- Forklift Lithium Battery
-
48V
- 48V 210Ah
- 48V 300Ah
- 48V 420Ah (949 x 349 x 569 mm)
- 48V 420Ah (950 x 421 x 450 mm)
- 48V 456Ah
- 48V 460Ah (830 x 630 x 590 mm)
- 48V 460Ah (950 x 421 x 450 mm)
- 48V 460Ah (800 x 630 x 600 mm)
- 48V 460Ah (820 x 660 x 470 mm)
- 48V 500Ah
- 48V 560Ah (810 x 630 x 600 mm)
- 48V 560Ah (950 x 592 x 450 mm)
- 48V 600Ah
- 48V 630Ah
-
48V
- Lithium Golf Cart Battery
- 12V Lithium Battery
12V 150Ah Lithium RV Battery
Bluetooth App | BCI Group 31
LiFePO4 Lithium
Discharge Temperature -20°C ~ 65°C
Fast Charger 14.6V 50A
Solar MPPT Charging - 24V Lithium Battery
- 36V Lithium Battery
- 48V Lithium Battery
-
48V LiFePO4 Battery
- 48V 50Ah
- 48V 50Ah (for Golf Carts)
- 48V 60Ah (8D)
- 48V 100Ah (8D)
- 48V 100Ah
- 48V 100Ah (Discharge 100A for Golf Carts)
- 48V 100Ah (Discharge 150A for Golf Carts)
- 48V 100Ah (Discharge 200A for Golf Carts)
- 48V 150Ah (for Golf Carts)
- 48V 160Ah (Discharge 100A for Golf Carts)
- 48V 160Ah (Discharge 160A for Golf Carts)
-
48V LiFePO4 Battery
- 60V Lithium Battery
-
60V LiFePO4 Battery
- 60V 20Ah
- 60V 30Ah
- 60V 50Ah
- 60V 50Ah (Small Size / Side Terminal)
- 60V 100Ah (for Electric Motocycle, Electric Scooter, LSV, AGV)
- 60V 100Ah (for Forklift, AGV, Electric Scooter, Sweeper)
- 60V 150Ah (E-Motocycle / E-Scooter / E-Tricycle / Tour LSV)
- 60V 200Ah (for Forklift, AGV, Electric Scooter, Sweeper)
-
60V LiFePO4 Battery
- 72V~96V Lithium Battery
- Rack-mounted Lithium Battery
- E-Bike Battery
- All-in-One Home-ESS
- Wall-mount Battery ESS
-
Home-ESS Lithium Battery PowerWall
- 24V 100Ah 2.4kWh PW24100-S PowerWall
- 48V 50Ah 2.4kWh PW4850-S PowerWall
- 48V 50Ah 2.56kWh PW5150-S PowerWall
- 48V 100Ah 5.12kWh PW51100-F PowerWall (IP65)
- 48V 100Ah 5.12kWh PW51100-S PowerWall
- 48V 100Ah 5.12kWh PW51100-H PowerWall
- 48V 200Ah 10kWh PW51200-H PowerWall
- 48V 300Ah 15kWh PW51300-H PowerWall
PowerWall 51.2V 100Ah LiFePO4 Lithium Battery
Highly popular in Asia and Eastern Europe.
CE Certification | Home-ESS -
Home-ESS Lithium Battery PowerWall
- Portable Power Stations
How to Convert Battery Amps to Amp-Hours
Converting battery amps to amp-hours is essential for understanding battery capacity and usage. Amp-hours (Ah) measure the total charge a battery can deliver over time, while amps (A) indicate the current flow. To convert between these two, you can use straightforward formulas based on the time of usage.
What are Amps and Amp-Hours?
Amps (A) represent the flow of electrical current, while amp-hours (Ah) quantify the total charge delivered over a specified time. For example, if a device draws 2 amps for 3 hours, it consumes 6 amp-hours of energy. Understanding this distinction is crucial for managing battery life effectively.
Chart: Relationship Between Amps and Amp-Hours
| Amps (A) | Time (Hours) | Amp-Hours (Ah) |
|---|---|---|
| 1 A | 1 | 1 Ah |
| 2 A | 3 | 6 Ah |
| 5 A | 2 | 10 Ah |
| 10 A | 4 | 40 Ah |
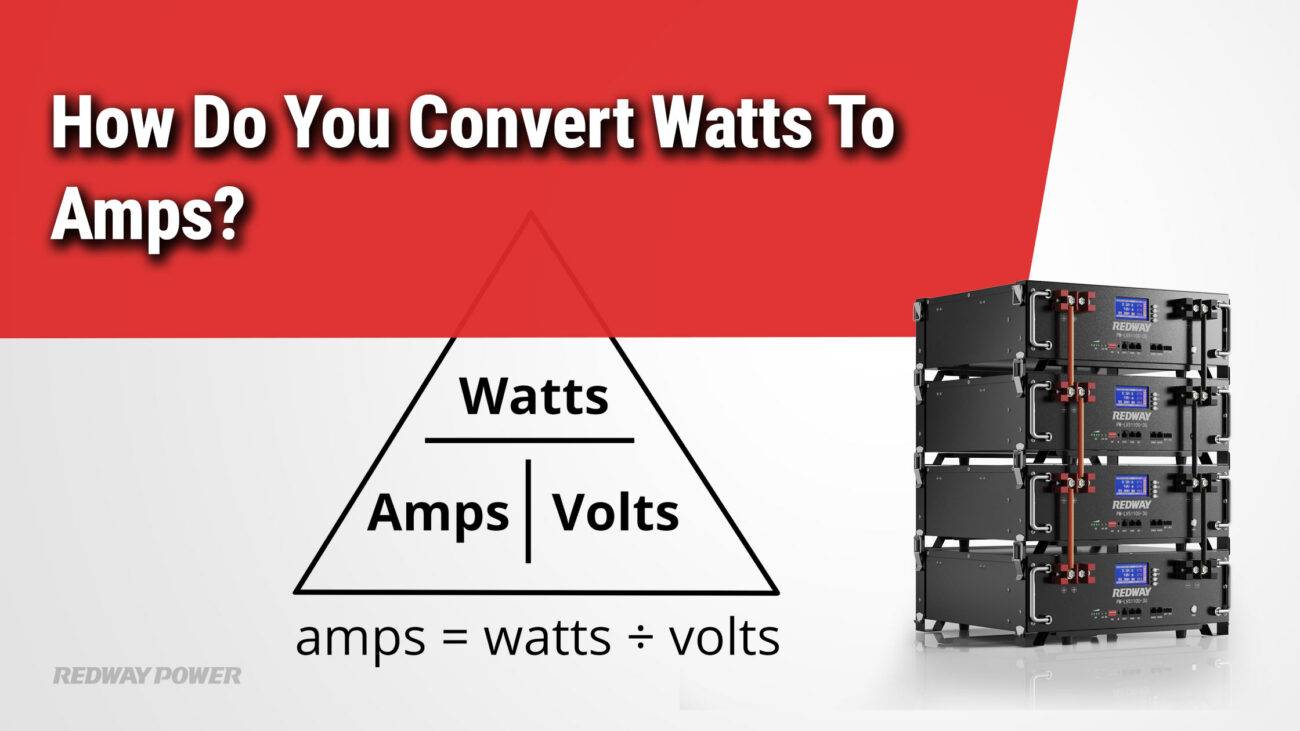
How Do You Convert Amps to Amp-Hours?
To convert amps to amp-hours, you multiply the current in amps by the time in hours:
Amp Hours Ah =Amps A ×Time h
For instance, if a device uses 3 amps over a period of 4 hours, the calculation would be:
3 A×4 h=12 Ah
Example Calculation
If you have a portable fan that draws 2 amps and operates for 5 hours, you can calculate the amp-hours as follows:
2 A×5 h=10 Ah
How Do You Convert Amp-Hours to Amps?
To convert amp-hours back to amps, divide the amp-hours by the time in hours:
Amps A =Amp Hours Ah / Time h
For example, if you have a battery rated at 50 amp-hours and want to know how many amps it can deliver over a period of 10 hours:
50 Ah/10 h=5 A
Chart: Conversion from Amp-Hours to Amps
| Amp-Hours (Ah) | Time (Hours) | Amps (A) |
|---|---|---|
| 50 Ah | 10 | 5 A |
| 100 Ah | 20 | 5 A |
| 30 Ah | 6 | 5 A |
Why is Understanding Battery Capacity Important?
Understanding how to convert between amps and amp-hours helps in selecting the right battery for your needs. It ensures that devices receive adequate power without exceeding battery capacity, which can lead to reduced performance or damage.
Application in Solar Power Systems
In solar power systems, knowing how many amp-hours your batteries can provide helps in designing an efficient system. For instance, if a solar panel system pulls an average of 15 amps during peak sunlight hours, calculating how long the battery will last becomes crucial for energy management.
Industrial News
Recent advancements in battery technology have focused on improving energy density and charging efficiency. Companies are now developing lithium-ion batteries with enhanced capacity that can deliver higher amperage while maintaining lighter weight. This trend is particularly significant for electric vehicles and renewable energy storage solutions.
Redway Power Expert Views
“Understanding the relationship between amps and amp-hours is fundamental for anyone working with batteries,” says an expert from Redway Power. “Accurate calculations ensure that systems run efficiently and that users maximize their battery life without risking over-discharge.”
Examples of Calculating Battery Amp-Hours
Here are some practical examples illustrating how to calculate battery amp-hours:
- Example 1: If you have a battery rated at 10 amps and it runs for 2 hours, the calculation would be 10 amps x 2 hours = 20 amp-hours.
- Example 2: For a device consuming 0.5 amps running continuously for 24 hours, the calculation is 0.5 amps x 24 hours = 12 amp-hours.
- Example 3: To determine how long a battery can power a device with a 6 amp-hour requirement:
Tips for Extending Battery Life
Extending the lifespan of your batteries is essential for optimal performance and cost-effectiveness. Here’s how you can achieve that:
- Avoid Deep Discharges: Don’t let your battery run completely flat before recharging to prolong its lifespan.
- Charge at Correct Voltage: Use the appropriate charger with the right voltage settings to prevent over or undercharging.
- Store Properly: Keep batteries in a cool, dry place away from extreme temperatures and direct sunlight.
- Use Compatible Accessories: Ensure accessories match your battery type to avoid damage.
- Clean Terminals: Periodically clean battery terminals to maintain efficient charging.
- Limit Fast Charging: Fast charging generates heat, which can stress battery cells over time. Opt for regular charging when possible.
- Avoid Extreme Temperatures: High temps increase resistance, while low temps reduce capacity temporarily or permanently.
Following these tips will optimize battery performance and save money by reducing replacements. Understanding battery amp-hours helps make informed energy decisions.
FAQs
How to calculate battery capacity using amp hours, watt hours, and voltage?
Calculating battery capacity is essential for determining how long your devices can run on a single charge. To calculate the battery’s capacity in watt hours, multiply the voltage by the amp hours. This formula gives you a more accurate representation of the total energy storage capabilities of the battery.
For example, if you have a 12-volt battery with 50 amp hours, multiplying these values will give you 600 watt hours of total capacity. Understanding this calculation allows you to estimate how long your device can operate before needing to be recharged.
Keep in mind that different batteries have varying capacities based on their voltage and amp hour ratings. It’s crucial to consider these factors when choosing a battery for your specific needs. By calculating the battery capacity using these metrics, you can make informed decisions about which type of battery best suits your requirements.
What is an amp-hour?
An amp-hour is a unit of measure that indicates how much charge a battery can deliver over one hour at a constant rate of one ampere.
How do I calculate my device’s power consumption?
To calculate power consumption in amp-hours, multiply the current draw in amps by the number of hours used.
Can I convert directly between CCA and Ah?
No, Cold Cranking Amps (CCA) and Amp Hours (Ah) serve different purposes and cannot be directly converted without considering specific battery characteristics.By understanding these conversions and their implications, users can better manage their energy needs and optimize their systems for efficiency.