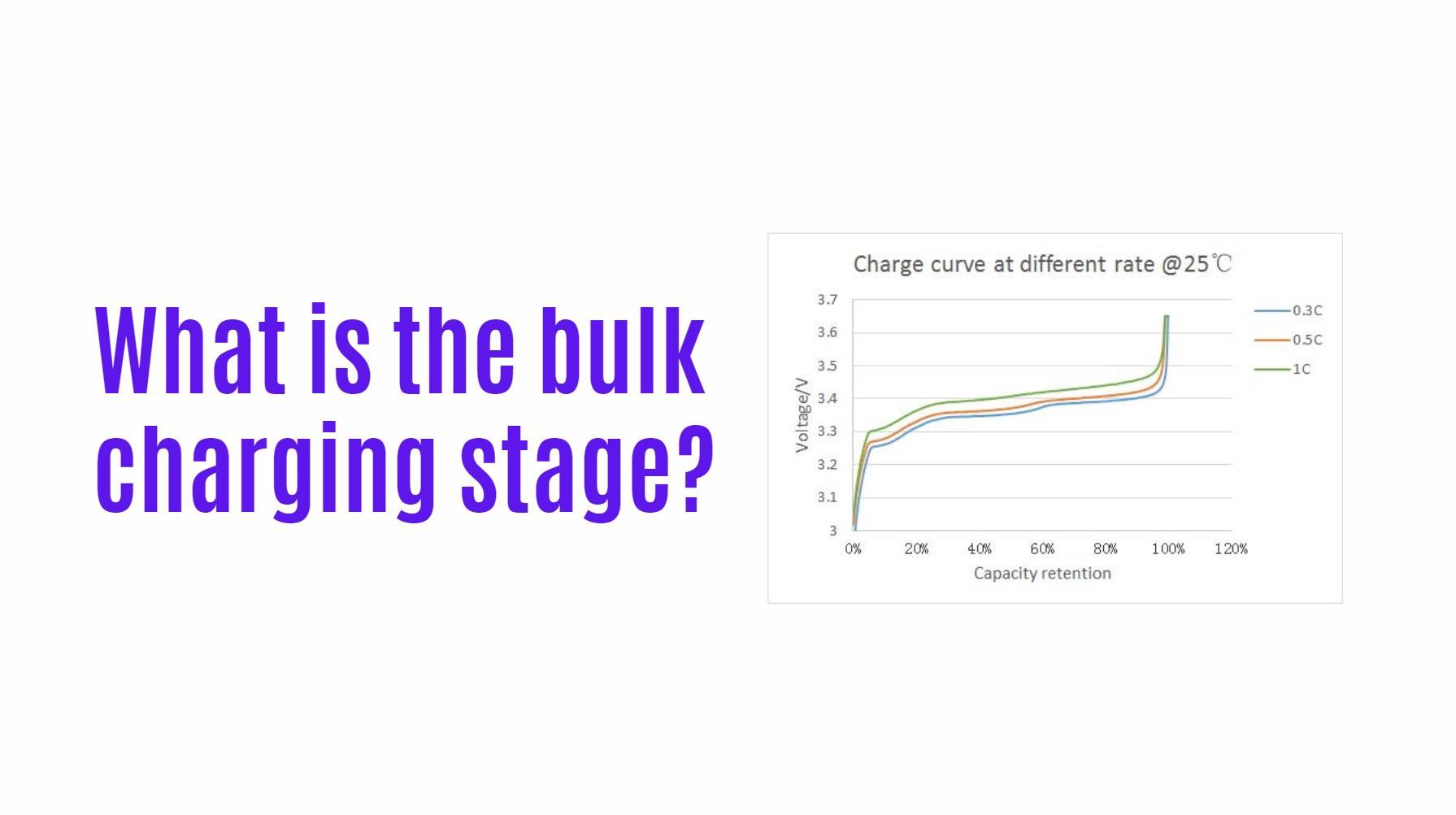
The bulk charging stage is the initial phase in the battery charging process where a charger delivers maximum current to quickly raise the battery’s state of charge to approximately 80-90%. This phase is crucial for efficiently replenishing battery capacity and is characterized by high current flow and increasing voltage.
What is the bulk charging stage in battery charging?
The bulk charging stage is the first step in the multi-stage battery charging process. During this phase, a charger applies a high current to the battery, allowing it to accept a significant amount of energy rapidly. The primary goal is to bring the battery up to about 80% of its total capacity efficiently. This stage ends when the voltage reaches a predetermined level, typically referred to as the absorption voltage, signaling that the next phase of charging can begin.
Bulk Charging Overview Chart
| Stage | Description | Current Level | Voltage Level |
|---|---|---|---|
| Bulk Charging | High current delivered to charge battery quickly | High | Higher than battery voltage |
How does bulk charging work in different battery systems?
Bulk charging operates similarly across various types of batteries, including lead-acid, lithium-ion, and solar batteries, but with some differences in voltage and current specifications.
- Lead-Acid Batteries: In lead-acid batteries, bulk charging typically involves delivering a constant current until reaching a set voltage (usually around 14.4V for flooded types). This process helps reverse sulfation and restore capacity.
- Lithium-Ion Batteries: Lithium-ion batteries also use a bulk charge phase but can handle higher currents and voltages without damage, allowing for faster recharge times.
- Solar Batteries: In solar applications, bulk charging occurs when solar panels deliver maximum current to quickly replenish energy reserves after periods of low sunlight.
Battery Charging Method Comparison Chart
| Battery Type | Bulk Charging Current | Typical Voltage Level |
|---|---|---|
| Lead-Acid | Up to 20% of Ah rating | ~14.4V |
| Lithium-Ion | Higher than lead-acid | ~14.6V |
| Solar | Maximum allowable current | ~14.5V |
What benefits does bulk charging provide for batteries?
Bulk charging offers several advantages:
- Fast Recharging: This stage allows for rapid energy transfer, significantly reducing downtime.
- Improved Battery Health: Regularly reaching high states of charge can help maintain overall battery health by preventing deep discharges.
- Efficiency: By maximizing current flow during this phase, batteries can be charged more efficiently compared to slower methods.
Benefits of Bulk Charging Chart
| Benefit | Description |
|---|---|
| Fast Recharging | Quickly brings batteries to usable levels |
| Improved Battery Health | Prevents deep discharge and maintains capacity |
| Efficiency | Maximizes energy transfer during initial phase |
What potential risks should be considered during bulk charging?
While beneficial, there are risks associated with bulk charging:
- Overcharging: If not properly regulated, excessive current can lead to overcharging, damaging cells.
- Heat Generation: High currents can cause batteries to heat up, which may shorten their lifespan if not managed correctly.
- Gassing: In lead-acid batteries, excessive gassing can occur at high voltages, leading to water loss and reduced capacity.
Risks of Bulk Charging Chart
| Risk | Description |
|---|---|
| Overcharging | Can damage cells if not monitored |
| Heat Generation | Excessive heat may reduce lifespan |
| Gassing | Leads to water loss in lead-acid batteries |
How does bulk charging vary among different battery types?
The specifics of bulk charging can differ significantly based on battery chemistry:
- Flooded Lead-Acid Batteries: Typically require careful management of voltage and current due to gassing.
- Sealed Lead-Acid Batteries (AGM/GEL): These require lower voltages during the bulk phase to avoid damage.
- Lithium-Ion Batteries: Can tolerate higher currents and voltages, allowing for faster recharges without damage.
Variations in Bulk Charging by Battery Type Chart
| Battery Type | Voltage Range | Current Handling |
|---|---|---|
| Flooded Lead-Acid | ~14.4V | Limited by Ah rating |
| Sealed Lead-Acid | ~14.2V | Moderate |
| Lithium-Ion | ~14.6V | High |
What are the overall stages of battery charging?
Battery charging generally consists of several stages:
- Bulk Charging: High current delivery until reaching about 80% capacity.
- Absorption Charging: Maintains constant voltage while current decreases as the battery approaches full charge.
- Float Charging: Keeps the battery at full charge with minimal current to prevent overcharging.
Stages of Battery Charging Chart
| Stage | Purpose |
|---|---|
| Bulk Charging | Rapidly charges up to ~80% |
| Absorption Charging | Completes charge while managing heat |
| Float Charging | Maintains full charge without overcharging |
FAQ Section
Q: How long does the bulk charging stage typically last?
A: The duration varies based on battery size and type but usually lasts a few hours until reaching approximately 80% charge.Q: Can I skip the bulk stage when charging my batteries?
A: Skipping this stage is not recommended as it ensures efficient energy transfer and maintains battery health.Q: Is bulk charging safe for all types of batteries?
A: While generally safe, it must be carefully monitored, especially for lead-acid batteries due to gassing risks.
Industrial News
Recent developments in battery technology emphasize optimizing bulk charging processes for improved efficiency and longevity. Innovations focus on advanced charge controllers that monitor temperature and voltage in real-time, reducing risks associated with overcharging and heat generation. These advancements aim to enhance performance across various applications including renewable energy systems and electric vehicles.
Redway Power Insight
“Understanding the nuances of each stage in battery charging is essential for maximizing performance,” states an expert from Redway Power. “The bulk stage sets the foundation for efficient energy storage; however, careful monitoring during this phase is crucial to avoid potential pitfalls like overheating or overcharging.”













