- Rack-mounted Lithium Battery
- Golf Cart Lithium Battery
-
Golf Cart Lithium Battery
- 36V 50Ah (for Golf Carts)
- 36V 80Ah (for Golf Carts)
- 36V 100Ah (for Golf Carts)
- 48V 50Ah (for Golf Carts)
- 48V 100Ah (Discharge 100A for Golf Carts)
- 48V 100Ah (Discharge 150A for Golf Carts)
- 48V 100Ah (Discharge 200A for Golf Carts)
- 48V 120Ah (for Golf Carts)
- 48V 150Ah (for Golf Carts)
- 48V 160Ah (Discharge 100A for Golf Carts)
- 48V 160Ah (Discharge 160A for Golf Carts)
-
Golf Cart Lithium Battery
- Forklift Lithium Battery
- 12V Lithium Battery
- 24V Lithium Battery
- 36V Lithium Battery
- 48V Lithium Battery
-
48V LiFePO4 Battery
- 48V 50Ah
- 48V 50Ah (for Golf Carts)
- 48V 60Ah (8D)
- 48V 100Ah (8D)
- 48V 100Ah
- 48V 100Ah (Discharge 100A for Golf Carts)
- 48V 100Ah (Discharge 150A for Golf Carts)
- 48V 100Ah (Discharge 200A for Golf Carts)
- 48V 150Ah (for Golf Carts)
- 48V 160Ah (Discharge 100A for Golf Carts)
- 48V 160Ah (Discharge 160A for Golf Carts)
-
48V LiFePO4 Battery
- 60V Lithium Battery
-
60V LiFePO4 Battery
- 60V 20Ah
- 60V 30Ah
- 60V 50Ah
- 60V 50Ah (Small Size / Side Terminal)
- 60V 100Ah (for Electric Motocycle, Electric Scooter, LSV, AGV)
- 60V 100Ah (for Forklift, AGV, Electric Scooter, Sweeper)
- 60V 150Ah (E-Motocycle / E-Scooter / E-Tricycle / Tour LSV)
- 60V 200Ah (for Forklift, AGV, Electric Scooter, Sweeper)
-
60V LiFePO4 Battery
- 72V~96V Lithium Battery
- E-Bike Battery
- All-in-One Home-ESS
- Wall-mount Battery ESS
-
Home-ESS Lithium Battery PowerWall
- 24V 100Ah 2.4kWh PW24100-S PowerWall
- 48V 50Ah 2.4kWh PW4850-S PowerWall
- 48V 50Ah 2.56kWh PW5150-S PowerWall
- 48V 100Ah 5.12kWh PW51100-F PowerWall (IP65)
- 48V 100Ah 5.12kWh PW51100-S PowerWall
- 48V 100Ah 5.12kWh PW51100-H PowerWall
- 48V 200Ah 10kWh PW51200-H PowerWall
- 48V 300Ah 15kWh PW51300-H PowerWall
PowerWall 51.2V 100Ah LiFePO4 Lithium Battery
Highly popular in Asia and Eastern Europe.
CE Certification | Home-ESS -
Home-ESS Lithium Battery PowerWall
- Portable Power Stations
How Do You Tell If A 12v Battery Is Fully Charged?

To determine if a 12V battery is fully charged, use a multimeter to measure voltage. Lead-acid batteries typically read 12.6V-13.2V, while LiFePO4 batteries show around 12.8V. Ensure cells are topped with electrolyte and test for damage. Maintaining terminals and monitoring usage patterns are crucial for optimal performance.
Get Your Custom B2B Quote for 12v Battery: Click HERE.
Understanding the Basics of a 12V Battery
Understanding 12V batteries is crucial for car owners. A lead-acid battery comprises six cells, yielding 12.6-13.2 volts fully charged, while a LiFePO4 battery has four cells, totaling about 12.8 volts. Each lead-acid cell produces 2.1-2.2 volts, while each LiFePO4 cell yields around 3.2 volts. The voltage output varies depending on the battery technology used.
A typical 12V lead-acid battery consists of six cells, each producing around 2.1V to 2.2V when fully charged, totaling approximately 12.6V to 13.2V.
On the other hand, a 12V lithium iron phosphate (LiFePO4) battery typically comprises four cells, with each cell producing around 3.2V, totaling approximately 12.8V when fully charged. So, it depends on the type of battery technology used.
Understanding the basics of a 12V battery, including its cell configuration and output voltage, is essential for various applications. This knowledge enables individuals to make informed decisions when selecting and utilizing 12V batteries for their specific needs.
Factors Affecting Battery Charge
Factors affecting 12V battery charge include temperature, usage patterns, age, maintenance, and discharging practices. Extreme temperatures, high-power demands, aging, poor maintenance, and frequent deep discharges impact battery performance and longevity. Managing these factors is crucial for maintaining optimal charging levels and ensuring reliable battery performance.
Here’s what you need to know:
- Temperature: Extreme cold or heat can impact battery performance, with cold temperatures slowing down chemical reactions and heat accelerating internal oxidation and water loss, both leading to reduced voltage output and capacity.
- Usage patterns: High-power demands from starting engines or running devices, along with leaving electronics connected while turned off, can drain the battery quickly.
- Age: As batteries age, their ability to hold and deliver charge naturally diminishes, resulting in decreased voltage levels even when fully charged.
- Maintenance: Improper maintenance, such as neglecting to clean terminals and remove corrosion, can hinder electrical conductivity and reduce charging efficiency.
- Discharging practices: Frequent discharging below recommended levels without proper recharging can permanently damage the battery’s chemistry.
Understanding these factors empowers you to maintain optimal charging levels for your 12V batteries, ensuring reliable performance and longevity.
Methods for Testing Lead-acid Battery Charge
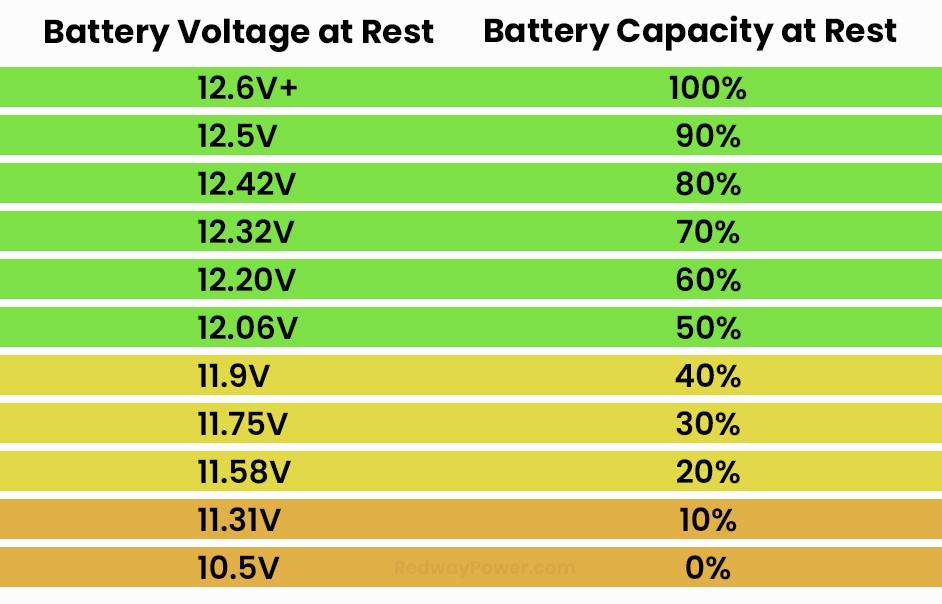
To test a 12V battery’s charge, options include using a multimeter, hydrometer, or visual inspection. A fully charged battery should read around 12.6V+. Regular checks are essential for longevity. Cross-verifying results ensures accuracy. Open-cell batteries allow a more rigorous check with a hydrometer. Maintaining a fully charged battery is crucial for performance and longevity.
Here’s a breakdown:
- Multimeter: Utilizing a multimeter to measure voltage by connecting probes to battery terminals. A fully charged 12V battery should read around 12.6V or higher.
- Hydrometer: Measuring electrolyte specific gravity with a hydrometer and comparing it to a chart to assess charge status accurately.
- Visual inspection: Checking for clear liquid in battery cells and ensuring no cracks or leaks indicate a fully charged battery.
Maintaining a fully charged battery is crucial for performance and longevity. Regular checks help prevent unexpected failures and extend overall lifespan. Remember to cross-verify results using different methods for accuracy.
How to Use a Multimeter to Check 12VBattery Voltage?
To check 12V battery voltage with a multimeter, set the dial to the DC voltage range. Connect the black lead to the battery’s negative terminal and the red lead to the positive terminal. The multimeter will display the voltage reading, indicating the battery’s voltage level.
How to Check 12V Battery Voltage with a Hydrometer?
How to Visually Inspect 12V Battery
Methods for Testing LiFePO4 Battery Charge
Maintaining a fully charged LiFePO4 battery involves not turning off the power until the battery reaches 100% charge. This practice ensures efficient operation and increases the battery’s lifespan. By fully charging the battery, you can optimize its usage and decrease the frequency of charging.
How to Maintain a Fully Charged Battery?
Get Your Custom B2B Quote for 12v Battery: Click HERE.
FAQs
What are some recommended products for battery monitoring and maintenance?
What are some common voltage readings for different states of charge of a battery?
How can a cranking test indicate the health of a car battery?
A cranking test helps determine the health of a car battery by subjecting it to high current draws, simulating engine starting. By measuring how much the battery charge drops during this test, it becomes possible to identify batteries that are going bad. This test provides valuable insight into the effectiveness and overall health of the car battery.
What are the voltage readings of LiFePO4 batteries?
How can I conduct a cranking test to measure the effectiveness of my car battery?
By conducting a cranking test and interpreting the voltage reading, you can determine the effectiveness of your car battery. This test helps identify potential issues and ensures reliable performance for your vehicle.
What impact does a lower voltage reading have on a car’s performance?
How can I measure the voltage of a 12-volt car battery at rest?

What voltage should a 12v battery show when the car is running?
How to prevent battery wear in rarely driven vehicles?
Discover the differences between Group 24 and Group 27 batteries. The Group 27 battery offers higher output current and capacity, making it ideal for heavy commercial and industrial equipment. With more power and extended performance, it provides reliable and long-lasting operation. Conversely, the Group 24 battery is suitable for applications with lower power requirements and limited space. Consider equipment compatibility, power needs, and available space to determine which battery is better suited for your specific requirements.
Why is regular battery cleaning important for service life?
Regular battery cleaning is crucial for maintaining the service life of the battery. By keeping the battery terminals free from corrosion, you ensure a strong and reliable connection between the battery and the electrical system, leading to improved performance. Additionally, proper maintenance, including regular cleaning, can help extend the lifespan of the battery.
How to check and top up battery electrolyte level?
Checking and topping up the battery electrolyte level is essential for battery maintenance. Follow these steps: ensure safety, clean the battery, check the electrolyte levels visually or with a hydrometer, top up with distilled water if necessary, and securely reseal the battery. Regular maintenance helps prolong battery life and ensures optimal performance.
How to extend the life of a lead-acid battery at home?
Extend the life of your lead-acid battery at home with these easy tips: avoid complete battery drain, don’t overcharge the battery, prevent equipment overload, store the battery in optimal conditions, and keep it clean. By following these practices, you can increase the lifespan of your lead-acid battery and ensure optimal performance.
What are the best practices for recharging Century Lithium Pro batteries?
Personal Experiences with Desulphation Devices on 12V Batteries:
Experiences vary, with some individuals reporting success in reviving old, sulphated batteries, extending their lifespan by months or even years. Others find limited effectiveness, particularly if the battery is severely damaged. Success often depends on the battery’s condition and the quality of the desulphation device.
Obtaining a Pulse Charger and Differences from Standard Chargers:
Consumers can purchase pulse chargers online or at automotive and electronics stores. Pulse chargers differ from standard chargers by sending short, high-frequency pulses to break down sulphate crystals on battery plates, improving battery capacity and lifespan, whereas standard chargers provide a constant current.
Effectiveness of Desulphation Methods on Different Battery Types:
Desulphation methods are most effective on lead-acid batteries, including flooded, AGM, and gel types. However, the effectiveness can vary based on the battery’s condition and design, with mixed results on sealed and maintenance-free batteries.
Experiences Shared in the Solar Cheapskate Forum Regarding Battery Revival:
Users in the Solar Cheapskate forum often share mixed experiences, with some achieving notable success in reviving old batteries using pulse chargers or homemade desulphation devices, while others report limited improvements or complete failure, especially with deeply sulphated or damaged batteries.
How Pulse Charging Methods Work for Desulphation of Batteries:
Pulse charging works by delivering high-frequency pulses of current to a battery, which can help dissolve lead sulfate crystals that form on the battery plates during discharge. This process can restore some lost capacity and prolong the battery’s life by maintaining a cleaner electrode surface.