- Lithium Golf Cart Battery
- Forklift Lithium Battery
-
48V
- 48V 210Ah
- 48V 300Ah
- 48V 420Ah (949 x 349 x 569 mm)
- 48V 420Ah (950 x 421 x 450 mm)
- 48V 456Ah
- 48V 460Ah (830 x 630 x 590 mm)
- 48V 460Ah (950 x 421 x 450 mm)
- 48V 460Ah (800 x 630 x 600 mm)
- 48V 460Ah (820 x 660 x 470 mm)
- 48V 500Ah
- 48V 560Ah (810 x 630 x 600 mm)
- 48V 560Ah (950 x 592 x 450 mm)
- 48V 600Ah
- 48V 630Ah
-
48V
- 12V Lithium Battery
12V 150Ah Lithium RV Battery
Bluetooth App | BCI Group 31
LiFePO4 Lithium
Discharge Temperature -20°C ~ 65°C
Fast Charger 14.6V 50A
Solar MPPT Charging - 24V Lithium Battery
- 36V Lithium Battery
- 48V Lithium Battery
-
48V LiFePO4 Battery
- 48V 50Ah
- 48V 50Ah (for Golf Carts)
- 48V 60Ah (8D)
- 48V 100Ah (8D)
- 48V 100Ah
- 48V 100Ah (Discharge 100A for Golf Carts)
- 48V 100Ah (Discharge 150A for Golf Carts)
- 48V 100Ah (Discharge 200A for Golf Carts)
- 48V 150Ah (for Golf Carts)
- 48V 160Ah (Discharge 100A for Golf Carts)
- 48V 160Ah (Discharge 160A for Golf Carts)
-
48V LiFePO4 Battery
- 60V Lithium Battery
-
60V LiFePO4 Battery
- 60V 20Ah
- 60V 30Ah
- 60V 50Ah
- 60V 50Ah (Small Size / Side Terminal)
- 60V 100Ah (for Electric Motocycle, Electric Scooter, LSV, AGV)
- 60V 100Ah (for Forklift, AGV, Electric Scooter, Sweeper)
- 60V 150Ah (E-Motocycle / E-Scooter / E-Tricycle / Tour LSV)
- 60V 200Ah (for Forklift, AGV, Electric Scooter, Sweeper)
-
60V LiFePO4 Battery
- 72V~96V Lithium Battery
- Rack-mounted Lithium Battery
- E-Bike Battery
- All-in-One Home-ESS
- Wall-mount Battery ESS
-
Home-ESS Lithium Battery PowerWall
- 24V 100Ah 2.4kWh PW24100-S PowerWall
- 48V 50Ah 2.4kWh PW4850-S PowerWall
- 48V 50Ah 2.56kWh PW5150-S PowerWall
- 48V 100Ah 5.12kWh PW51100-F PowerWall (IP65)
- 48V 100Ah 5.12kWh PW51100-S PowerWall
- 48V 100Ah 5.12kWh PW51100-H PowerWall
- 48V 200Ah 10kWh PW51200-H PowerWall
- 48V 300Ah 15kWh PW51300-H PowerWall
PowerWall 51.2V 100Ah LiFePO4 Lithium Battery
Highly popular in Asia and Eastern Europe.
CE Certification | Home-ESS -
Home-ESS Lithium Battery PowerWall
- Portable Power Stations
How Do Car Batteries Compare to Marine Batteries, and Can a Car Battery Be Used as a Marine Battery?
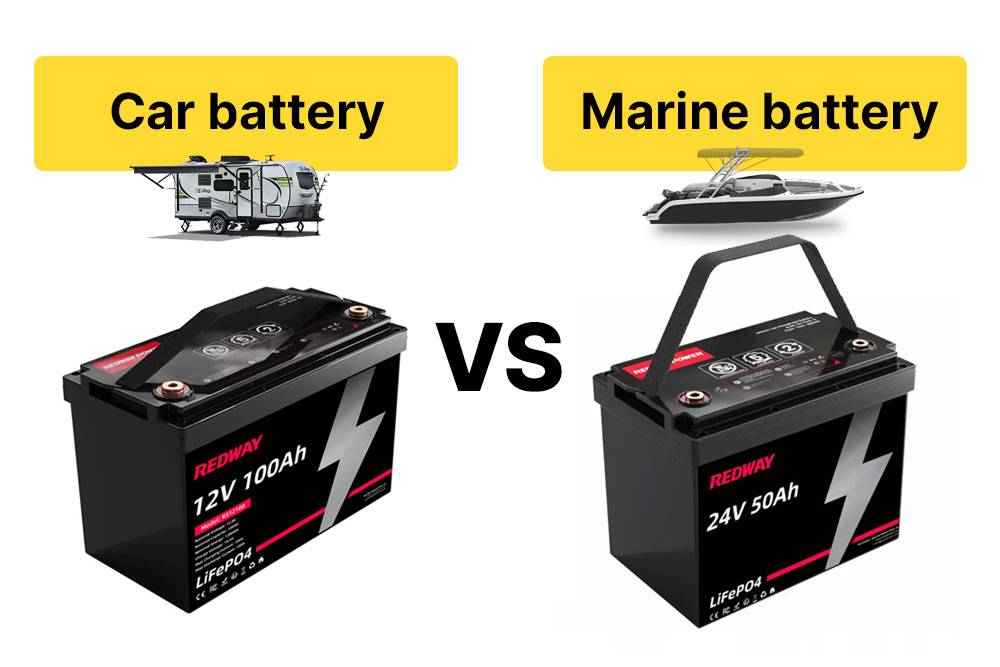
When comparing car batteries to marine batteries, it’s essential to understand their distinct purposes and designs. While both types of batteries provide power, marine batteries are specifically engineered to withstand harsh aquatic environments and deliver sustained energy over time. In contrast, car batteries are optimized for quick bursts of power to start engines. Using a car battery in a marine application is not recommended due to potential performance issues and safety risks.
What are the key differences between marine and car batteries?
Marine and car batteries differ significantly in construction, capacity, and intended use. Marine batteries are built with thicker plates to handle deep cycling and prolonged discharges, while car batteries focus on delivering high cranking amps for short durations. This fundamental difference affects their performance in various applications.Chart: Key Differences Between Marine and Car Batteries
| Feature | Marine Battery | Car Battery |
|---|---|---|
| Plate Thickness | Thicker plates for durability | Thinner plates for quick starts |
| Amp-Hour Rating | Higher ratings for extended use | Lower ratings focused on starting power |
| Cycling Capability | Designed for deep cycling | Not designed for deep cycling |
| Reserve Capacity | Higher reserve capacity | Lower reserve capacity |
How is the design of marine batteries suited for aquatic environments?
Marine batteries feature robust construction to withstand vibrations, moisture, and corrosion associated with boating conditions. They often include enhanced sealing and protective casings to prevent damage from water exposure. This durability ensures reliable performance even in challenging environments.
Why do marine batteries have higher amp-hour ratings than car batteries?
Marine batteries typically have higher amp-hour (Ah) ratings because they need to provide power over longer periods, such as running lights, pumps, or electronics while anchored. This sustained energy output is crucial for maintaining functionality during extended outings on the water.
What are the cycling capabilities of marine versus car batteries?
Marine batteries are designed for deep cycling, allowing them to be discharged significantly without damage. In contrast, car batteries are primarily starter batteries that should not be deeply discharged frequently as it can shorten their lifespan. This difference makes marine batteries more suitable for applications requiring prolonged energy use.
How does the reserve capacity differ between marine and car batteries?
Reserve capacity refers to how long a battery can deliver a specific amount of current before its voltage drops below usable levels. Marine batteries usually have a higher reserve capacity than car batteries, enabling them to sustain power for longer periods without needing a recharge.
Why are car batteries designed primarily for starting engines?
Car batteries are engineered to provide high bursts of power needed to start an engine. This design includes many thin plates that maximize surface area, allowing rapid discharge of energy. Once started, the vehicle’s alternator recharges the battery during operation.

What unique features do marine batteries offer that make them suitable for boats?
Marine batteries often include features such as:
- Vibration Resistance: Built to withstand rough conditions on water.
- Corrosion Resistance: Enhanced materials protect against saltwater corrosion.
- Multiple Terminals: Allow connections for various accessories like lights and pumps.
These features ensure reliable operation in demanding environments where typical automotive components may fail.
Can a car battery be used in a marine application, and what are the risks?
While it may be tempting to use a car battery in a boat due to cost considerations, it is generally not advisable. Risks include:
- Shorter Lifespan: Car batteries may fail prematurely when subjected to deep discharges.
- Poor Performance: Inability to sustain power over extended periods can lead to operational failures.
- Safety Hazards: Increased risk of damage due to vibrations and moisture exposure can create safety concerns.
Using the correct type of battery designed specifically for marine applications ensures optimal performance and safety.
Industrial News
The battery industry is witnessing significant advancements in both automotive and marine technologies. Manufacturers are focusing on enhancing durability and efficiency while developing hybrid models that combine features of both types. These innovations aim to meet increasing demands from consumers who seek reliable power sources whether on land or at sea.
Redway Power Expert Views
“Choosing the right battery type is crucial for performance,” states an industry expert. “Marine environments present unique challenges that standard automotive solutions cannot address effectively. Opting for specialized marine batteries ensures longevity and reliability, reducing risks associated with improper usage.”
Frequently Asked Questions
- What are the key differences between marine and car batteries?
- Marine batteries have thicker plates, higher amp-hour ratings, and deeper cycling capabilities compared to thinner-plated car batteries designed primarily for starting engines.
- How is the design of marine batteries suited for aquatic environments?
- They feature robust construction with enhanced sealing to withstand vibrations, moisture, and corrosion found in boating conditions.
- Why do marine batteries have higher amp-hour ratings than car batteries?
- Marine applications require sustained power output over longer periods, necessitating higher amp-hour ratings.
- What are the cycling capabilities of marine versus car batteries?
- Marine batteries support deep cycling without damage; car batteries should not be deeply discharged frequently.
- How does the reserve capacity differ between marine and car batteries?
- Marine batteries typically offer higher reserve capacity, allowing longer operation before needing recharging.
- Why are car batteries designed primarily for starting engines?
- They provide high bursts of power needed for engine ignition but require recharging from an alternator during operation.
- What unique features do marine batteries offer that make them suitable for boats?
- Features include vibration resistance, corrosion resistance, and multiple terminals for connecting various accessories.
- Can a car battery be used in a marine application, and what are the risks?
- It’s not advisable due to risks like shorter lifespan, poor performance under sustained loads, and safety hazards from moisture exposure.

Can a Car Battery be Used as a Marine Battery?
Using a car battery as a marine battery may seem tempting, but it’s not ideal due to their different purposes and construction. Car batteries provide short bursts of power for engine starting, while marine batteries offer sustained power for boat accessories. Marine batteries are specifically designed to withstand marine conditions, unlike car batteries.

When selecting a battery for your boat, consider factors like capacity, reserve capacity, and cold-cranking amps to meet boating requirements. Proper maintenance, including regular inspection, cleaning, and storage, is crucial to extend the lifespan of your marine battery and ensure safety on the water.
It’s recommended to invest in a dedicated marine battery rather than using a car battery. Choosing the right battery ensures reliable performance for all your boating activities, providing peace of mind during your aquatic adventures.
Can a marine battery charger be used for car battery charging?
Yes, you can use a marine battery charger to charge a car battery, but there are considerations. Ensure the charger’s voltage is compatible with the car battery (usually 12V), adjust the charging rate if needed, and follow safety precautions. However, using a dedicated car battery charger is generally more efficient for car batteries.
FAQs
Are lithium-ion batteries considered dangerous and what precautions should be taken?
Lithium-ion batteries can pose risks such as overheating, fire, and explosion if damaged or improperly charged. Precautions include using quality chargers, avoiding overcharging, storing them in cool places, and regularly inspecting for damage.
What type of battery is recommended for a trolling motor to last the longest?
Deep cycle batteries are recommended for trolling motors as they are designed to be discharged and recharged repeatedly. Lithium batteries are particularly favored for their longevity and lighter weight compared to traditional lead-acid options.
What are the advantages of lithium batteries compared to traditional lead-acid batteries?
Lithium batteries offer several advantages over lead-acid batteries, including longer lifespan, faster charging times, lighter weight, higher energy density, and deeper discharge capabilities without damaging the battery.
What are the drawbacks of deep cycle lithium batteries, particularly in terms of upfront costs and amperage output?
Deep cycle lithium batteries typically have higher upfront costs compared to lead-acid batteries. Additionally, while they provide consistent power output, their amperage may not match that of larger lead-acid batteries for high-demand applications.
What is a battery management system (BMS) and how does it benefit lithium batteries?
A Battery Management System (BMS) monitors and manages the charging and discharging of lithium batteries, ensuring optimal performance and safety. It protects against overcharging, overheating, and short circuits, extending battery life.
How can Marine Batteries be distinguished by their chemical composition?
Marine batteries can be distinguished by their chemical composition into three main types: flooded lead-acid, absorbed glass mat (AGM), and lithium-ion. Each type has unique characteristics affecting performance, maintenance needs, and suitability for marine applications.
What are the battery requirements for living-on-board vessels like houseboats, sailboats, and catamarans?
Living-on-board vessels typically require deep cycle batteries with sufficient capacity to power appliances and systems. A minimum of 100 amp-hours is recommended per day of use, along with a reliable charging system to maintain battery health.
What are the applications and limitations of using a marine battery in a car?
Marine batteries can be used in cars primarily for starting or auxiliary power; however, they may not provide the same cranking power as dedicated automotive batteries. Their design also makes them less suitable for frequent short trips.
How do marine batteries perform in comparison to regular batteries?
Marine batteries are designed for deep cycling and can handle repeated discharges better than regular automotive batteries. They often have higher reserve capacity but may lack the cranking power needed for starting engines.
What are the considerations when using a marine battery in a car?
When using a marine battery in a car, consider its capacity to deliver cranking amps needed for starting. Ensure compatibility with the vehicle’s electrical system and be aware that marine batteries may not recharge as quickly as automotive ones.
Is it possible to charge a car battery using a marine charger?
Yes, you can charge a car battery using a marine charger if it is compatible with the car’s battery type. Ensure that the charger settings match the voltage and chemistry of the car battery for safe charging.
What types of marine batteries are available based on their chemical composition?
Marine batteries are available in several types based on chemical composition: flooded lead-acid, absorbed glass mat (AGM), gel cell, and lithium-ion. Each type offers different benefits regarding maintenance, weight, and discharge characteristics.























