- Lithium Golf Cart Battery
- Forklift Lithium Battery
-
48V
- 48V 210Ah
- 48V 300Ah
- 48V 420Ah (949 x 349 x 569 mm)
- 48V 420Ah (950 x 421 x 450 mm)
- 48V 456Ah
- 48V 460Ah (830 x 630 x 590 mm)
- 48V 460Ah (950 x 421 x 450 mm)
- 48V 460Ah (800 x 630 x 600 mm)
- 48V 460Ah (820 x 660 x 470 mm)
- 48V 500Ah
- 48V 560Ah (810 x 630 x 600 mm)
- 48V 560Ah (950 x 592 x 450 mm)
- 48V 600Ah
- 48V 630Ah
-
48V
- 12V Lithium Battery
12V 150Ah Lithium RV Battery
Bluetooth App | BCI Group 31
LiFePO4 Lithium
Discharge Temperature -20°C ~ 65°C
Fast Charger 14.6V 50A
Solar MPPT Charging - 24V Lithium Battery
- 36V Lithium Battery
- 48V Lithium Battery
-
48V LiFePO4 Battery
- 48V 50Ah
- 48V 50Ah (for Golf Carts)
- 48V 60Ah (8D)
- 48V 100Ah (8D)
- 48V 100Ah
- 48V 100Ah (Discharge 100A for Golf Carts)
- 48V 100Ah (Discharge 150A for Golf Carts)
- 48V 100Ah (Discharge 200A for Golf Carts)
- 48V 150Ah (for Golf Carts)
- 48V 160Ah (Discharge 100A for Golf Carts)
- 48V 160Ah (Discharge 160A for Golf Carts)
-
48V LiFePO4 Battery
- 60V Lithium Battery
-
60V LiFePO4 Battery
- 60V 20Ah
- 60V 30Ah
- 60V 50Ah
- 60V 50Ah (Small Size / Side Terminal)
- 60V 100Ah (for Electric Motocycle, Electric Scooter, LSV, AGV)
- 60V 100Ah (for Forklift, AGV, Electric Scooter, Sweeper)
- 60V 150Ah (E-Motocycle / E-Scooter / E-Tricycle / Tour LSV)
- 60V 200Ah (for Forklift, AGV, Electric Scooter, Sweeper)
-
60V LiFePO4 Battery
- 72V~96V Lithium Battery
- Rack-mounted Lithium Battery
- E-Bike Battery
- All-in-One Home-ESS
- Wall-mount Battery ESS
-
Home-ESS Lithium Battery PowerWall
- 24V 100Ah 2.4kWh PW24100-S PowerWall
- 48V 50Ah 2.4kWh PW4850-S PowerWall
- 48V 50Ah 2.56kWh PW5150-S PowerWall
- 48V 100Ah 5.12kWh PW51100-F PowerWall (IP65)
- 48V 100Ah 5.12kWh PW51100-S PowerWall
- 48V 100Ah 5.12kWh PW51100-H PowerWall
- 48V 200Ah 10kWh PW51200-H PowerWall
- 48V 300Ah 15kWh PW51300-H PowerWall
PowerWall 51.2V 100Ah LiFePO4 Lithium Battery
Highly popular in Asia and Eastern Europe.
CE Certification | Home-ESS -
Home-ESS Lithium Battery PowerWall
- Portable Power Stations
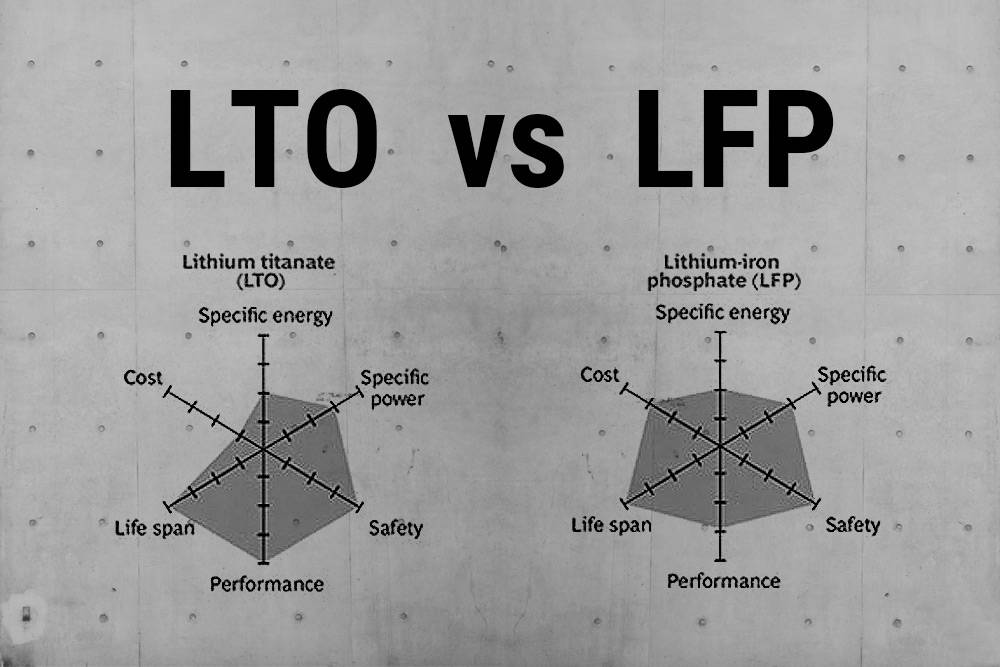
Lithium Titanate Battery (LTO) vs LiFePO4 Battery: Which is Better?

Lithium Titanate (LTO) and LiFePO4 batteries are compared for their performance, cost, and application. LTO batteries have fast charging, long lifespan, and wide temperature range, but they are expensive. LiFePO4 batteries offer high energy density, safety, and affordability. Choosing the better battery depends on specific needs and priorities. Lithium Titanate Battery (LTO) vs LiFePO4 Battery – Which is Better? Let’s dive in!
Differences between Lithium Titanate (LTO) and LiFePO4 Batteries
Unlocking the Differences: Lithium Titanate vs. LiFePO4 Batteries. Lithium Titanate batteries allow rapid charging and discharging without compromising efficiency or lifespan. LiFePO4 batteries offer good charging rates but may experience reduced capacity with continuous high discharge rates.

- Chemical Composition:
- Lithium Titanate batteries use lithium titanate as the anode material.
- LiFePO4 batteries utilize lithium iron phosphate, setting them apart in terms of chemical composition.
- Voltage Output:
- Lithium Titanate batteries typically operate at a lower nominal voltage of 2.4 volts per cell.
- LiFePO4 batteries, in contrast, have a higher nominal voltage at 3.2 volts per cell.
- Charging and Discharging:
- Lithium Titanate batteries allow rapid charging and discharging without compromising efficiency or lifespan.
- LiFePO4 batteries offer good charging rates but may experience reduced capacity with continuous high discharge rates.
- Cycle Life:
- Lithium Titanate batteries shine with an impressive cycle life of up to 20,000 cycles, ideal for demanding applications like electric vehicles.
- LiFePO4 batteries provide excellent longevity with around 2000-5000 cycles under normal conditions.
- Safety Features:
- Lithium Titanate batteries are known for extreme stability, exhibiting low thermal runaway potential even under challenging conditions.
- LiFePO4 batteries are recognized for superior thermal stability and resistance against overheating or combustion, ensuring safety.
In conclusion, both Lithium Titanate and LiFePO4 batteries have unique characteristics, offering varied advantages for specific applications. Understanding these differences is crucial for selecting the right battery based on your needs and requirements.
Yinlong vs Lithium 1500$ vs 1500$
Pros and Cons of Lithium Titanate Batteries (LTO)
Lithium Titanate (LTO) batteries offer significant advantages. They have a longer cycle life, rapid charging ability, and can operate in a wide temperature range. LTO batteries also prioritize safety, reducing the risk of overheating. Although they have lower energy density and higher costs, LTO batteries are reliable and safe for applications like electric vehicles and renewable energy storage.
Explain:
- Long Lifespan:
- Advantage: Lithium titanate batteries boast an extended lifespan, enduring numerous charge-discharge cycles without significant capacity loss. This makes them ideal for applications requiring frequent cycling.
- Fast Charge Rate:
- Advantage: These batteries exhibit a rapid charge rate, facilitating quick recharges in situations where time is a critical factor.
- Exceptional Safety:
- Advantage: Lithium titanate batteries are highly stable, reducing the risk of thermal runaway or combustion. This enhanced safety profile is advantageous, especially in applications prioritizing safety.
- Lower Energy Density:
- Drawback: Lithium titanate batteries have lower energy density compared to certain lithium-ion counterparts like LiFePO4. This limitation makes them less suitable for applications demanding sustained high-energy output.
- Cost Considerations:
- Drawback: While prices have been decreasing, lithium titanate batteries remain relatively more expensive than other battery technologies, impacting their widespread adoption.
- Environmental Impact:
- Advantage: Lithium titanate batteries do not contain heavy metals or toxic materials. However, their manufacturing processes may still have some negative environmental effects due to resource extraction and production emissions.
In summary, lithium titanate batteries excel in longevity and safety, making them suitable for specific applications. However, factors like energy density, cost, and environmental impact need consideration depending on the specific requirements of the intended use.
Pros and Cons of LiFePO4 Batteries
LiFePO4 batteries, or Lithium Iron Phosphate batteries, offer several advantages. They have a longer lifespan, are safer, and more environmentally friendly than traditional lead-acid batteries. LiFePO4 batteries charge quickly and store more energy in a smaller space. However, they are more expensive upfront and sensitive to high temperatures. Consider these factors when choosing the right battery for your needs.

Pros:
- High Energy Density:
- Advantage: LiFePO4 batteries excel in high energy density, allowing them to store substantial energy in a compact form. This is particularly advantageous in space-limited applications.
- Long Cycle Life:
- Advantage: Among the most significant benefits, LiFePO4 batteries boast an extended cycle life—up to 10 times longer than some lithium-ion counterparts. This longevity contributes to their cost-effectiveness over time.
- Enhanced Safety:
- Advantage: The LiFePO4 chemistry inherently enhances safety, displaying lower susceptibility to thermal runaway or explosions, even under extreme conditions. This safety feature is a notable advantage.
LiFePO4 batteries (Lithium Iron Phosphate) have some drawbacks to consider. They tend to be more expensive upfront and have a lower energy density compared to other lithium-ion batteries. LiFePO4 batteries are also sensitive to high temperatures, which can affect their performance. Despite these limitations, they are valued for their safety features, longer lifespan, and environmental friendliness. Consider these factors when choosing the right battery for your needs.
Cons:
- Lower Voltage:
- Drawback: LiFePO4 batteries have a lower nominal voltage (around 3.2 volts per cell) compared to other lithium-ion types. This may necessitate connecting more cells in series for applications requiring higher voltages.
- Limited Charging Speed:
- Drawback: While maintaining good capacity retention during fast charging, LiFePO4 batteries generally charge at slower rates compared to certain lithium-ion chemistries like Li-Po or NMC.
- Higher Cost:
- Drawback: Despite decreasing prices, LiFePO4 batteries still pose a higher upfront cost compared to traditional lead-acid or nickel-based rechargeable alternatives.
In conclusion, the suitability of LiFePO4 batteries hinges on specific needs and preferences. Their long cycle life, safety features, and energy density make them a strong contender, but considerations like voltage requirements, charging speed, and cost should be carefully weighed based on intended applications.
LTO vs LiFePO4 Batteries in Performance
LTO batteries have an impressive cycle life of up to 20,000 cycles, ideal for electric vehicles. LiFePO4 batteries offer good longevity with 2000-5000 cycles. LTO batteries allow rapid charging and discharging, while LiFePO4 batteries have a higher voltage. Consider these factors when choosing the right battery.
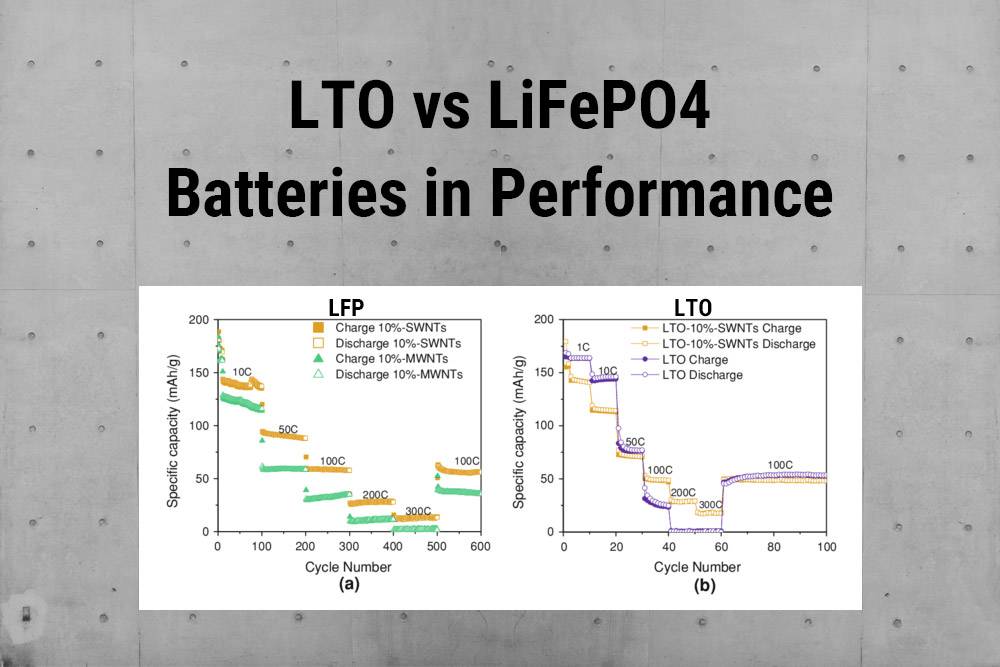
- Charging Time:
- Li-Ti: Excels in ultra-fast charging, reaching full capacity within minutes.
- LiFePO4: Offers good charging times, known for stable voltage output during discharge cycles.
- Energy Density:
- LiFePO4: Boasts higher energy density, providing more power for a similar size and weight.
- Li-Ti: While having commendable energy storage, may have lower energy density compared to LiFePO4.
- Cycle Life:
- Li-Ti: Stands out with exceptional cycle life, enduring thousands of charge-discharge cycles with minimal degradation.
- LiFePO4: Offers a long cycle life, though slightly lower than Li-Ti under certain usage conditions.
- Safety and Thermal Stability:
- LiFePO4: Known for superior thermal stability, less prone to overheating or thermal runaway.
- Li-Ti: Exhibits enhanced safety features, reducing the risk of combustion or explosion.
In summary, Li-Ti excels in fast charging and extended cycle life, making it ideal for applications requiring rapid charging and longevity. LiFePO4 shines in higher energy density and superior thermal stability, suitable for applications emphasizing power efficiency and safety. Understanding these distinctions helps make informed choices based on specific needs.
LTO vs LiFePO4 Batteries in Cost
LTO batteries are generally more expensive than LiFePO4 batteries due to their complexity and material rarity. LiFePO4 batteries are cheaper and more abundant, offering affordability and efficiency. LTO prioritizes longevity and performance. Consider your priorities when choosing between the two.

- Lithium Titanate (Li-Ti):
- High Initial Cost: Li-Ti batteries have a higher upfront cost due to expensive materials like titanium dioxide and complex manufacturing processes.
- Longer Lifespan: Despite the initial investment, they offer a longer lifespan, proving more cost-effective over time.
- Superior Performance: Li-Ti batteries provide superior performance, including faster charging and enhanced safety features.
- LiFePO4 (Lithium Iron Phosphate):
- Affordable Upfront: LiFePO4 batteries are more affordable initially, with relatively inexpensive raw materials compared to Li-Ti batteries.
- Good Cycle Life: They have a good cycle life, allowing multiple recharges without significant degradation, enhancing overall cost-effectiveness.
- Specific Considerations: While LiFePO4 is budget-friendly upfront, evaluate factors like longevity and performance for a well-informed decision.
In conclusion, Li-Ti batteries offer long-term cost-effectiveness with superior performance, while LiFePO4 provides an affordable upfront option with good cycle life. Consider specific needs and factors beyond cost for a well-rounded decision.
LTO vs LiFePO4 Batteries in Application
Lithium Titanate (LTO) batteries are ideal for fast charging and have a long cycle life, making them suitable for electric vehicles and heavy machinery. LiFePO4 batteries offer higher energy density and superior thermal stability, making them great for portable devices and radio communication equipment. Choose LTO for rapid charging and longevity, and LiFePO4 for power efficiency and safety.

Lithium Titanate Batteries (Li-Ti):
- High Power Output: Excellent for Electric Vehicles (EVs) and Hybrid Electric Vehicles (HEVs) due to high power output and fast charging.
- Renewable Energy Systems: Suitable for renewable energy systems, enduring frequent charge-discharge cycles efficiently.
- Grid Energy Storage: Efficiently stores excess electricity, supplying it back to the grid during peak demand with a long cycle life.
LiFePO4 Batteries:
- Consumer Electronics: Popular for smartphones, laptops, tablets, and portable power banks due to superior safety features.
- Versatile Applications: Used in solar-powered systems, Uninterruptible Power Supplies (UPS), marine vessels, RVs/campers, and remote monitoring equipment.
- Consistent Performance: Provides consistent performance in diverse temperatures, making them suitable for outdoor use in harsh environments.
Understanding the specific applications of lithium titanate and LiFePO4 batteries enables informed decisions based on unique requirements in various scenarios.
Related Knowledge
Comparing NMC and LMO Battery Chemistries
I was wrong about Lithium Titanate batteries. But should you use them for solar? 2020 Update
How do lithium-based battery systems compare in specific energy, specific power, and thermal stability?
What are the differences between different types of lithium-based batteries, such as NCA, LFP, and LTO?
NCA batteries offer high energy density, making them suitable for electric vehicles (EVs). LFP batteries are known for their safety and long cycle life, making them a robust choice for EVs. LTO batteries excel in rapid charging and have a long cycle life, making them ideal for EVs, buses, and energy storage. Consider the specific properties and strengths of each battery type for your application needs.
What are some applications where each battery type (NCA, LFP, LTO) is commonly used?
NCA batteries are commonly used in high-energy applications like electric vehicles (EVs). LFP batteries are found in smaller and entry-level EVs, while also being a sustainable and lower-cost option. LTO batteries excel in applications that require long cycle life, rapid charging, and safety, such as electric cars, buses, energy storage systems, and hybrid electric vehicles (HEVs). Choose the battery type based on your specific needs and requirements.
Which battery types are suitable for specific applications such as electric powertrains, medical devices, and energy storage?
What are the Future of Battery Technology?
The future of battery technology looks promising with advancements such as solid-state batteries, improved Li-ion batteries, and alternative anodes. Solid-state batteries offer higher energy density and faster charging, while alternative anodes promise better performance and safety. Sodium-ion batteries and iron-air batteries are also being researched for their potential. These innovations aim to enhance performance, safety, and affordability as we transition to renewable energy. Exciting times lie ahead for battery technology!























