- Forklift Lithium Battery
-
48V
- 48V 210Ah
- 48V 300Ah
- 48V 420Ah (949 x 349 x 569 mm)
- 48V 420Ah (950 x 421 x 450 mm)
- 48V 456Ah
- 48V 460Ah (830 x 630 x 590 mm)
- 48V 460Ah (950 x 421 x 450 mm)
- 48V 460Ah (800 x 630 x 600 mm)
- 48V 460Ah (820 x 660 x 470 mm)
- 48V 500Ah
- 48V 560Ah (810 x 630 x 600 mm)
- 48V 560Ah (950 x 592 x 450 mm)
- 48V 600Ah
- 48V 630Ah
-
48V
- Lithium Golf Cart Battery
- 12V Lithium Battery
12V 150Ah Lithium RV Battery
Bluetooth App | BCI Group 31
LiFePO4 Lithium
Discharge Temperature -20°C ~ 65°C
Fast Charger 14.6V 50A
Solar MPPT Charging - 24V Lithium Battery
- 36V Lithium Battery
- 48V Lithium Battery
-
48V LiFePO4 Battery
- 48V 50Ah
- 48V 50Ah (for Golf Carts)
- 48V 60Ah (8D)
- 48V 100Ah (8D)
- 48V 100Ah
- 48V 100Ah (Discharge 100A for Golf Carts)
- 48V 100Ah (Discharge 150A for Golf Carts)
- 48V 100Ah (Discharge 200A for Golf Carts)
- 48V 150Ah (for Golf Carts)
- 48V 160Ah (Discharge 100A for Golf Carts)
- 48V 160Ah (Discharge 160A for Golf Carts)
-
48V LiFePO4 Battery
- 60V Lithium Battery
-
60V LiFePO4 Battery
- 60V 20Ah
- 60V 30Ah
- 60V 50Ah
- 60V 50Ah (Small Size / Side Terminal)
- 60V 100Ah (for Electric Motocycle, Electric Scooter, LSV, AGV)
- 60V 100Ah (for Forklift, AGV, Electric Scooter, Sweeper)
- 60V 150Ah (E-Motocycle / E-Scooter / E-Tricycle / Tour LSV)
- 60V 200Ah (for Forklift, AGV, Electric Scooter, Sweeper)
-
60V LiFePO4 Battery
- 72V~96V Lithium Battery
- Rack-mounted Lithium Battery
- E-Bike Battery
- All-in-One Home-ESS
- Wall-mount Battery ESS
-
Home-ESS Lithium Battery PowerWall
- 24V 100Ah 2.4kWh PW24100-S PowerWall
- 48V 50Ah 2.4kWh PW4850-S PowerWall
- 48V 50Ah 2.56kWh PW5150-S PowerWall
- 48V 100Ah 5.12kWh PW51100-F PowerWall (IP65)
- 48V 100Ah 5.12kWh PW51100-S PowerWall
- 48V 100Ah 5.12kWh PW51100-H PowerWall
- 48V 200Ah 10kWh PW51200-H PowerWall
- 48V 300Ah 15kWh PW51300-H PowerWall
PowerWall 51.2V 100Ah LiFePO4 Lithium Battery
Highly popular in Asia and Eastern Europe.
CE Certification | Home-ESS -
Home-ESS Lithium Battery PowerWall
- Portable Power Stations
What Are Cold Cranking Amps (CCA)?

Cold Cranking Amps (CCA) is a critical measurement that indicates a battery’s ability to start an engine in cold temperatures. Specifically, it represents the maximum current a fully charged battery can deliver at 0°F (-18°C) for 30 seconds without dropping below 7.2 volts. Understanding CCA is essential for selecting the right battery for your vehicle, especially in colder climates.
What is the definition of cold cranking amps (CCA)?
Cold Cranking Amps (CCA) measures a battery’s ability to start an engine under cold conditions. It quantifies how much current (in amps) a battery can provide at 0°F for 30 seconds while maintaining a minimum voltage of 7.2 volts. A higher CCA rating indicates better performance in cold weather, which is crucial for reliable vehicle operation.Chart: Understanding CCA Definition
| Measurement | Value |
|---|---|
| Temperature | 0°F (-18°C) |
| Duration | 30 seconds |
| Minimum Voltage | 7.2 volts |
How is CCA measured in batteries?
To measure CCA, manufacturers typically follow these steps:
- Fully Charge the Battery: Ensure that the battery is fully charged before testing.
- Cool to Specified Temperature: Place the battery in a controlled environment at 0°F (-18°C) for at least 24 hours.
- Apply Load: Use a load tester to apply a discharge current equal to the specified CCA rating.
- Monitor Voltage: Record whether the voltage remains above 7.2 volts during the discharge period.
Chart: Measurement Process Overview
| Step | Description |
|---|---|
| Fully Charge | Ensure battery is fully charged |
| Cool Battery | Place in cold environment |
| Apply Load | Use load tester to discharge |
| Monitor Voltage | Check voltage remains above 7.2 volts |
Why is CCA important for vehicle performance?
CCA is crucial because it directly impacts a vehicle’s ability to start in cold weather. In colder temperatures, engine oil thickens, making it harder for engines to turn over. A battery with a high CCA rating can provide sufficient power to crank the engine, ensuring reliable starts even in harsh conditions.
What factors affect a battery’s CCA rating?
Several factors can influence a battery’s CCA rating:
- Battery Chemistry: Different types of batteries (e.g., lead-acid, AGM, lithium) have varying capabilities.
- Temperature: Lower temperatures generally reduce available capacity and performance.
- Age and Condition: Older batteries or those that have been poorly maintained may have reduced capacity and lower CCA ratings.
Chart: Factors Influencing CCA Rating
| Factor | Impact on Rating |
|---|---|
| Battery Chemistry | Determines baseline performance |
| Temperature | Lower temps reduce effective capacity |
| Age | Older batteries lose capacity over time |
How do cold cranking amps impact starting power?
Cold cranking amps significantly impact starting power by determining how much current can be delivered to the starter motor during cold conditions. A higher CCA means more power is available, which translates to better starting performance when temperatures drop.
What is the typical CCA range for car batteries?
The typical range for car batteries varies based on type and application:
- Standard Lead-Acid Batteries: Generally range from 400 to 600 CCA.
- AGM Batteries: Often rated between 600 and 800 CCA, providing better performance.
- High-Performance Batteries: Some specialized batteries can exceed 900 CCA, suitable for high-demand vehicles.
Chart: Typical CCA Ranges
| Battery Type | Typical CCA Range |
|---|---|
| Standard Lead-Acid | 400 – 600 |
| AGM | 600 – 800 |
| High-Performance | Up to 900+ |
Why should you choose a battery with high CCA?
Choosing a battery with high CCA is beneficial because:
- Improved Cold Weather Performance: Higher ratings ensure reliable starts during winter months.
- Enhanced Reliability: Provides peace of mind knowing your vehicle will start under adverse conditions.
- Compatibility with Larger Engines: Higher CCAs are often necessary for vehicles with larger engines or additional electrical demands.
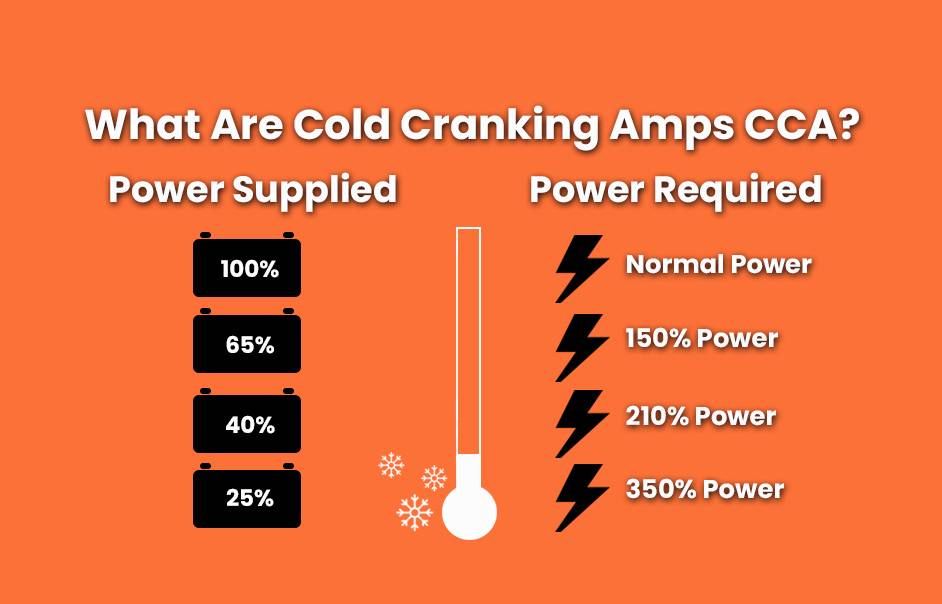
How does temperature influence CCA ratings?
Temperature has a significant effect on battery performance:
- Cold Temperatures: As temperatures drop, chemical reactions within the battery slow down, reducing available power and lowering effective capacity.
- Warm Temperatures: Higher temperatures can enhance performance but may also accelerate degradation over time.
Chart: Temperature Effects on Battery Performance
| Temperature Range | Impact on Capacity |
|---|---|
| Below 0°F | Significant reduction in available power |
| Above 32°F | Improved performance but potential long-term damage |
What are the differences between CCA and MCA?
Cold Cranking Amps (CCA) and Marine Cranking Amps (MCA) are both measurements of starting power but differ in testing conditions:
- CCA measures performance at 0°F, while
- MCA measures at 32°F, typically used for marine applications where conditions may vary.
Both ratings are important but serve different purposes based on environmental conditions.
How can you test the CCA of your battery?
To test your battery’s CCA:
- Use a dedicated load tester designed for measuring cranking amps.
- Fully charge your battery before testing.
- Follow manufacturer instructions to apply load and measure voltage drop during testing.
This will provide an accurate assessment of your battery’s cold cranking capability.
Why do different vehicles require different CCA ratings?
Different vehicles require varying levels of starting power based on:
- Engine Size: Larger engines typically need more power to start.
- Environmental Conditions: Vehicles operating in colder climates need higher CCAs to ensure reliability.
- Electrical Demands: Vehicles with additional electrical accessories may require batteries with higher ratings.
Industrial News
The market for automotive batteries continues to evolve, particularly as electric vehicles gain popularity and traditional lead-acid batteries face competition from advanced technologies like lithium-ion systems. Recent innovations focus on improving energy density and reducing costs while enhancing safety features, making modern batteries more efficient and reliable across various applications.
Redway Power Insights
“Understanding Cold Cranking Amps is essential for selecting the right battery,” states an industry expert. “With winter approaching, ensuring that your vehicle has adequate starting power can make all the difference in reliability and peace of mind.”

FAQs
What Signals Need for Battery Replacement?
How Do Climate and Habits Affect Battery Life?
What’s the Difference Between CA and CCA?
How Does CCA Relate to Battery Size and Weight?
How Does CCA Impact Cold-Weather Starting?
Why Choose a Higher CCA Battery?
Why More Power Needed to Start in Cold?
How Temperature Affects Battery Power?
Why Do Battery Reactions Slow in Cold?
What are the potential hazards of using lead acid batteries with high cold cranking amps in cold climates?
Using lead-acid batteries with high cold cranking amps (CCA) in cold climates can lead to potential hazards such as reduced battery performance due to increased internal resistance, shorter battery life, and potential for freezing if the battery is not adequately maintained or if it’s older and less effective.
How do cold cranking amps differ from marine cranking amps (MCA) and hot cranking amps (HCA)?
- Cold Cranking Amps (CCA): Measures the battery’s ability to start an engine in cold temperatures (0°F or -18°C).
- Marine Cranking Amps (MCA): Measures starting power at 32°F (0°C) and is used for marine batteries.
- Hot Cranking Amps (HCA): Measures the battery’s starting power at 80°F (27°C), reflecting performance in warmer conditions.
What are the differences between cranking and deep cycling in batteries?
- Cranking Batteries: Designed to deliver a high burst of power for starting engines. They have a high CCA rating and are not intended for deep discharge.
- Deep Cycle Batteries: Designed for sustained power output over a long period and frequent deep discharges. They have thicker plates to withstand deep cycling and provide steady, reliable energy.