- Lithium Golf Cart Battery
- Forklift Lithium Battery
-
48V
- 48V 210Ah
- 48V 300Ah
- 48V 420Ah (949 x 349 x 569 mm)
- 48V 420Ah (950 x 421 x 450 mm)
- 48V 456Ah
- 48V 460Ah (830 x 630 x 590 mm)
- 48V 460Ah (950 x 421 x 450 mm)
- 48V 460Ah (800 x 630 x 600 mm)
- 48V 460Ah (820 x 660 x 470 mm)
- 48V 500Ah
- 48V 560Ah (810 x 630 x 600 mm)
- 48V 560Ah (950 x 592 x 450 mm)
- 48V 600Ah
- 48V 630Ah
-
48V
- 12V Lithium Battery
12V 150Ah Lithium RV Battery
Bluetooth App | BCI Group 31
LiFePO4 Lithium
Discharge Temperature -20°C ~ 65°C
Fast Charger 14.6V 50A
Solar MPPT Charging - 24V Lithium Battery
- 36V Lithium Battery
- 48V Lithium Battery
-
48V LiFePO4 Battery
- 48V 50Ah
- 48V 50Ah (for Golf Carts)
- 48V 60Ah (8D)
- 48V 100Ah (8D)
- 48V 100Ah
- 48V 100Ah (Discharge 100A for Golf Carts)
- 48V 100Ah (Discharge 150A for Golf Carts)
- 48V 100Ah (Discharge 200A for Golf Carts)
- 48V 150Ah (for Golf Carts)
- 48V 160Ah (Discharge 100A for Golf Carts)
- 48V 160Ah (Discharge 160A for Golf Carts)
-
48V LiFePO4 Battery
- 60V Lithium Battery
-
60V LiFePO4 Battery
- 60V 20Ah
- 60V 30Ah
- 60V 50Ah
- 60V 50Ah (Small Size / Side Terminal)
- 60V 100Ah (for Electric Motocycle, Electric Scooter, LSV, AGV)
- 60V 100Ah (for Forklift, AGV, Electric Scooter, Sweeper)
- 60V 150Ah (E-Motocycle / E-Scooter / E-Tricycle / Tour LSV)
- 60V 200Ah (for Forklift, AGV, Electric Scooter, Sweeper)
-
60V LiFePO4 Battery
- 72V~96V Lithium Battery
- Rack-mounted Lithium Battery
- E-Bike Battery
- All-in-One Home-ESS
- Wall-mount Battery ESS
-
Home-ESS Lithium Battery PowerWall
- 24V 100Ah 2.4kWh PW24100-S PowerWall
- 48V 50Ah 2.4kWh PW4850-S PowerWall
- 48V 50Ah 2.56kWh PW5150-S PowerWall
- 48V 100Ah 5.12kWh PW51100-F PowerWall (IP65)
- 48V 100Ah 5.12kWh PW51100-S PowerWall
- 48V 100Ah 5.12kWh PW51100-H PowerWall
- 48V 200Ah 10kWh PW51200-H PowerWall
- 48V 300Ah 15kWh PW51300-H PowerWall
PowerWall 51.2V 100Ah LiFePO4 Lithium Battery
Highly popular in Asia and Eastern Europe.
CE Certification | Home-ESS -
Home-ESS Lithium Battery PowerWall
- Portable Power Stations
What You Need to Know About Sodium-Ion Batteries

Sodium-ion batteries are emerging as a promising alternative to lithium-ion batteries, utilizing sodium ions as charge carriers. They offer advantages such as cost-effectiveness and abundant raw materials, making them suitable for various applications in energy storage and electric vehicles.
What Is a Sodium-Ion Battery and How Does It Work?
A sodium-ion battery (NIB) operates similarly to a lithium-ion battery but uses sodium ions (Na⁺) instead of lithium ions. The basic components include:
- Anode: Typically made from hard carbon, which allows sodium ions to intercalate during charging.
- Cathode: Composed of sodium-based materials like layered oxides or polyanionic compounds that can reversibly host sodium ions.
- Electrolyte: A sodium salt dissolved in a solvent that facilitates ion movement between the anode and cathode.
During charging, sodium ions move from the cathode to the anode, while electrons flow through an external circuit. During discharge, this process is reversed, providing electrical power.Chart: Components of a Sodium-Ion Battery
| Component | Description |
|---|---|
| Anode | Hard carbon or alternative materials |
| Cathode | Layered oxides or polyanionic compounds |
| Electrolyte | Sodium salt solution enabling ion movement |
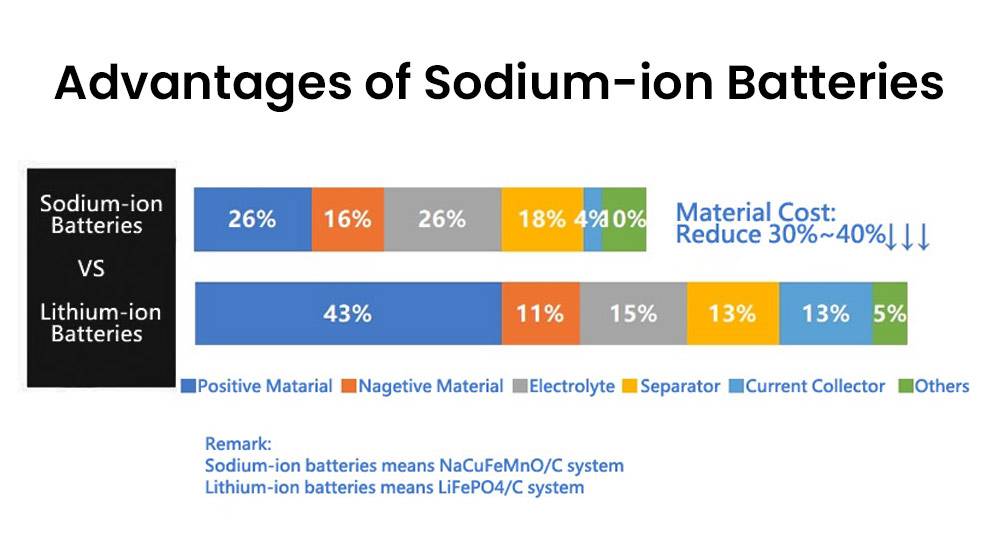
What Are the Advantages of Sodium-Ion Batteries?
Sodium-ion batteries offer several advantages:
- Abundant Raw Materials: Sodium is widely available and inexpensive compared to lithium.
- Cost-Effectiveness: Lower material costs can lead to cheaper battery production.
- Safety: They exhibit lower risks of thermal runaway compared to lithium-ion batteries.
- Environmental Impact: Generally more environmentally friendly due to less toxic materials.
Chart: Advantages of Sodium-Ion Batteries
| Advantage | Description |
|---|---|
| Abundant Materials | Utilizes widely available sodium |
| Cost-Effectiveness | Potentially lower production costs |
| Safety | Reduced risk of overheating |
| Environmental Impact | Less toxic materials used |
What Challenges Do Sodium-Ion Batteries Face?
Despite their benefits, sodium-ion batteries face several challenges:
- Lower Energy Density: Typically, they have lower energy density (90-150 Wh/kg) compared to lithium-ion batteries (250 Wh/kg), which may limit their use in high-performance applications.
- Development Stage: The technology is still maturing, with less commercial availability than lithium-ion counterparts.
- Performance at High Temperatures: While they perform well in cold conditions, their efficiency at high temperatures can be limited.
Chart: Challenges of Sodium-Ion Batteries
| Challenge | Description |
|---|---|
| Lower Energy Density | Stores less energy per weight |
| Development Stage | Less mature technology with limited availability |
| Performance at High Temperatures | Efficiency may drop under extreme heat |
How Do Sodium-Ion Batteries Compare to Lithium-Ion Batteries?
When comparing sodium-ion batteries to lithium-ion batteries:
- Energy Density: Lithium-ion batteries generally have higher energy density, making them more suitable for portable electronics and electric vehicles.
- Cost: Sodium-ion batteries may offer lower costs due to abundant raw materials.
- Safety: Sodium-ion technology tends to be safer with a lower risk of thermal runaway.
Chart: Comparison Between Battery Types
| Feature | Lithium-Ion | Sodium-Ion |
|---|---|---|
| Energy Density | ~250 Wh/kg | ~90-150 Wh/kg |
| Cost | Higher due to lithium sourcing | Potentially lower due to abundant sodium |
| Safety | Risk of thermal runaway | Generally safer under various conditions |
What Are the Common Applications for Sodium-Ion Batteries?
Sodium-ion batteries are being explored for various applications, including:
- Grid Energy Storage: Ideal for large-scale energy storage systems due to their cost-effectiveness.
- Electric Vehicles: Emerging use in low-cost electric vehicles where weight is less critical.
- Renewable Energy Systems: Suitable for storing energy from renewable sources like solar and wind.
Chart: Applications of Sodium-Ion Batteries
| Application Type | Description |
|---|---|
| Grid Energy Storage | Large-scale systems for stabilizing power supply |
| Electric Vehicles | Cost-effective options for budget-friendly EVs |
| Renewable Energy Systems | Storing energy generated from solar/wind |
Tips for Battery Wholesale Buyers: How to Choose a Reliable Manufacturer?
When considering wholesale purchases or OEM orders for batteries, it’s crucial to choose a reliable manufacturer. Here are some tips:
- Research Manufacturer Reputation: Look for established companies like Redway Power, known for quality and reliability.
- Evaluate Product Range: Ensure they offer various battery types suitable for your needs.
- Check Certifications: Confirm compliance with industry standards.
For OEM orders from a reputable manufacturer like Redway Power, which has over 13 years of experience in lithium battery manufacturing, ensure clear communication regarding specifications and delivery timelines. This approach helps secure high-quality products that serve as excellent alternatives to lead-acid batteries.
Redway Power Expert Views
“Sodium-ion batteries represent a significant advancement in energy storage technology. With their cost advantages and safety features, they are poised to complement existing lithium technologies, especially in applications where weight is less critical,” states an expert from Redway Power.
FAQ Section
- What are sodium-ion batteries?
Sodium-ion batteries are rechargeable batteries that use sodium ions as charge carriers, similar in function to lithium-ion batteries but with different materials. - What are the advantages of sodium-ion batteries?
They offer abundant raw materials, cost-effectiveness, safety benefits, and reduced environmental impact. - What challenges do sodium-ion batteries face?
Challenges include lower energy density compared to lithium-ion batteries and being less commercially available.