- Forklift Lithium Battery
-
48V
- 48V 210Ah
- 48V 300Ah
- 48V 420Ah (949 x 349 x 569 mm)
- 48V 420Ah (950 x 421 x 450 mm)
- 48V 456Ah
- 48V 460Ah (830 x 630 x 590 mm)
- 48V 460Ah (950 x 421 x 450 mm)
- 48V 460Ah (800 x 630 x 600 mm)
- 48V 460Ah (820 x 660 x 470 mm)
- 48V 500Ah
- 48V 560Ah (810 x 630 x 600 mm)
- 48V 560Ah (950 x 592 x 450 mm)
- 48V 600Ah
- 48V 630Ah
-
48V
- Lithium Golf Cart Battery
- 12V Lithium Battery
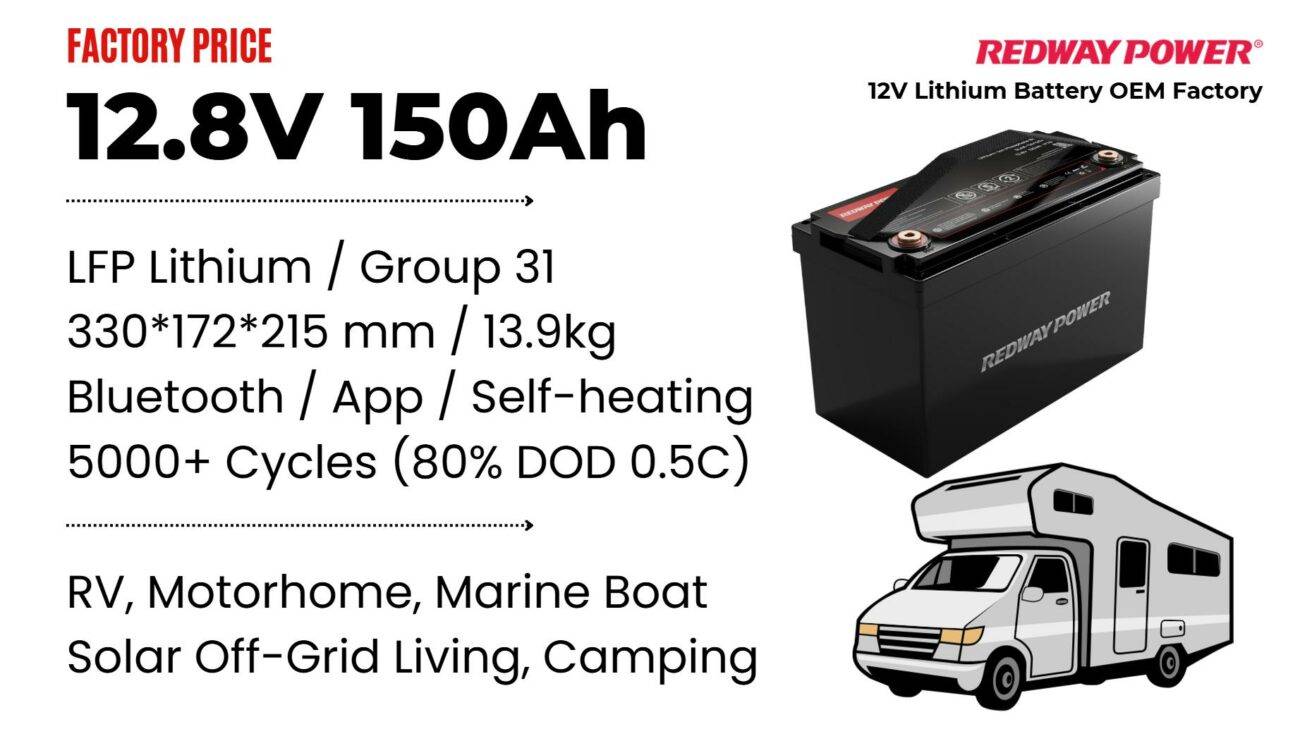
12V 150Ah Lithium RV Battery
Bluetooth App | BCI Group 31
LiFePO4 Lithium
Discharge Temperature -20°C ~ 65°C
Fast Charger 14.6V 50A
Solar MPPT Charging - 24V Lithium Battery
- 36V Lithium Battery
- 48V Lithium Battery
-
48V LiFePO4 Battery
- 48V 50Ah
- 48V 50Ah (for Golf Carts)
- 48V 60Ah (8D)
- 48V 100Ah (8D)
- 48V 100Ah
- 48V 100Ah (Discharge 100A for Golf Carts)
- 48V 100Ah (Discharge 150A for Golf Carts)
- 48V 100Ah (Discharge 200A for Golf Carts)
- 48V 150Ah (for Golf Carts)
- 48V 160Ah (Discharge 100A for Golf Carts)
- 48V 160Ah (Discharge 160A for Golf Carts)
-
48V LiFePO4 Battery
- 60V Lithium Battery
-
60V LiFePO4 Battery
- 60V 20Ah
- 60V 30Ah
- 60V 50Ah
- 60V 50Ah (Small Size / Side Terminal)
- 60V 100Ah (for Electric Motocycle, Electric Scooter, LSV, AGV)
- 60V 100Ah (for Forklift, AGV, Electric Scooter, Sweeper)
- 60V 150Ah (E-Motocycle / E-Scooter / E-Tricycle / Tour LSV)
- 60V 200Ah (for Forklift, AGV, Electric Scooter, Sweeper)
-
60V LiFePO4 Battery
- 72V~96V Lithium Battery
- Rack-mounted Lithium Battery
- E-Bike Battery
- All-in-One Home-ESS
- Wall-mount Battery ESS
-
Home-ESS Lithium Battery PowerWall
- 24V 100Ah 2.4kWh PW24100-S PowerWall
- 48V 50Ah 2.4kWh PW4850-S PowerWall
- 48V 50Ah 2.56kWh PW5150-S PowerWall
- 48V 100Ah 5.12kWh PW51100-F PowerWall (IP65)
- 48V 100Ah 5.12kWh PW51100-S PowerWall
- 48V 100Ah 5.12kWh PW51100-H PowerWall
- 48V 200Ah 10kWh PW51200-H PowerWall
- 48V 300Ah 15kWh PW51300-H PowerWall
PowerWall 51.2V 100Ah LiFePO4 Lithium Battery
Highly popular in Asia and Eastern Europe.
CE Certification | Home-ESS -
Home-ESS Lithium Battery PowerWall
- Portable Power Stations
How Do Temperature Extremes Affect the Performance of My 12V Lithium Battery?

Understanding how temperature extremes impact the performance of 12V lithium batteries is essential for optimizing their use in various applications. The behavior of these batteries can vary significantly under cold and hot conditions, affecting not only their capacity but also their overall lifespan.
Effects of Cold Temperatures
Reduced Capacity: At low temperatures, the chemical reactions within lithium batteries slow down. For instance, when temperatures drop to 0°F (-18°C), a lithium battery may only discharge at 70% of its rated capacity. In contrast, lead-acid batteries perform even worse under similar conditions, discharging at about 45% capacity. This reduction in capacity can severely limit the effectiveness of batteries in cold environments.
Charging Limitations: Charging lithium batteries in cold conditions presents challenges. Typically, these batteries cannot accept a charge below 32°F (0°C). Attempting to charge under such conditions can lead to lithium plating, where lithium ions deposit on the anode instead of being absorbed. This phenomenon can damage the battery and reduce its lifespan significantly.
Increased Internal Resistance: Cold temperatures also increase internal resistance within the battery. This heightened resistance prolongs charging times and decreases discharge efficiency, which can hinder performance in applications requiring immediate power delivery.
Effects of Hot Temperatures
Increased Capacity but Reduced Lifespan: While lithium batteries may perform well at elevated temperatures, showing higher discharge rates, prolonged exposure to heat can accelerate aging. For example, operating at temperatures around 130°F (54°C) can lead to rapid degradation of the battery’s internal components, significantly shortening its lifespan.
Risk of Thermal Runaway: High temperatures increase the risk of thermal runaway, a dangerous condition characterized by uncontrolled overheating. This can result in safety hazards, including fires or explosions, particularly if the battery is not managed properly.
Self-Discharge Rates: Elevated temperatures can also lead to increased self-discharge rates, further reducing available capacity over time. This means that batteries exposed to high heat may not only perform poorly but also lose charge more quickly when not in use.
Optimal Operating Temperature Range
For optimal performance and longevity, maintaining a specific temperature range is crucial. The ideal temperature range for 12V lithium batteries is typically between 32°F (0°C) and 113°F (45°C). Operating within this range allows batteries to function efficiently without significant risks to their health or performance.
Implementing proper thermal management strategies—such as insulation or cooling systems—can help keep batteries within this optimal range, maximizing both their lifespan and effectiveness.
Conclusion
Temperature extremes have profound effects on the performance of 12V lithium batteries. Cold temperatures can lead to reduced capacity and hinder charging, while high temperatures may enhance short-term performance but contribute to long-term damage. Understanding these impacts and employing effective thermal management practices is essential for ensuring safety, performance, and longevity in various applications.
For high-quality lithium LiFePO4 batteries and customized solutions tailored to your specific needs, contact Redway Power, a reliable factory wholesaler with over 12 years of expertise in providing innovative energy storage solutions.