- Forklift Lithium Battery
-
48V
- 48V 210Ah
- 48V 300Ah
- 48V 420Ah (949 x 349 x 569 mm)
- 48V 420Ah (950 x 421 x 450 mm)
- 48V 456Ah
- 48V 460Ah (830 x 630 x 590 mm)
- 48V 460Ah (950 x 421 x 450 mm)
- 48V 460Ah (800 x 630 x 600 mm)
- 48V 460Ah (820 x 660 x 470 mm)
- 48V 500Ah
- 48V 560Ah (810 x 630 x 600 mm)
- 48V 560Ah (950 x 592 x 450 mm)
- 48V 600Ah
- 48V 630Ah
-
48V
- Lithium Golf Cart Battery
- 12V Lithium Battery
12V 150Ah Lithium RV Battery
Bluetooth App | BCI Group 31
LiFePO4 Lithium
Discharge Temperature -20°C ~ 65°C
Fast Charger 14.6V 50A
Solar MPPT Charging - 24V Lithium Battery
- 36V Lithium Battery
- 48V Lithium Battery
-
48V LiFePO4 Battery
- 48V 50Ah
- 48V 50Ah (for Golf Carts)
- 48V 60Ah (8D)
- 48V 100Ah (8D)
- 48V 100Ah
- 48V 100Ah (Discharge 100A for Golf Carts)
- 48V 100Ah (Discharge 150A for Golf Carts)
- 48V 100Ah (Discharge 200A for Golf Carts)
- 48V 150Ah (for Golf Carts)
- 48V 160Ah (Discharge 100A for Golf Carts)
- 48V 160Ah (Discharge 160A for Golf Carts)
-
48V LiFePO4 Battery
- 60V Lithium Battery
-
60V LiFePO4 Battery
- 60V 20Ah
- 60V 30Ah
- 60V 50Ah
- 60V 50Ah (Small Size / Side Terminal)
- 60V 100Ah (for Electric Motocycle, Electric Scooter, LSV, AGV)
- 60V 100Ah (for Forklift, AGV, Electric Scooter, Sweeper)
- 60V 150Ah (E-Motocycle / E-Scooter / E-Tricycle / Tour LSV)
- 60V 200Ah (for Forklift, AGV, Electric Scooter, Sweeper)
-
60V LiFePO4 Battery
- 72V~96V Lithium Battery
- Rack-mounted Lithium Battery
- E-Bike Battery
- All-in-One Home-ESS
- Wall-mount Battery ESS
-
Home-ESS Lithium Battery PowerWall
- 24V 100Ah 2.4kWh PW24100-S PowerWall
- 48V 50Ah 2.4kWh PW4850-S PowerWall
- 48V 50Ah 2.56kWh PW5150-S PowerWall
- 48V 100Ah 5.12kWh PW51100-F PowerWall (IP65)
- 48V 100Ah 5.12kWh PW51100-S PowerWall
- 48V 100Ah 5.12kWh PW51100-H PowerWall
- 48V 200Ah 10kWh PW51200-H PowerWall
- 48V 300Ah 15kWh PW51300-H PowerWall
PowerWall 51.2V 100Ah LiFePO4 Lithium Battery
Highly popular in Asia and Eastern Europe.
CE Certification | Home-ESS -
Home-ESS Lithium Battery PowerWall
- Portable Power Stations
How Do You Convert Watts to Amps?
Converting watts to amps is essential for understanding electrical systems, whether for household appliances or larger installations. This article will guide you through the conversion process, provide formulas, and explain why knowing this relationship is crucial for safety and efficiency.
How do you convert watts to amps?
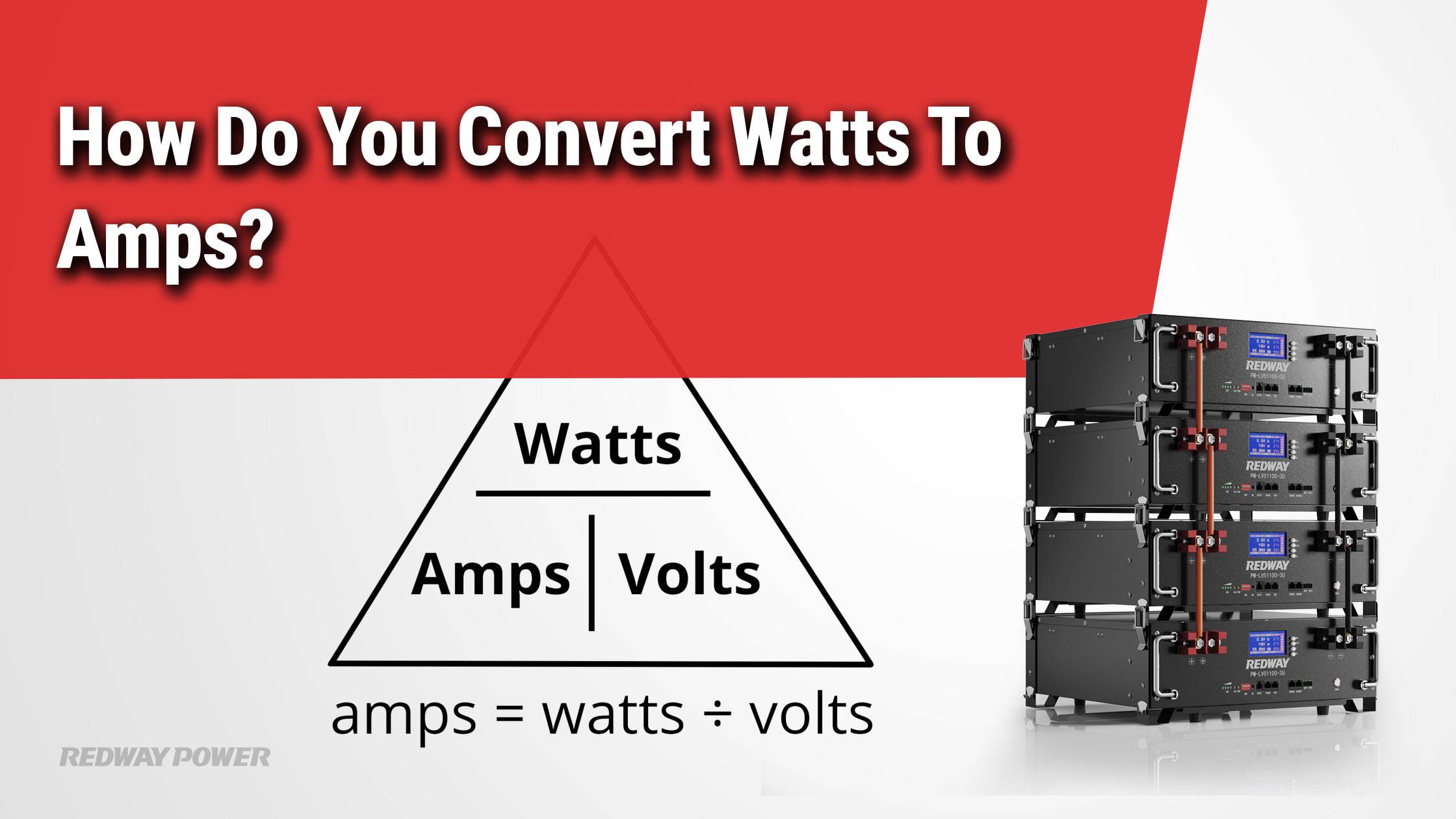
To convert watts (W) to amps (A), you need to know the voltage (V) of your system. The basic formula used is:
Amps(A)=Watts(W)/Volts(V)
This means that if you have a specific wattage and voltage, you can easily calculate the current in amperes. Chart: Simple Conversion Example
| Watts (W) | Volts (V) | Amps (A) |
|---|---|---|
| 120 | 120 | 1 |
| 240 | 120 | 2 |
| 600 | 120 | 5 |
| 1200 | 240 | 5 |
Watts to Amps Converter
Enter the values in the boxes, press ‘Convert’, and see the result.
Current (Amps):
Related Calculators
What is the formula for converting watts to amps?
The formula for converting watts to amps is derived from Ohm’s Law, which states that power equals voltage times current. Rearranging this gives us:
Amps=Watts/Volts
For example, if you have a device that uses 600 watts on a 120-volt circuit:
Amps=600 W/120 V=5 A
This calculation helps ensure that your electrical system can handle the current load.Chart: Formula Breakdown
| Variable | Description |
|---|---|
| Watts (W) | Power consumption of the device |
| Volts (V) | Voltage supplied by the electrical system |
| Amps (A) | Current flowing through the circuit |
Why is it important to understand the relationship between watts and amps?
Understanding the relationship between watts and amps is crucial for several reasons:
- Safety: Knowing how much current your devices draw helps prevent overloading circuits, which can lead to fires or equipment damage.
- Efficiency: Proper calculations ensure that electrical systems operate within safe limits, optimizing performance and reducing energy waste.
- Equipment Compatibility: It helps in selecting appropriate wiring and circuit breakers based on current requirements.
Chart: Importance of Understanding Watts and Amps
| Reason | Explanation |
|---|---|
| Safety | Prevents circuit overloads and potential hazards |
| Efficiency | Optimizes performance while minimizing energy waste |
| Equipment Compatibility | Ensures proper selection of wiring and breakers |
What factors affect the conversion between watts and amps?
Several factors influence how you convert watts to amps:
- Voltage Level: The higher the voltage, the lower the current for a given wattage. Conversely, lower voltages result in higher currents.
- Type of Current: AC (Alternating Current) and DC (Direct Current) systems may have different characteristics affecting how power is distributed.
- Power Factor: In AC systems, especially those with inductive loads, the power factor affects how much of the apparent power is used effectively.
Chart: Factors Affecting Conversion
| Factor | Description |
|---|---|
| Voltage Level | Higher voltage leads to lower current |
| Type of Current | AC vs. DC affects distribution characteristics |
| Power Factor | Influences effective power usage in AC circuits |
How do you convert watts to amps for AC and DC circuits?
The conversion process differs slightly between AC and DC systems:
- DC Circuits: Use the simple formula A=W/V. For example, if a device uses 300W at 12V:
A=300/12=25 A
- AC Circuits: For single-phase AC circuits, consider the power factor:
A=W/(V×PF)Where PF is the power factor (typically between 0 and 1). If a device uses 2400W at 120V with a PF of 0.9:A=2400/(120×0.9)=22.22 A
Chart: Conversion Methods
| Circuit Type | Formula |
|---|---|
| DC | A=W/V |
| Single-phase AC | A=W/(V×PF) |
Industrial News
Recent developments in energy efficiency standards have prompted manufacturers to focus on improving electrical devices’ design by optimizing their wattage ratings relative to amperage requirements. This shift aims not only at compliance with regulations but also at enhancing consumer safety by reducing risks associated with overcurrent situations. As technology advances, understanding these conversions becomes increasingly vital in both residential and industrial applications.
How to convert Watts to amps? How to convert amperes to watts?
Redway Power Insights
“Understanding how to convert watts to amps is fundamental for anyone working with electrical systems,” states Redway Power’s expert team. “Proper calculations ensure safety, efficiency, and compatibility across various devices, making it essential knowledge for both professionals and DIY enthusiasts.”
FAQ Section
Q: Can I use any voltage when converting watts to amps?
A: No, you must use the specific voltage that corresponds with your application or device.
Q: What happens if I overload my circuit?
A: Overloading a circuit can cause overheating, tripped breakers, or even electrical fires.
Q: How does power factor affect my calculations?
A: The power factor indicates how effectively electricity is being used; it must be included in calculations for accurate results in AC circuits.



















