- Lithium Golf Cart Battery
- Forklift Lithium Battery
-
48V
- 48V 210Ah
- 48V 300Ah
- 48V 420Ah (949 x 349 x 569 mm)
- 48V 420Ah (950 x 421 x 450 mm)
- 48V 456Ah
- 48V 460Ah (830 x 630 x 590 mm)
- 48V 460Ah (950 x 421 x 450 mm)
- 48V 460Ah (800 x 630 x 600 mm)
- 48V 460Ah (820 x 660 x 470 mm)
- 48V 500Ah
- 48V 560Ah (810 x 630 x 600 mm)
- 48V 560Ah (950 x 592 x 450 mm)
- 48V 600Ah
- 48V 630Ah
-
48V
- 12V Lithium Battery
12V 150Ah Lithium RV Battery
Bluetooth App | BCI Group 31
LiFePO4 Lithium
Discharge Temperature -20°C ~ 65°C
Fast Charger 14.6V 50A
Solar MPPT Charging - 24V Lithium Battery
- 36V Lithium Battery
- 48V Lithium Battery
-
48V LiFePO4 Battery
- 48V 50Ah
- 48V 50Ah (for Golf Carts)
- 48V 60Ah (8D)
- 48V 100Ah (8D)
- 48V 100Ah
- 48V 100Ah (Discharge 100A for Golf Carts)
- 48V 100Ah (Discharge 150A for Golf Carts)
- 48V 100Ah (Discharge 200A for Golf Carts)
- 48V 150Ah (for Golf Carts)
- 48V 160Ah (Discharge 100A for Golf Carts)
- 48V 160Ah (Discharge 160A for Golf Carts)
-
48V LiFePO4 Battery
- 60V Lithium Battery
-
60V LiFePO4 Battery
- 60V 20Ah
- 60V 30Ah
- 60V 50Ah
- 60V 50Ah (Small Size / Side Terminal)
- 60V 100Ah (for Electric Motocycle, Electric Scooter, LSV, AGV)
- 60V 100Ah (for Forklift, AGV, Electric Scooter, Sweeper)
- 60V 150Ah (E-Motocycle / E-Scooter / E-Tricycle / Tour LSV)
- 60V 200Ah (for Forklift, AGV, Electric Scooter, Sweeper)
-
60V LiFePO4 Battery
- 72V~96V Lithium Battery
- Rack-mounted Lithium Battery
- E-Bike Battery
- All-in-One Home-ESS
- Wall-mount Battery ESS
-
Home-ESS Lithium Battery PowerWall
- 24V 100Ah 2.4kWh PW24100-S PowerWall
- 48V 50Ah 2.4kWh PW4850-S PowerWall
- 48V 50Ah 2.56kWh PW5150-S PowerWall
- 48V 100Ah 5.12kWh PW51100-F PowerWall (IP65)
- 48V 100Ah 5.12kWh PW51100-S PowerWall
- 48V 100Ah 5.12kWh PW51100-H PowerWall
- 48V 200Ah 10kWh PW51200-H PowerWall
- 48V 300Ah 15kWh PW51300-H PowerWall
PowerWall 51.2V 100Ah LiFePO4 Lithium Battery
Highly popular in Asia and Eastern Europe.
CE Certification | Home-ESS -
Home-ESS Lithium Battery PowerWall
- Portable Power Stations
How Many Watts Is An Amp?

When converting amps to watts, the relationship is defined by the formula: Watts = Amps × Volts. Therefore, the number of watts in one amp depends on the voltage of the system. For example, at 120 volts, one amp equals 120 watts. Understanding this conversion is essential for managing electrical systems effectively.
How do Amps, Volts, and Watts relate to each other?
Amps (A) measure electric current, volts (V) measure electrical potential, and watts (W) quantify power. The relationship among these units is expressed by the formula:
Watts=Amps×Volts
This equation shows that power (watts) is the product of current (amps) and voltage (volts).
What is the significance of understanding these units?
Understanding amps, volts, and watts is essential for anyone working with electrical systems. It allows for safe and efficient energy use in homes and industries.
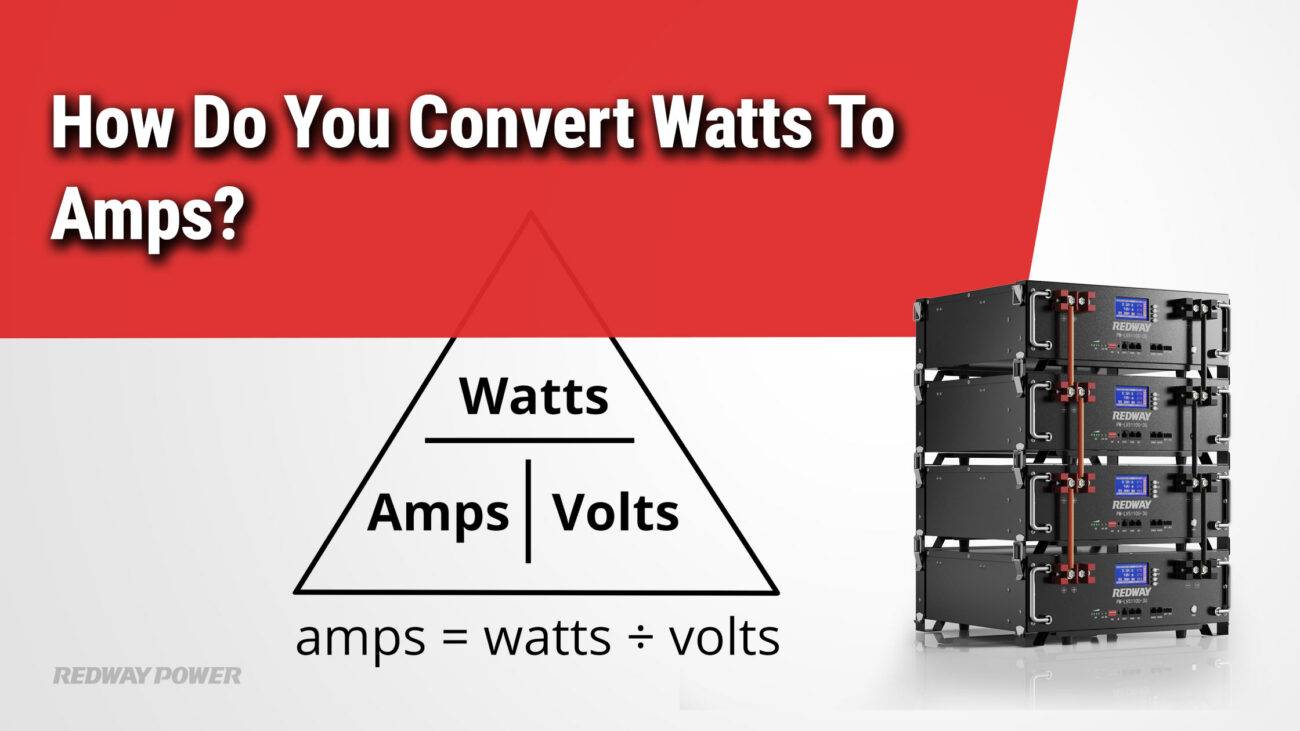
How can you convert amps to watts for DC power?
For direct current (DC), the conversion is straightforward:
Watts=Amps×Volts
For example, if you have 2 amps at 12 volts:
2A×12V=24W
How does AC power conversion differ?
In alternating current (AC) systems, you must consider the power factor:
Watts=Power Factor×Amps×Volts
The power factor accounts for inefficiencies in the system due to reactive loads.
How does the power factor affect calculations?
The power factor varies depending on the type of load:
| Load Type | Power Factor |
|---|---|
| Resistive Load | 1 |
| Inductive Load | ~0.8 |
| Capacitive Load | ~0.9 |
For resistive loads like heaters, the power factor is 1. For inductive loads like motors, it can be significantly lower.
How does this knowledge impact electrical safety?
Understanding how to convert between amps and watts helps prevent overloading circuits, which can lead to electrical fires or equipment damage. Proper calculations ensure that devices are used safely within their rated capacities.
What are common applications in daily life?
This knowledge is crucial when selecting appliances or designing electrical systems in homes and businesses. For example, knowing how many watts a device uses helps in choosing appropriate circuit breakers.
What are Volts? Amps? Ohms? Watts?
Industrial News
Recent developments in electrical safety standards emphasize the importance of accurate calculations regarding amps and watts. New regulations are being introduced to ensure that residential and commercial buildings adhere to updated safety protocols. These changes aim to reduce electrical hazards and improve energy efficiency across various sectors.
Redway Power Expert Views
“Understanding the relationship between amps, volts, and watts is fundamental for anyone involved in electrical work,” says an expert from Redway Power. “Not only does it enhance safety by preventing overloads, but it also promotes energy efficiency by ensuring devices operate within their designed limits.”
FAQ Section
What is the formula for converting amps to watts?
The formula for converting amps to watts is: Watts = Amps × Volts.How do I calculate watts if I know amps and voltage?
Simply multiply the number of amps by the voltage: Watts = Amps × Volts.Why do I need to consider the power factor in AC systems?
The power factor accounts for inefficiencies in AC systems due to reactive loads, affecting how much actual power is delivered compared to what is apparent.What happens if I exceed the wattage rating of a circuit?
Exceeding wattage ratings can lead to overheating, tripped breakers, or even electrical fires.Can I use this formula for all types of devices?
While it applies broadly, specific devices may require additional considerations based on their load type (resistive vs. inductive).By understanding these principles and calculations, individuals can better manage their electrical consumption safely and efficiently.