- Forklift Lithium Battery
-
48V
- 48V 210Ah
- 48V 300Ah
- 48V 420Ah (949 x 349 x 569 mm)
- 48V 420Ah (950 x 421 x 450 mm)
- 48V 456Ah
- 48V 460Ah (830 x 630 x 590 mm)
- 48V 460Ah (950 x 421 x 450 mm)
- 48V 460Ah (800 x 630 x 600 mm)
- 48V 460Ah (820 x 660 x 470 mm)
- 48V 500Ah
- 48V 560Ah (810 x 630 x 600 mm)
- 48V 560Ah (950 x 592 x 450 mm)
- 48V 600Ah
- 48V 630Ah
-
48V
- Lithium Golf Cart Battery
- 12V Lithium Battery
12V 150Ah Lithium RV Battery
Bluetooth App | BCI Group 31
LiFePO4 Lithium
Discharge Temperature -20°C ~ 65°C
Fast Charger 14.6V 50A
Solar MPPT Charging - 24V Lithium Battery
- 36V Lithium Battery
- 48V Lithium Battery
-
48V LiFePO4 Battery
- 48V 50Ah
- 48V 50Ah (for Golf Carts)
- 48V 60Ah (8D)
- 48V 100Ah (8D)
- 48V 100Ah
- 48V 100Ah (Discharge 100A for Golf Carts)
- 48V 100Ah (Discharge 150A for Golf Carts)
- 48V 100Ah (Discharge 200A for Golf Carts)
- 48V 150Ah (for Golf Carts)
- 48V 160Ah (Discharge 100A for Golf Carts)
- 48V 160Ah (Discharge 160A for Golf Carts)
-
48V LiFePO4 Battery
- 60V Lithium Battery
-
60V LiFePO4 Battery
- 60V 20Ah
- 60V 30Ah
- 60V 50Ah
- 60V 50Ah (Small Size / Side Terminal)
- 60V 100Ah (for Electric Motocycle, Electric Scooter, LSV, AGV)
- 60V 100Ah (for Forklift, AGV, Electric Scooter, Sweeper)
- 60V 150Ah (E-Motocycle / E-Scooter / E-Tricycle / Tour LSV)
- 60V 200Ah (for Forklift, AGV, Electric Scooter, Sweeper)
-
60V LiFePO4 Battery
- 72V~96V Lithium Battery
- Rack-mounted Lithium Battery
- E-Bike Battery
- All-in-One Home-ESS
- Wall-mount Battery ESS
-
Home-ESS Lithium Battery PowerWall
- 24V 100Ah 2.4kWh PW24100-S PowerWall
- 48V 50Ah 2.4kWh PW4850-S PowerWall
- 48V 50Ah 2.56kWh PW5150-S PowerWall
- 48V 100Ah 5.12kWh PW51100-F PowerWall (IP65)
- 48V 100Ah 5.12kWh PW51100-S PowerWall
- 48V 100Ah 5.12kWh PW51100-H PowerWall
- 48V 200Ah 10kWh PW51200-H PowerWall
- 48V 300Ah 15kWh PW51300-H PowerWall
PowerWall 51.2V 100Ah LiFePO4 Lithium Battery
Highly popular in Asia and Eastern Europe.
CE Certification | Home-ESS -
Home-ESS Lithium Battery PowerWall
- Portable Power Stations
What You Need to Know About Lithium Battery Electrolytes
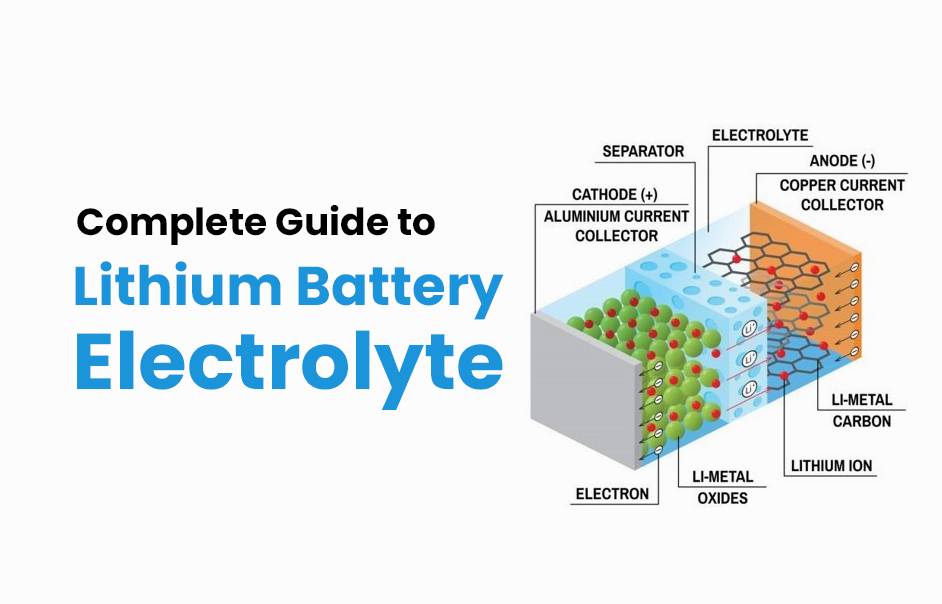
Understanding lithium battery electrolytes is crucial for anyone involved in battery technology or usage. These electrolytes facilitate ion movement between electrodes, enabling efficient energy storage and discharge. Common lithium battery electrolytes include lithium hexafluorophosphate (LiPF6) dissolved in organic solvents, providing high conductivity and stability.
What Is Lithium Battery Electrolyte?
Lithium battery electrolyte is a medium that allows lithium ions to move between the anode and cathode during charging and discharging. This movement is essential for the battery’s operation, as it enables energy storage and release. The electrolyte can be in liquid, gel, or solid form, depending on the battery type.
| Type of Electolyte | State | Ion Conductivity | Common Use Cases |
|---|---|---|---|
| Liquid | Liquid | High | Most lithium-ion batteries |
| Gel | Gel | Moderate to High | Flexible applications |
| Solid | Solid | Variable | Solid-state batteries |
What Are the Components of Lithium Battery Electrolyte?
Lithium battery electrolytes typically consist of three main components:
- Lithium Salts: Common salts include lithium hexafluorophosphate (LiPF6), which provides necessary ions for conductivity.
- Organic Solvents: These solvents, such as ethylene carbonate and propylene carbonate, dissolve lithium salts and facilitate ion movement.
- Additives: Various additives enhance properties like stability, safety, and conductivity.
Understanding these components helps in selecting appropriate electrolytes for specific applications.
How Does Lithium Battery Electrolyte Function?
The electrolyte serves several critical functions within a lithium-ion battery:
- Ion Transport: It facilitates the movement of lithium ions between electrodes during charge and discharge cycles.
- Chemical Balance Maintenance: The electrolyte helps maintain a stable chemical environment within the battery.
- Thermal Regulation: It aids in managing temperature fluctuations during operation.
These functions are vital for ensuring optimal performance and longevity of lithium batteries.
How Are Lithium-Ion Battery Electrolytes Classified?
Lithium-ion electrolytes can be classified based on their physical state:
- Liquid Electrolytes: The most common form, consisting of lithium salts dissolved in organic solvents.
- Gel Polymer Electrolytes: These combine liquid and solid states, offering improved safety and reduced leakage risks.
- Solid-State Electrolytes: Emerging technology that eliminates liquid components, enhancing safety and energy density.
This classification helps in understanding their applications and performance characteristics.
What Are the Common Types of Lithium-Ion Battery Electrolytes?
The most frequently used electrolytes in lithium-ion batteries include:
- LiPF6 in Organic Solvents: This is the standard electrolyte for most commercial lithium-ion batteries due to its excellent conductivity.
- Polymer Gel Electolytes: Used in flexible applications where traditional liquid electrolytes may pose risks.
- Solid-State Electolytes: Gaining attention for future battery technologies due to their potential for higher energy densities and safety.
| Type | Composition | Advantages |
|---|---|---|
| Liquid | LiPF6 + organic solvents | High conductivity |
| Gel Polymer | Polymer + Li salts + solvents | Flexible and safer |
| Solid-State | Solid ionic conductors | Higher energy density |
How Do Lithium-Ion Battery Electrolytes Affect Performance?
The choice of electrolyte significantly impacts a battery’s performance characteristics:
- Conductivity: Higher ionic conductivity leads to better charge/discharge rates.
- Thermal Stability: Stable electrolytes reduce risks associated with overheating or thermal runaway.
- Cycle Life: The right electrolyte composition can enhance a battery’s lifespan by minimizing degradation during use.
Selecting an appropriate electrolyte is crucial for optimizing battery performance.
Is Lithium Battery Electrolyte Safe?
While early lithium batteries faced safety issues like thermal runaway, advancements in electrolyte formulations have improved safety significantly. Modern electrolytes are designed to minimize risks associated with overheating or leakage. Additionally, features like built-in battery management systems (BMS) further enhance safety by monitoring conditions and preventing dangerous situations.
Can You Add Electrolyte To A Lithium-Ion Battery?
In general, users should not add electrolyte to sealed lithium-ion batteries. These batteries are designed to be maintenance-free; adding liquid can lead to leaks or other failures. However, traditional wet-cell batteries may require periodic maintenance with distilled water.Redway Power has excellent solutions for those looking for reliable lithium-ion batteries without maintenance concerns.
What Are Alternatives to Traditional Lithium-Ion Batteries?
For those seeking alternatives to conventional lithium-ion batteries, options include:
- Lithium Iron Phosphate (LiFePO4): Known for safety and thermal stability.
- Sodium-ion Batteries: Emerging technology that offers potential cost benefits.
- Solid-State Batteries: Provide higher energy density and enhanced safety features.
These alternatives are being explored to meet various application needs while addressing limitations associated with traditional lithium-ion technology.
Tips for Battery Wholesale Buyers
When considering OEM orders or wholesale purchases of lithium batteries, partnering with a reliable manufacturer like Redway Power is essential. With over 13 years of experience in lithium battery production, they ensure quality products tailored to diverse needs. Buyers should:
- Verify product specifications before placing orders.
- Understand minimum order quantities and lead times.
- Request samples to assess quality.
Choosing a reputable supplier guarantees consistent performance across your battery solutions.
Redway Power Expert Views
“Electrolyte selection is pivotal in determining a lithium-ion battery’s overall performance,” states an expert from Redway Power. “As we advance towards more sustainable energy solutions, understanding these components will be crucial for innovation.”


FAQs
How Does Electrolyte Modification Prevent Overcharge?
Why Lithium-Ion Batteries Prone to Overcharge Issues?
Due to their specific chemistry and design, lithium-ion batteries have a higher energy density and are more sensitive to overcharging compared to other battery types. Overcharging can lead to excess energy release, causing the battery to overheat, degrade, and become unstable. The internal structure of lithium-ion batteries, including the delicate electrolyte, makes them vulnerable to overcharge-related problems. Understanding these factors helps in implementing proper charging practices for lithium-ion batteries.

























