- Forklift Lithium Battery
-
48V
- 48V 210Ah
- 48V 300Ah
- 48V 420Ah (949 x 349 x 569 mm)
- 48V 420Ah (950 x 421 x 450 mm)
- 48V 456Ah
- 48V 460Ah (830 x 630 x 590 mm)
- 48V 460Ah (950 x 421 x 450 mm)
- 48V 460Ah (800 x 630 x 600 mm)
- 48V 460Ah (820 x 660 x 470 mm)
- 48V 500Ah
- 48V 560Ah (810 x 630 x 600 mm)
- 48V 560Ah (950 x 592 x 450 mm)
- 48V 600Ah
- 48V 630Ah
-
48V
- Lithium Golf Cart Battery
- 12V Lithium Battery
12V 150Ah Lithium RV Battery
Bluetooth App | BCI Group 31
LiFePO4 Lithium
Discharge Temperature -20°C ~ 65°C
Fast Charger 14.6V 50A
Solar MPPT Charging - 24V Lithium Battery
- 36V Lithium Battery
- 48V Lithium Battery
-
48V LiFePO4 Battery
- 48V 50Ah
- 48V 50Ah (for Golf Carts)
- 48V 60Ah (8D)
- 48V 100Ah (8D)
- 48V 100Ah
- 48V 100Ah (Discharge 100A for Golf Carts)
- 48V 100Ah (Discharge 150A for Golf Carts)
- 48V 100Ah (Discharge 200A for Golf Carts)
- 48V 150Ah (for Golf Carts)
- 48V 160Ah (Discharge 100A for Golf Carts)
- 48V 160Ah (Discharge 160A for Golf Carts)
-
48V LiFePO4 Battery
- 60V Lithium Battery
-
60V LiFePO4 Battery
- 60V 20Ah
- 60V 30Ah
- 60V 50Ah
- 60V 50Ah (Small Size / Side Terminal)
- 60V 100Ah (for Electric Motocycle, Electric Scooter, LSV, AGV)
- 60V 100Ah (for Forklift, AGV, Electric Scooter, Sweeper)
- 60V 150Ah (E-Motocycle / E-Scooter / E-Tricycle / Tour LSV)
- 60V 200Ah (for Forklift, AGV, Electric Scooter, Sweeper)
-
60V LiFePO4 Battery
- 72V~96V Lithium Battery
- Rack-mounted Lithium Battery
- E-Bike Battery
- All-in-One Home-ESS
- Wall-mount Battery ESS
-
Home-ESS Lithium Battery PowerWall
- 24V 100Ah 2.4kWh PW24100-S PowerWall
- 48V 50Ah 2.4kWh PW4850-S PowerWall
- 48V 50Ah 2.56kWh PW5150-S PowerWall
- 48V 100Ah 5.12kWh PW51100-F PowerWall (IP65)
- 48V 100Ah 5.12kWh PW51100-S PowerWall
- 48V 100Ah 5.12kWh PW51100-H PowerWall
- 48V 200Ah 10kWh PW51200-H PowerWall
- 48V 300Ah 15kWh PW51300-H PowerWall
PowerWall 51.2V 100Ah LiFePO4 Lithium Battery
Highly popular in Asia and Eastern Europe.
CE Certification | Home-ESS -
Home-ESS Lithium Battery PowerWall
- Portable Power Stations
How Do Bulk, Absorption, and Float Charging Stages Work?
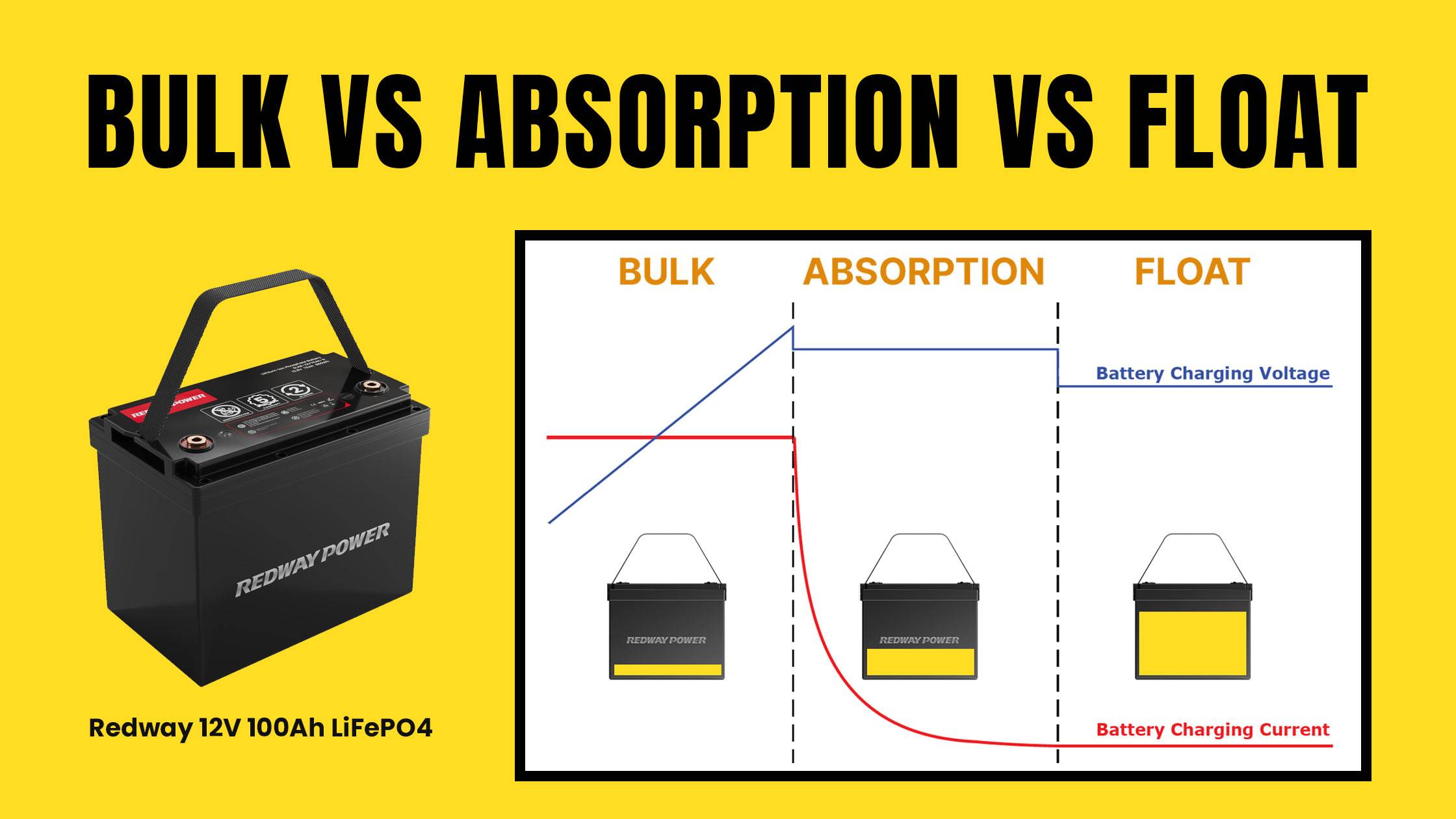
The battery charging process typically involves three key stages: bulk, absorption, and float. Each stage plays a crucial role in efficiently charging batteries while ensuring their longevity. Understanding these stages helps optimize battery performance and prolong its lifespan.
What is the bulk charging stage in battery charging?
The bulk charging stage is the initial phase where the maximum allowable current is delivered to the battery. This stage aims to rapidly increase the battery’s state of charge (SoC) from a low level to approximately 80% to 90%. During this phase, the voltage rises as the battery absorbs energy, typically reaching around 14.4 to 14.6 volts for a standard 12V lead-acid battery.
| Stage | Description | Voltage Level |
|---|---|---|
| Bulk | Maximum current supplied until 80%-90% charged | 14.4 – 14.6 volts |
How does absorption charging function in the charging cycle?
Once the bulk stage is complete and the battery reaches about 80% to 90% SoC, it transitions into absorption charging. In this phase, a constant voltage is maintained while the current gradually decreases as the battery approaches full charge. This prevents overheating and excessive gassing, allowing for safe and efficient energy transfer until the battery reaches approximately 98% SoC.
| Stage | Description | Voltage Level |
|---|---|---|
| Absorption | Constant voltage applied; current decreases | Typically around 14.4 volts |
Why is float charging necessary after the absorption phase?
After absorption charging, the battery enters the float charging stage. This phase maintains the battery at full charge without overcharging it. The voltage is reduced to a lower level (typically around 13.2 to 13.8 volts) to prevent gassing and electrolyte loss while compensating for self-discharge. Float charging ensures that batteries remain ready for use without degrading over time.
| Stage | Description | Voltage Level |
|---|---|---|
| Float | Maintenance charge to keep battery full | 13.2 – 13.8 volts |
What are the key differences between bulk, absorption, and float charging?
The primary differences between these three stages lie in their objectives, voltage levels, and current behavior:
- Bulk Charging: Focuses on rapid energy transfer with maximum current until reaching about 80%-90% SoC.
- Absorption Charging: Maintains a constant voltage while allowing current to taper off as it approaches full charge.
- Float Charging: Provides a low-level maintenance charge to keep batteries fully charged without overcharging.
| Aspect | Bulk | Absorption | Float |
|---|---|---|---|
| Objective | Rapid charge | Safe completion | Maintenance |
| Voltage Level | High (14.4 – 14.6V) | Constant (14.4V) | Lower (13.2 – 13.8V) |
| Current Behavior | Maximum | Decreasing | Minimal |
How do these charging stages affect battery life and performance?
Properly managing these three charging stages significantly impacts battery life and performance:
- Bulk Stage: Rapidly charges batteries but must be monitored to prevent overheating.
- Absorption Stage: Critical for achieving full capacity while minimizing damage from gassing.
- Float Stage: Essential for maintaining charge without causing degradation or loss of electrolyte.
Neglecting any of these stages can lead to reduced efficiency, shorter lifespan, or even catastrophic failure of batteries.
Industrial News
Recent advancements in battery management systems emphasize optimizing charging cycles through enhanced algorithms that better manage bulk, absorption, and float stages. These improvements aim to maximize battery life while improving efficiency across various applications such as electric vehicles and renewable energy storage systems. Manufacturers are increasingly focusing on integrating smart technology that adapts to different battery chemistries for optimal performance.
Redway Power Insights
“Understanding the intricacies of bulk, absorption, and float charging stages is vital for anyone looking to maximize their battery’s lifespan,” states industry expert John Smith from Redway Power. “By ensuring that each stage is properly managed, users can significantly enhance performance and reliability.”
FAQ Section
Q1: What happens if I skip the float stage?
A1: Skipping the float stage can lead to overcharging, which may cause gassing and electrolyte loss in lead-acid batteries.Q2: How long does each charging stage typically last?
A2: The duration varies by battery type; bulk can take several hours, while absorption may last from one to several hours depending on conditions.Q3: Can I use a charger that doesn’t have a float mode?
A3: While possible, chargers without a float mode may risk overcharging your batteries if not monitored closely.Q4: Is it necessary to monitor voltage during these stages?
A4: Yes, monitoring voltage during each stage ensures safe operation and helps prevent damage or inefficiency in your batteries.














