Gel batteries use a gel-like electrolyte, making them safer, vibration-resistant, and longer-lasting. They are commonly used in solar/wind systems. Lead-acid batteries can be flooded or sealed and are commonly used in motor vehicles and backup power supplies. Understanding these differences helps in choosing the right battery for specific needs.
What is Gel Battery? What are its advantages?
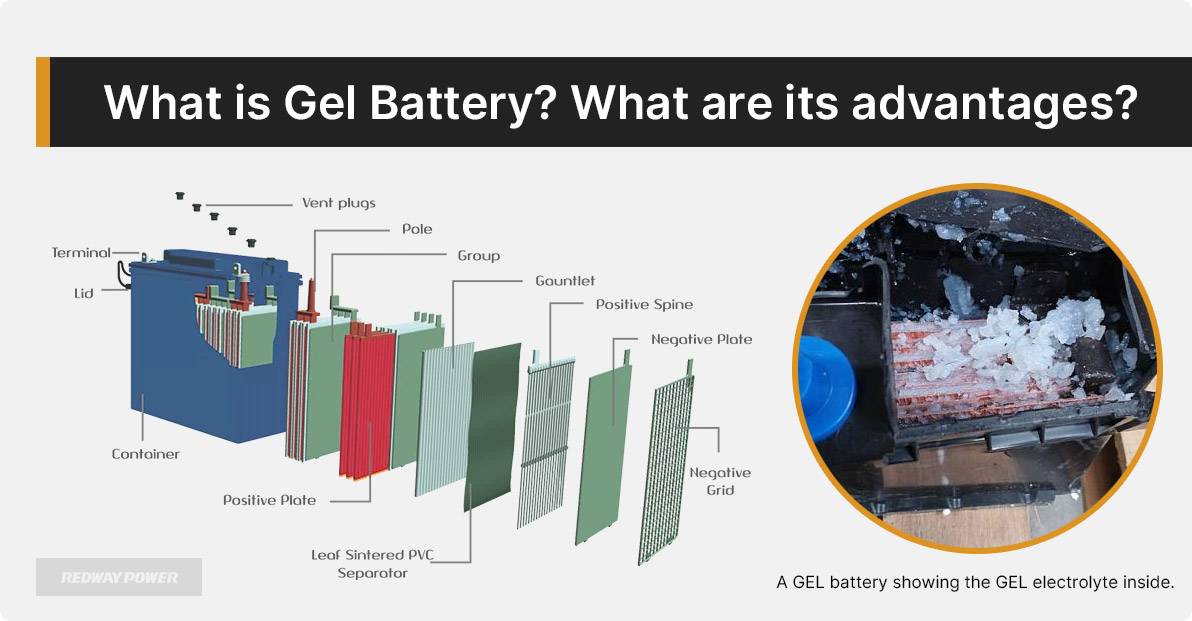
Discover Gel Batteries: Gel batteries, known as Gel Cells, are a type of sealed acid battery. They use a gel-like electrolyte made by mixing sulfuric acid with silica gel, ensuring no spills. These batteries are maintenance-free, last up to 6 years, and can be installed in any position. They’re safe, heat-resistant, and suitable for various applications, like solar systems and marine use.
Discover the perks of gel batteries: They’re maintenance-free, lasting 6+ years with flexible installation options. With heat tolerance, no leaks, and vibration resistance, they ensure stable performance. Perfect for solar systems and UPS, gel batteries offer hassle-free power solutions.
Let’s explore why gel batteries are a popular choice and what advantages they offer:
- Maintenance-Free: Gel batteries require little upkeep, saving time and effort. Unlike some other types, you don’t need to regularly add water to them.
- Long Lifespan: Gel batteries can last for around 6 years or even more, providing reliable power over an extended period.
- Versatile Installation: You can install gel batteries in various positions without worrying about leaks. This flexibility makes them suitable for different applications.
- Heat Tolerance: Gel batteries handle temperature changes well, remaining stable in both hot and cold environments.
- Leak Prevention: Gel batteries are designed to prevent leaks, ensuring safety and minimizing cleanup hassles.
These advantages make gel batteries a preferred choice for many applications, offering durability, reliability, and ease of use.
How long do Gel batteries last?
Gel batteries can last for different durations depending on their type and usage. A 12-volt gel or AGM battery typically lasts up to six years if maintained properly. On the other hand, 2-volt traction gel batteries can last at least 15 years with intensive use. Temperature and charging practices also affect their lifespan.
Let’s dive into understanding how long gel batteries last and what factors influence their lifespan:
- 12-Volt Gel or AGM Batteries:
- These batteries typically last around six years if they’re well taken care of.
- Even after six years, they usually retain about 80% of their original capacity, which is still quite good.
- The temperature where they’re kept matters too; if it’s too hot, their lifespan could be shorter.
- 2-Volt Traction Gel Batteries:
- These are built to last even longer, with a lifespan of at least 15 years.
- They’re designed for heavy use, so they can withstand lots of charging and discharging cycles.
- However, it’s important to remember that how you use and care for them will ultimately determine how long they’ll last.
Understanding these timelines can help you make informed decisions about using gel batteries for your needs.
Is a lithium battery a Gel battery?
Wondering if lithium batteries are the same as gel batteries? No, they’re different. Lithium batteries use lithium, while gel batteries have electrolytes in a gel. Each has its own advantages. It’s essential to know their disparities to pick the right one for your needs, whether it’s longevity or energy density.
Here’s a simple breakdown:
- Different Materials: Lithium batteries use lithium as their main material, while gel batteries have electrolytes suspended in a gel.
- Unique Characteristics: Each type has its advantages and disadvantages, including performance, lifespan, and maintenance needs.
- Consider Your Needs: Understanding these differences helps you choose the right battery for your specific requirements, whether it’s longevity or energy density.
Knowing these distinctions empowers you to make informed decisions when selecting batteries for your devices.

Can I replace Gel batteries with lithium?
Considering swapping gel batteries for lithium? Gel batteries are hassle-free and leak-resistant, while lithium batteries offer more power and durability. However, switching may require adjustments for voltage and charging. Consult a professional for safety and compatibility. Both types have pros and cons, so choose based on your needs and budget. Always handle batteries safely.
Here’s what you need to know in simple terms:
- Gel Batteries: These are easy to maintain and don’t leak, but they have limited power.
- Lithium Batteries: They offer more power and last longer, but may need adjustments for voltage and charging.
- Considerations: Before switching, consult an expert for safety and compatibility advice. Choose based on your needs and budget, and always handle batteries with care.
What is Lead-Acid Battery? What are its advantages?
Lead-acid batteries are one of the oldest rechargeable battery types, invented in 1859 by Gaston Planté. They contain lead electrodes and a sulfuric acid electrolyte. Despite their low energy density, they’re used in motor vehicles for their high surge currents. Common in backup power supplies, they offer reliability but have a shorter lifespan compared to modern batteries.
Lead-acid batteries offer cost-effective power solutions with their ability to supply high surge currents, durability against shocks and vibrations, and recyclability. Widely available and commonly used for backup power needs, they remain a practical choice for various applications, including emergency lighting and uninterruptible power supplies.
Do lead-acid batteries work in cold weather?
In cold weather, lead-acid batteries lose capacity. They drop about 20% in normal to freezing temperatures and up to 50% at around -22°F. To prevent freezing, keep batteries warm and fully charged. Consider temperature compensation for charging. In extreme cold, lithium batteries might be a better option, as they maintain performance when lead-acid batteries weaken.
Let’s break down how cold weather affects lead-acid batteries and what you can do about it:
- Temperature Impact:
- When it’s cold, lead-acid batteries lose capacity. In normal to freezing weather, they can lose about 20% of their power. In extremely cold conditions around -22°F, their capacity can drop to 50%.
- Temperature Compensation:
- Adjust charging voltage based on temperature. Higher voltage is needed in cold (below 50°F) and lower in heat (above 85°F). Ideal charging temperature is around 77°F.
- Preventing Freezing:
- Keep batteries warm to prevent electrolyte freezing. Ensure they’re fully charged and monitor electrolyte gravity for freezing point.
Consider lithium batteries for better cold performance. They maintain power in extreme cold unlike lead-acid ones.
Key Differences Between Gel Batteries and Lead-Acid Batteries
Gel batteries use a gel-like electrolyte, while lead-acid batteries use liquid sulfuric acid. Gel batteries are sealed to prevent leakage, whereas lead-acid batteries may leak if damaged. Gel batteries are common in solar/wind systems, while lead-acid batteries are used in motor vehicles and backup power supplies.
Let’s break down the differences between gel and lead-acid batteries in simpler terms:
- Battery Composition:
- Gel Batteries: These use a gel-like substance to hold the electrolyte, preventing spills.
- Lead-Acid Batteries: They contain liquid electrolyte, which needs periodic checks.
- Applications:
- Gel Batteries: Often found in solar systems, telecom, and marine equipment for safety and low maintenance.
- Lead-Acid Batteries: Commonly used in vehicles and backup power systems due to cost-effectiveness.
- Lifespan and Temperature Sensitivity:
- Gel Batteries: Last longer (about 6 years) but may lose efficiency in extreme temperatures.
- Lead-Acid Batteries: Have a shorter lifespan and may struggle in cold weather.
Understanding these differences helps choose the right battery for specific needs.

How do you charge a Gel cell battery? Do you need a special charger for gel batteries?
To charge a gel cell battery, use a smart charger designed for gel batteries. Set a low amperage, ensuring a slow and steady charge to prevent overcharging. Monitor the charging process continuously, checking the charging rate, voltage level, and temperature. Avoid using ordinary chargers to prevent damage. Follow these steps to safely charge your gel battery for optimal performance and longevity.
Here’s how to do it:
- Use a Smart Charger: Opt for a charger designed specifically for gel batteries. These chargers have built-in technology to regulate the charging process, preventing overcharging and damage to the battery.
- Slow and Steady Charging: Set the charger to a low amperage to deliver a slow and steady charge. This helps prevent overheating and ensures a thorough and safe charging process.
- Continuous Monitoring: Keep an eye on the charging rate, voltage level, and temperature throughout the charging process. Disconnect the charger once the battery is fully charged to avoid overcharging and potential damage.
By following these steps, you can effectively charge your gel battery and prolong its lifespan while maintaining safety standards.
Gel batteries require special chargers due to their unique gel-like electrolyte. Ordinary chargers designed for regular lead-acid batteries may not work well with gel batteries. Special chargers, equipped with microprocessors, monitor and adjust the charging process to prevent overcharging and extend the battery’s lifespan. This ensures safety and optimal performance for critical applications like medical equipment and backup power systems.
Here’s why they need special chargers:
- Different Electrolyte: Gel batteries use a special gel-like electrolyte, which requires specific charging conditions.
- Microprocessor Monitoring: Special chargers for gel batteries have built-in microprocessors that monitor and adjust the charging process.
- Preventing Overcharging: These chargers prevent overcharging, which can damage the gel battery and reduce its lifespan.
Using the right charger ensures the safety and longevity of gel batteries, especially in critical applications like medical equipment and backup power systems.
Do gel batteries need maintenance?
Yes. Gel batteries need basic maintenance for optimal performance. Here’s what to do:
- Keep Charged: Charge regularly to maintain capacity.
- Prevent Overcharging: Use a smart charger and disconnect when fully charged.
- Check Terminals: Look for corrosion and tighten connections.
- Monitor Electrolyte: Ensure proper levels if applicable.
- Avoid Deep Discharges: Minimize for longer lifespan.
- Watch Temperature: Keep in a cool place to avoid extremes.
- Inspect Regularly: Look for damage or leaks and address promptly.
Can a lead acid battery charger charge a gel battery?
No. Using a standard lead-acid battery charger to charge a gel battery can cause overheating and damage. Gel batteries have different charging needs, requiring specialized chargers to prevent overcharging. These chargers ensure safe and efficient charging, maximizing the gel battery’s performance and lifespan. Always use the appropriate charger to avoid risks and maintain battery health.
Let’s break it down in an easy-to-understand way:
- Different Batteries, Different Chargers: Gel batteries and regular car batteries need different chargers.
- Why Not Use Regular Chargers?: Regular chargers can cause problems for gel batteries. They might overcharge and hurt the battery.
- Stay Safe, Use the Right Charger: It’s important to use a charger made for gel batteries. That way, you keep your battery safe and make it last longer.
So, remember: always use the right charger for your battery to keep it safe and working well.

Can I mix lead-acid and Gel batteries?
Mixing lead-acid and gel batteries isn’t a good idea. Lead-acid ones have liquid inside, while gel batteries have a thick gel. They charge differently, which can mess up how they work. It’s safer and better to stick to one type for your battery system.
Here’s why:
- Chemical Differences:
- Lead-acid batteries use liquid inside, while gel batteries have a thick gel electrolyte.
- These differences can cause problems when they’re used together.
- Charging Challenges:
- Lead-acid and gel batteries need different charging voltages.
- Charging them together might not work well, leading to issues.
- Safety Concerns:
- Mixing batteries can cause overcharging, undercharging, or even short circuits.
- It’s safer to stick with one type for your battery system.
In summary, it’s best to avoid mixing lead-acid and gel batteries to keep your system working smoothly and safely.
FAQs
Are lead-acid and Gel batteries the same?
Lead-acid batteries and gel batteries are different. Lead-acid batteries use liquid sulfuric acid as the electrolyte, while gel batteries have a gel-like electrolyte that is immobilized to prevent leakage. Gel batteries are sealed, spill-proof, and maintenance-free, making them suitable for solar/wind systems and deep-cycle applications. Lead-acid batteries, on the other hand, are commonly used in motor vehicles and backup power supplies.
Do Gel batteries need maintenance? Do gel batteries need acid?
Gel batteries are low-maintenance and don’t require adding acid or checking water levels. They use a gel-like substance made of fumed silica and sulfuric acid, preventing leaks and making installation easier. Gel batteries release less hydrogen gas, enhancing safety compared to wet cell batteries. They are a reliable and hassle-free power solution for various applications.
Do lead-acid batteries work in cold weather?
Lead-acid batteries are impacted by cold weather. In freezing temperatures, their capacity can decrease by up to 50% due to slower chemical reactions. It’s important to consider temperature compensation during charging to maintain battery health. Taking these precautions will ensure optimal performance and longevity of lead-acid batteries in cold weather conditions.
Can I replace Gel batteries with lithium?
When considering replacing gel batteries with lithium batteries, there are important factors to consider. Gel batteries are low maintenance, leak-free, and commonly used in various applications. On the other hand, lithium batteries offer advantages like high energy density and fast charging. However, they come with a higher upfront cost. Choose based on your specific needs, with gel batteries providing reliability and lithium batteries offering power density and fast charging. Consider the requirements of your application before making the switch.
Is a lithium battery a Gel battery?
Lithium batteries and gel batteries are not the same. Gel batteries are valve-regulated lead-acid batteries with a gel-like electrolyte, while lithium batteries use lithium metal compounds. Gel batteries are commonly used in marine equipment and electric vehicles, while lithium batteries are popular for portable electronics and renewable energy systems. They have distinct compositions and serve different purposes based on their unique features.
What are the advantages of a Gel battery?
Gel batteries offer several advantages. They are leak-free, making them safer to use. They require minimal maintenance and can withstand vibrations. Gel batteries also emit minimal fumes during operation. These benefits make them suitable for applications like electric vehicles, golf carts, and floor scrubbers. Enjoy the convenience and reliability of gel batteries for various purposes!
What is a Gel battery and what is lead acid?
How Does a Gel Battery Operate?
What Are the Cons of Using Gel Batteries?
How to Extend Gel Battery Lifespan?
How Does Heat Impact Gel Batteries?
What Issues Arise from Incorrect Charging?
What Are Gel Battery Charging Requirements?
To charge a gel battery safely and efficiently, follow these steps: Use a charger designed for gel batteries and connect it correctly. Set the voltage and current according to the manufacturer’s specifications. Monitor the charging process and avoid overcharging. When fully charged, disconnect the charger. By following these guidelines, you can ensure proper charging and maximize the lifespan and performance of your gel battery.
Why Are Gel Batteries Costly?
How does a gel battery work?
A gel battery uses a silica-based gel electrolyte that immobilizes the sulfuric acid, making it less prone to spillage and leakage. The gel electrolyte provides efficient chemical reactions for energy storage and discharge, while the sealed design allows for safe, maintenance-free operation.





















