- Forklift Lithium Battery
-
48V
- 48V 210Ah
- 48V 300Ah
- 48V 420Ah (949 x 349 x 569 mm)
- 48V 420Ah (950 x 421 x 450 mm)
- 48V 456Ah
- 48V 460Ah (830 x 630 x 590 mm)
- 48V 460Ah (950 x 421 x 450 mm)
- 48V 460Ah (800 x 630 x 600 mm)
- 48V 460Ah (820 x 660 x 470 mm)
- 48V 500Ah
- 48V 560Ah (810 x 630 x 600 mm)
- 48V 560Ah (950 x 592 x 450 mm)
- 48V 600Ah
- 48V 630Ah
-
48V
- Lithium Golf Cart Battery
- 12V Lithium Battery
12V 150Ah Lithium RV Battery
Bluetooth App | BCI Group 31
LiFePO4 Lithium
Discharge Temperature -20°C ~ 65°C
Fast Charger 14.6V 50A
Solar MPPT Charging - 24V Lithium Battery
- 36V Lithium Battery
- 48V Lithium Battery
-
48V LiFePO4 Battery
- 48V 50Ah
- 48V 50Ah (for Golf Carts)
- 48V 60Ah (8D)
- 48V 100Ah (8D)
- 48V 100Ah
- 48V 100Ah (Discharge 100A for Golf Carts)
- 48V 100Ah (Discharge 150A for Golf Carts)
- 48V 100Ah (Discharge 200A for Golf Carts)
- 48V 150Ah (for Golf Carts)
- 48V 160Ah (Discharge 100A for Golf Carts)
- 48V 160Ah (Discharge 160A for Golf Carts)
-
48V LiFePO4 Battery
- 60V Lithium Battery
-
60V LiFePO4 Battery
- 60V 20Ah
- 60V 30Ah
- 60V 50Ah
- 60V 50Ah (Small Size / Side Terminal)
- 60V 100Ah (for Electric Motocycle, Electric Scooter, LSV, AGV)
- 60V 100Ah (for Forklift, AGV, Electric Scooter, Sweeper)
- 60V 150Ah (E-Motocycle / E-Scooter / E-Tricycle / Tour LSV)
- 60V 200Ah (for Forklift, AGV, Electric Scooter, Sweeper)
-
60V LiFePO4 Battery
- 72V~96V Lithium Battery
- Rack-mounted Lithium Battery
- E-Bike Battery
- All-in-One Home-ESS
- Wall-mount Battery ESS
-
Home-ESS Lithium Battery PowerWall
- 24V 100Ah 2.4kWh PW24100-S PowerWall
- 48V 50Ah 2.4kWh PW4850-S PowerWall
- 48V 50Ah 2.56kWh PW5150-S PowerWall
- 48V 100Ah 5.12kWh PW51100-F PowerWall (IP65)
- 48V 100Ah 5.12kWh PW51100-S PowerWall
- 48V 100Ah 5.12kWh PW51100-H PowerWall
- 48V 200Ah 10kWh PW51200-H PowerWall
- 48V 300Ah 15kWh PW51300-H PowerWall
PowerWall 51.2V 100Ah LiFePO4 Lithium Battery
Highly popular in Asia and Eastern Europe.
CE Certification | Home-ESS -
Home-ESS Lithium Battery PowerWall
- Portable Power Stations
How to Calculate Amps from 5000 Watts at 240 Volts

To determine how many amps 5000 watts draws at 240 volts, you can use the formula: Amps = Watts / Volts. Therefore, 5000 watts divided by 240 volts equals approximately 20.83 amps. Understanding this calculation is essential for electrical planning and ensuring that circuits are not overloaded.
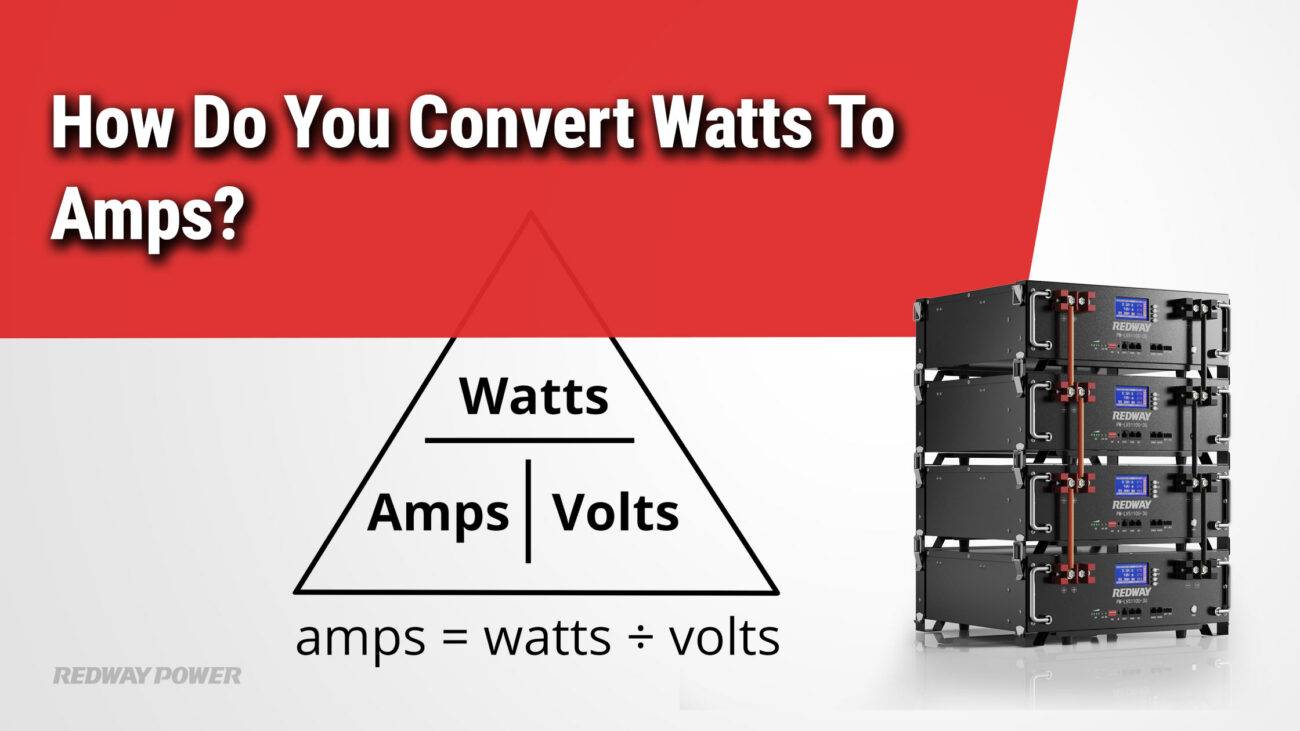
What Is the Formula for Converting Watts to Amps?
The formula for converting watts to amps is straightforward:
Amps = Watts / Volts.
This formula allows you to calculate how much current (in amps) a device will draw based on its power consumption (in watts) and the voltage of the circuit it operates on.
How Do You Calculate Amps from 5000 Watts at 240 Volts?
To calculate the amperage draw of a device using 5000 watts at 240 volts, use the formula:
Amps = 5000 watts / 240 volts, which equals approximately 20.83 amps.
This calculation is crucial for ensuring that your electrical system can handle the load without tripping breakers or causing overheating.
Why Is It Important to Know the Amperage Draw?
Knowing the amperage draw is essential for several reasons:
- Circuit Safety: Ensures that circuits are not overloaded, preventing electrical fires.
- Equipment Compatibility: Helps determine if your wiring and circuit breakers can handle the load.
- Energy Efficiency: Assists in selecting energy-efficient appliances that minimize electricity costs.
Understanding amperage helps maintain safe and efficient electrical systems.
What Factors Can Affect Amperage Draw in Electrical Systems?
Several factors can influence amperage draw:
| Factor | Description |
|---|---|
| Voltage Level | Higher voltages reduce amperage for the same wattage. |
| Appliance Type | Different devices have varying efficiencies and power requirements. |
| Load Characteristics | Inductive loads (like motors) may draw more current during startup than when running continuously. |
These factors must be considered when planning electrical installations.
How Does Voltage Impact the Current Draw of Appliances?
Voltage directly impacts current draw according to Ohm’s Law:
- Higher Voltage: For a given wattage, higher voltage results in lower current draw (amps). For example, using 240 volts instead of 120 volts halves the current required for the same power output.
- Lower Voltage: Conversely, lower voltage requires higher current to achieve the same wattage, which can lead to increased heat and potential circuit overloads.
Understanding this relationship is crucial for designing efficient electrical systems.
What Are Common Applications for 5000-Watt Devices?
Common applications for devices that require approximately 5000 watts include:
| Application | Description |
|---|---|
| Electric Water Heaters | Used in residential settings for heating water quickly. |
| Generators | Portable generators often provide around 5000 watts for backup power during outages. |
| HVAC Systems | Certain heating or cooling units may require this wattage to operate effectively. |
These applications highlight the need for careful consideration of amperage when selecting equipment.
How Can You Ensure Your Circuit Can Handle the Load?
To ensure your circuit can handle a load of approximately 20.83 amps:
- Check Circuit Breaker Ratings: Ensure your circuit breaker is rated above this amperage (typically a 30-amp breaker is suitable).
- Inspect Wiring: Use appropriately sized wiring (e.g., AWG 10 or larger) to prevent overheating.
- Avoid Daisy Chaining: Minimize connections on a single circuit to reduce load and potential hazards.
Following these steps helps maintain safety and efficiency in your electrical system.
What are Volts? Amps? Ohms? Watts?
Frequently Asked Questions About Amps and Watts
Q1: How many amps does a typical household circuit carry?
A1: Most household circuits are rated for either 15 or 20 amps, depending on their intended use.
Q2: Can I use a lower amp rating than required?
A2: Using a lower amp rating than required can lead to overheating and tripping breakers, posing safety risks.
Q3: What happens if I exceed my circuit’s amp rating?
A3: Exceeding your circuit’s amp rating can cause circuit breakers to trip or potentially lead to electrical fires due to overheating.
Industrial News: Trends in Electrical Power Management
The electrical power management industry continues to evolve with advancements in energy efficiency and smart grid technologies. Recent trends include increased adoption of renewable energy sources and improved battery storage solutions, enhancing overall power reliability and reducing reliance on traditional fossil fuels. These developments reflect a growing emphasis on sustainability within the energy sector.
Redway Power Expert Views on Electrical Calculations
“Understanding how to calculate amps from watts is fundamental for anyone working with electrical systems,” states an expert from Redway Power. “Accurate calculations ensure safety and efficiency, allowing users to make informed decisions about their power needs while minimizing risks associated with overloads.”