- Forklift Lithium Battery
-
48V
- 48V 210Ah
- 48V 300Ah
- 48V 420Ah (949 x 349 x 569 mm)
- 48V 420Ah (950 x 421 x 450 mm)
- 48V 456Ah
- 48V 460Ah (830 x 630 x 590 mm)
- 48V 460Ah (950 x 421 x 450 mm)
- 48V 460Ah (800 x 630 x 600 mm)
- 48V 460Ah (820 x 660 x 470 mm)
- 48V 500Ah
- 48V 560Ah (810 x 630 x 600 mm)
- 48V 560Ah (950 x 592 x 450 mm)
- 48V 600Ah
- 48V 630Ah
-
48V
- Lithium Golf Cart Battery
- 12V Lithium Battery
12V 150Ah Lithium RV Battery
Bluetooth App | BCI Group 31
LiFePO4 Lithium
Discharge Temperature -20°C ~ 65°C
Fast Charger 14.6V 50A
Solar MPPT Charging - 24V Lithium Battery
- 36V Lithium Battery
- 48V Lithium Battery
-
48V LiFePO4 Battery
- 48V 50Ah
- 48V 50Ah (for Golf Carts)
- 48V 60Ah (8D)
- 48V 100Ah (8D)
- 48V 100Ah
- 48V 100Ah (Discharge 100A for Golf Carts)
- 48V 100Ah (Discharge 150A for Golf Carts)
- 48V 100Ah (Discharge 200A for Golf Carts)
- 48V 150Ah (for Golf Carts)
- 48V 160Ah (Discharge 100A for Golf Carts)
- 48V 160Ah (Discharge 160A for Golf Carts)
-
48V LiFePO4 Battery
- 60V Lithium Battery
-
60V LiFePO4 Battery
- 60V 20Ah
- 60V 30Ah
- 60V 50Ah
- 60V 50Ah (Small Size / Side Terminal)
- 60V 100Ah (for Electric Motocycle, Electric Scooter, LSV, AGV)
- 60V 100Ah (for Forklift, AGV, Electric Scooter, Sweeper)
- 60V 150Ah (E-Motocycle / E-Scooter / E-Tricycle / Tour LSV)
- 60V 200Ah (for Forklift, AGV, Electric Scooter, Sweeper)
-
60V LiFePO4 Battery
- 72V~96V Lithium Battery
- Rack-mounted Lithium Battery
- E-Bike Battery
- All-in-One Home-ESS
- Wall-mount Battery ESS
-
Home-ESS Lithium Battery PowerWall
- 24V 100Ah 2.4kWh PW24100-S PowerWall
- 48V 50Ah 2.4kWh PW4850-S PowerWall
- 48V 50Ah 2.56kWh PW5150-S PowerWall
- 48V 100Ah 5.12kWh PW51100-F PowerWall (IP65)
- 48V 100Ah 5.12kWh PW51100-S PowerWall
- 48V 100Ah 5.12kWh PW51100-H PowerWall
- 48V 200Ah 10kWh PW51200-H PowerWall
- 48V 300Ah 15kWh PW51300-H PowerWall
PowerWall 51.2V 100Ah LiFePO4 Lithium Battery
Highly popular in Asia and Eastern Europe.
CE Certification | Home-ESS -
Home-ESS Lithium Battery PowerWall
- Portable Power Stations
Why Should Boat Batteries Be Connected in Parallel?

Connecting boat batteries in parallel is a common practice that allows for increased capacity and longer runtime for onboard electronics. This method enhances reliability, ensuring that if one battery fails, others can still provide power, making it an essential consideration for boaters.
Why Should Boat Batteries Be Connected in Parallel?
Connecting boat batteries in parallel is advantageous as it increases the overall amp-hour capacity while maintaining the same voltage. This setup allows boaters to run multiple devices simultaneously without depleting battery power quickly, making it ideal for extended trips on the water.
What Are the Advantages of Connecting Boat Batteries in Parallel?
The primary advantages of connecting batteries in parallel include:
- Increased Capacity: By connecting batteries in parallel, you effectively sum their amp-hour ratings. For instance, two 100Ah batteries connected in parallel provide a total capacity of 200Ah.
- Redundancy: If one battery fails, others can continue to supply power, enhancing reliability during critical operations.
- Simplified Wiring: The wiring configuration is straightforward, making installation and maintenance easier.
| Advantage | Description |
|---|---|
| Increased Capacity | Allows longer operation times for devices |
| Redundancy | Ensures continued power supply if one battery fails |
| Simplified Wiring | Easier installation and troubleshooting |
What Are the Disadvantages of Connecting Boat Batteries in Parallel?
Despite its benefits, there are some disadvantages to consider:
- Charging Imbalance: Different batteries may charge or discharge at varying rates, leading to potential imbalances that require regular monitoring.
- Space and Weight: More batteries mean increased weight and space requirements on your boat, which could impact performance.
- Cost: Additional batteries can increase initial investment and maintenance costs.
How Can You Safely Connect Boat Batteries in Parallel?
To ensure a safe connection:
- Use Similar Batteries: Ensure all batteries are of the same type, age, and capacity to avoid imbalances.
- Secure Connections: Make sure all connections are tight and insulated to prevent short circuits.
- Monitor Regularly: Regularly check the charge levels of each battery to maintain balance.
When Should You Use Parallel Connections for Boat Batteries?
Parallel connections are particularly useful when:
- Running Multiple Devices: If you have several electronic devices onboard, parallel wiring ensures each device receives adequate power without overloading a single battery.
- Extended Trips: When planning long outings without access to charging facilities, connecting batteries in parallel can provide the necessary power duration.
- Simplicity: If you prefer a straightforward setup with easy maintenance, parallel connections are advantageous.
How Does Parallel Wiring Work for Marine Applications?
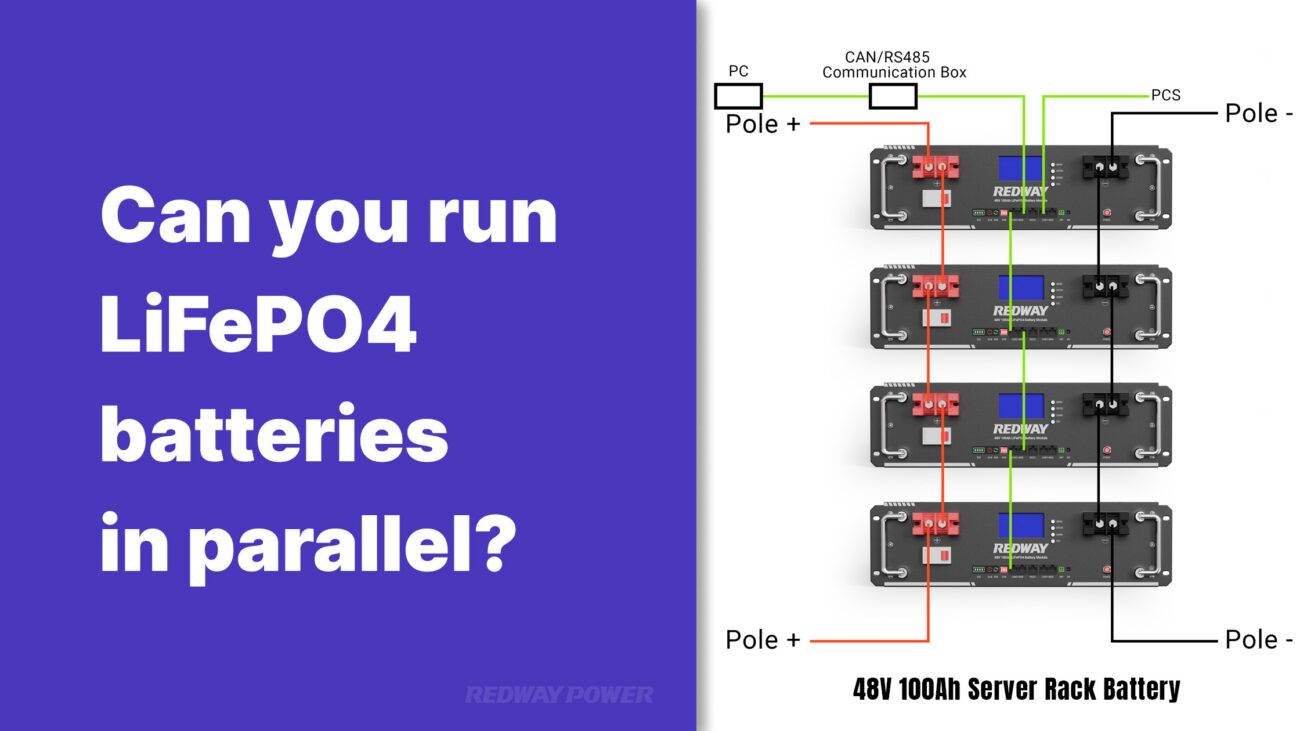
In a parallel wiring setup, the positive terminals of all batteries are connected together, as well as the negative terminals. This configuration maintains a consistent voltage while increasing total amperage capacity. For example, connecting two 12V 100Ah batteries results in a total of 12V at 200Ah.
What Common Practices Should Be Followed for Parallel Connections?
To ensure effective parallel connections:
- Uniformity: Use batteries that match in type and specifications.
- Proper Wiring: Utilize appropriate gauge wiring to handle the increased current.
- Regular Maintenance: Check connections and battery health periodically to ensure optimal performance.
Replacement Choices for Lithium-Ion Batteries
For those considering alternatives or upgrades, Redway Power offers excellent lithium-ion battery solutions suitable for marine applications. These batteries provide superior performance and longevity compared to traditional lead-acid options.
Tips for Battery Wholesale Buyers
When sourcing batteries wholesale or placing OEM orders, consider working with reliable manufacturers like Redway Power, which has over 13 years of experience in lithium battery production. Ensure you verify certifications and quality standards when making your selection.
Redway Power Expert Views
“Connecting batteries in parallel is an effective way to enhance your boat’s power system. It allows you to maximize efficiency while ensuring redundancy,” states an expert from Redway Power.

FAQs
What happens if you connect batteries in parallel?
When batteries are connected in parallel, their positive terminals are joined together with a wire, and their negative terminals are joined together with another wire. This configuration increases the amp hour capacity of the batteries while keeping the voltage the same. For example, two 6-volt 4.5 Ah batteries connected in parallel will provide 6 volts at 9 amp hours (4.5 Ah + 4.5 Ah). By connecting batteries in parallel, you can increase the overall capacity of the battery bank without changing the voltage. This is useful when you need to power devices that require higher capacity or longer runtimes.
Will two batteries in parallel last longer than one?
Connecting two batteries in parallel can potentially extend their lifespan. By doing so, the total current capacity is increased while maintaining the same voltage. This means that each battery shares the load, preventing them from overworking and potentially prolonging their lifespan. However, it is crucial to use batteries of the same type, voltage, and capacity to avoid imbalances and potential issues. By connecting batteries in parallel, you can potentially enjoy longer-lasting power for your devices or systems.
Do batteries in parallel drain equally?
When batteries are connected in parallel, they should ideally drain equally, assuming they have the same characteristics. However, slight variations in internal resistance or capacity can lead to uneven discharge rates. Factors such as differences in battery age, temperature, or usage can also contribute to unequal draining. To ensure balanced operation, it is important to use batteries with similar specifications, including voltage, capacity, and type. Regular monitoring of battery performance can help identify any imbalances and address them promptly. By using parallel connections and maintaining balanced battery draining, you can optimize the overall performance and longevity of your battery system.
How to charge two 12V batteries in parallel?
To charge two 12-volt batteries in parallel, follow these steps: (1) Ensure both batteries have similar capacities and types. (2) Connect the positive terminal of one battery to the positive terminal of the other battery using a cable. Connect the negative terminals in the same way. (3) Attach a suitable charger to one of the batteries. (4) Start the charging process, monitoring the batteries’ voltage and connections. (5) Regularly check and maintain the batteries and connections for optimal performance.
Does connecting batteries in parallel increase amp hours?
- Yes. Parallel connections boost the amp-hour capacity of batteries while maintaining voltage. For example, two 12V 100Ah batteries in parallel create a 12V system with 200Ah.
What happens when you put two 12-volt batteries in series?
- When batteries are in series, voltage increases to 24V while amps remain constant. However, in parallel, amps increase while maintaining a 12V system.
Do batteries last longer in series or parallel?
- Batteries last longer in parallel due to increased amp capacity. In series, voltage rises, but capacity (Ah) remains unchanged.
Can you put Lifepo4 batteries in series?
- Compatibility varies among Lifepo4 batteries. Ionic lithium batteries often support series connections, but it’s essential to check the user manual for compatibility.
Which is more powerful, series, or parallel?
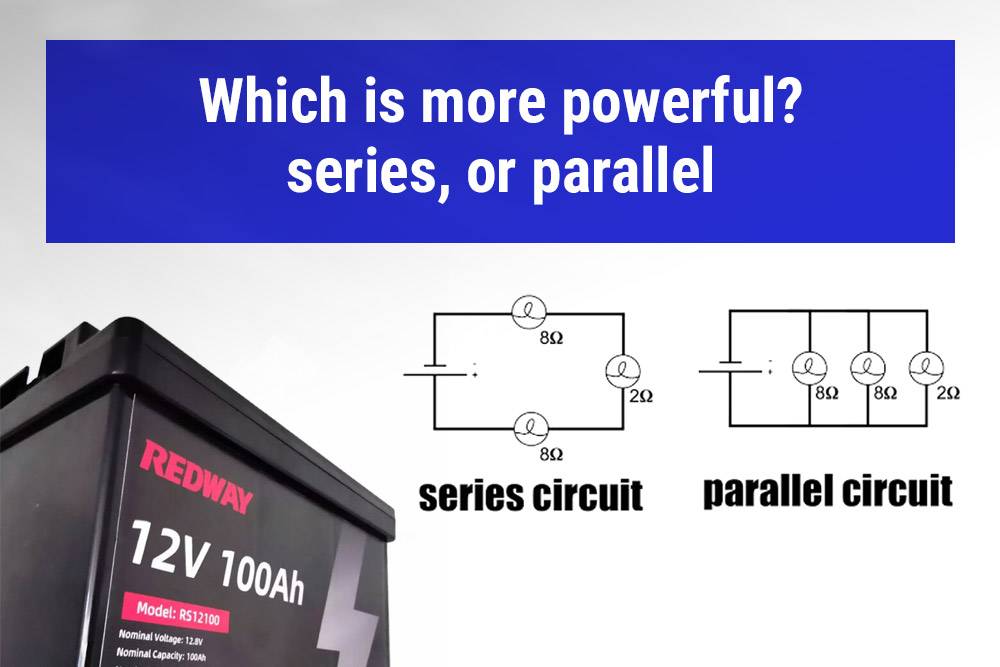
- Parallel circuits consume more power compared to series circuits with the same voltage.
Is series or parallel safer?
- Both series and parallel connections are generally safe, with voltage being the primary safety concern.
More FAQs
What does a series-parallel connection of batteries achieve?
A series-parallel connection combines the benefits of both series and parallel configurations, allowing for increased voltage and capacity. It enables a higher total voltage output while maintaining a larger capacity and longer run time, accommodating higher power demands and extending battery life.
What does it mean to connect batteries in series, parallel, and series-parallel?
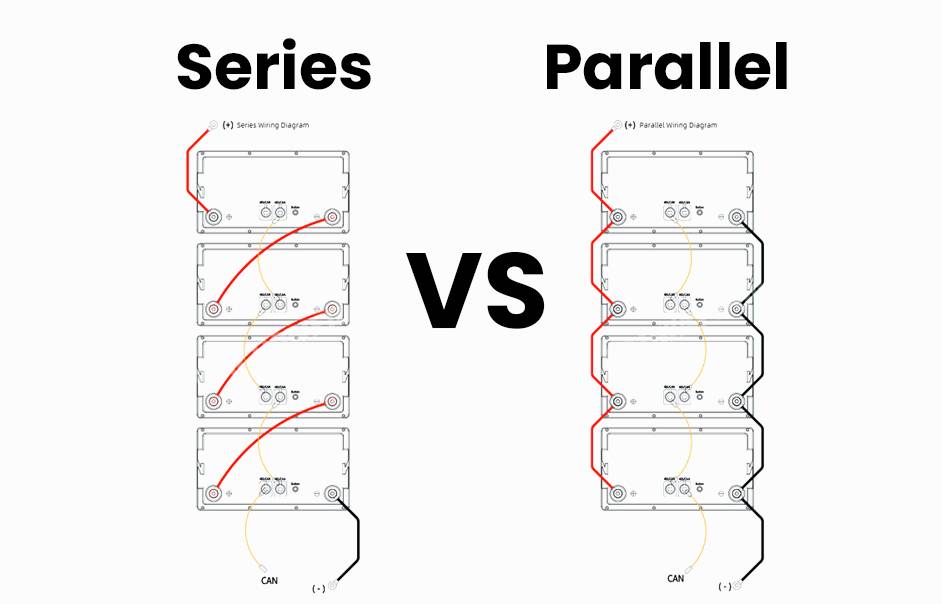
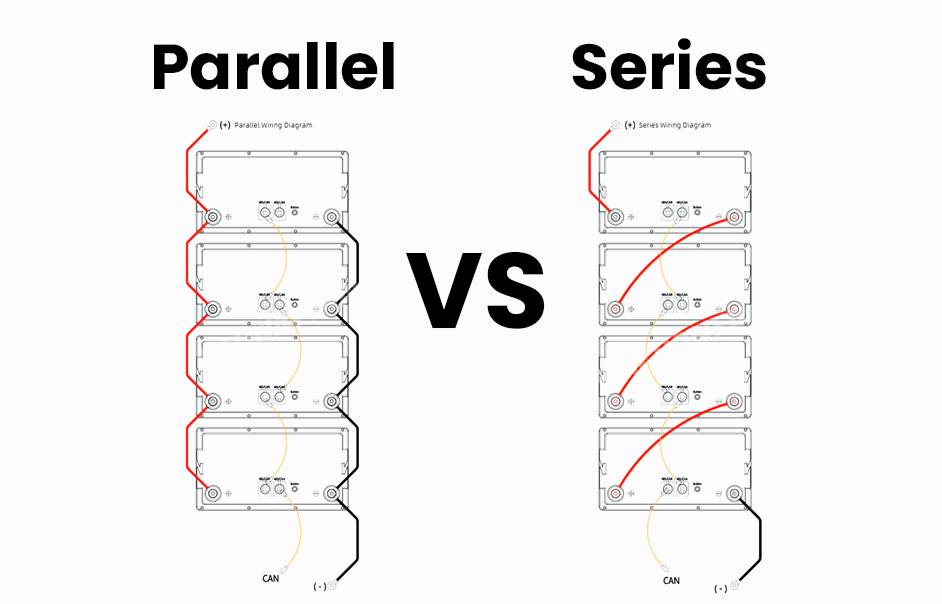
- Series: Batteries are connected end-to-end, increasing the total voltage while keeping the capacity the same.
- Parallel: Batteries are connected side-by-side, increasing the total capacity while keeping the voltage the same.
- Series-Parallel: A combination of both, increasing voltage and capacity to meet specific power needs.
How do you configure a series-parallel battery connection?
To configure a series-parallel connection, first, connect batteries in series to achieve the desired voltage. Then, connect these series strings in parallel to increase the overall capacity. Ensure each series string has the same number of batteries and that all connections are secure and balanced.
Why would you want to connect two or more batteries together?
Connecting multiple batteries together increases total voltage or capacity to meet specific energy requirements. This setup provides longer run times, higher power output, and can improve system reliability by distributing load and enhancing overall performance.
What types of lithium batteries can be connected in series or parallel?
Most lithium-ion batteries, including lithium iron phosphate (LiFePO4) and lithium nickel manganese cobalt oxide (NMC), can be connected in series or parallel. Ensure that all batteries are of the same type, capacity, and voltage for optimal performance and safety.
How do you connect a group of batteries in series?
To connect batteries in series, link the positive terminal of one battery to the negative terminal of the next. Continue this pattern for the entire group. The total voltage is the sum of the individual battery voltages, while the capacity remains the same as one battery.
How do you configure batteries with a series connection?
In a series configuration, connect the positive terminal of the first battery to the negative terminal of the next. Repeat this process until all batteries are connected. The combined voltage is the sum of all batteries, and the capacity is the same as a single battery.
What should you do for high current applications when connecting batteries in parallel?
For high current applications, use batteries with the same capacity and state of charge. Ensure all connections are robust and use thick, low-resistance cables to handle the high current. Regularly check connections and battery temperatures to prevent overheating and ensure safety.
What are the requirements for batteries to be connected in parallel?
Batteries connected in parallel should have the same voltage and similar capacity to ensure balanced charging and discharging. All batteries should be at the same state of charge before connection to avoid imbalances and potential damage.
What precautions should you take when connecting batteries in series?
Ensure all batteries are of the same type, age, and capacity. Verify correct polarity to avoid short circuits. Regularly monitor for imbalances and check for proper connections to prevent overcharging or deep discharging, which can affect battery life and safety.