- Lithium Golf Cart Battery
- Forklift Lithium Battery
-
48V
- 48V 210Ah
- 48V 300Ah
- 48V 420Ah (949 x 349 x 569 mm)
- 48V 420Ah (950 x 421 x 450 mm)
- 48V 456Ah
- 48V 460Ah (830 x 630 x 590 mm)
- 48V 460Ah (950 x 421 x 450 mm)
- 48V 460Ah (800 x 630 x 600 mm)
- 48V 460Ah (820 x 660 x 470 mm)
- 48V 500Ah
- 48V 560Ah (810 x 630 x 600 mm)
- 48V 560Ah (950 x 592 x 450 mm)
- 48V 600Ah
- 48V 630Ah
-
48V
- 12V Lithium Battery
12V 150Ah Lithium RV Battery
Bluetooth App | BCI Group 31
LiFePO4 Lithium
Discharge Temperature -20°C ~ 65°C
Fast Charger 14.6V 50A
Solar MPPT Charging - 24V Lithium Battery
- 36V Lithium Battery
- 48V Lithium Battery
-
48V LiFePO4 Battery
- 48V 50Ah
- 48V 50Ah (for Golf Carts)
- 48V 60Ah (8D)
- 48V 100Ah (8D)
- 48V 100Ah
- 48V 100Ah (Discharge 100A for Golf Carts)
- 48V 100Ah (Discharge 150A for Golf Carts)
- 48V 100Ah (Discharge 200A for Golf Carts)
- 48V 150Ah (for Golf Carts)
- 48V 160Ah (Discharge 100A for Golf Carts)
- 48V 160Ah (Discharge 160A for Golf Carts)
-
48V LiFePO4 Battery
- 60V Lithium Battery
-
60V LiFePO4 Battery
- 60V 20Ah
- 60V 30Ah
- 60V 50Ah
- 60V 50Ah (Small Size / Side Terminal)
- 60V 100Ah (for Electric Motocycle, Electric Scooter, LSV, AGV)
- 60V 100Ah (for Forklift, AGV, Electric Scooter, Sweeper)
- 60V 150Ah (E-Motocycle / E-Scooter / E-Tricycle / Tour LSV)
- 60V 200Ah (for Forklift, AGV, Electric Scooter, Sweeper)
-
60V LiFePO4 Battery
- 72V~96V Lithium Battery
- Rack-mounted Lithium Battery
- E-Bike Battery
- All-in-One Home-ESS
- Wall-mount Battery ESS
-
Home-ESS Lithium Battery PowerWall
- 24V 100Ah 2.4kWh PW24100-S PowerWall
- 48V 50Ah 2.4kWh PW4850-S PowerWall
- 48V 50Ah 2.56kWh PW5150-S PowerWall
- 48V 100Ah 5.12kWh PW51100-F PowerWall (IP65)
- 48V 100Ah 5.12kWh PW51100-S PowerWall
- 48V 100Ah 5.12kWh PW51100-H PowerWall
- 48V 200Ah 10kWh PW51200-H PowerWall
- 48V 300Ah 15kWh PW51300-H PowerWall
PowerWall 51.2V 100Ah LiFePO4 Lithium Battery
Highly popular in Asia and Eastern Europe.
CE Certification | Home-ESS -
Home-ESS Lithium Battery PowerWall
- Portable Power Stations
Can you trickle charge a lithium battery?

In our daily lives, lithium batteries power our devices, transforming the way we use energy. Exploring the concept of trickle charging, this blog post delves into charging methods for these powerful batteries. Join us on an electrifying journey to understand the benefits, drawbacks, considerations, and alternative charging methods for lithium batteries. Grab your charger, and let’s dive in!
Understanding Lithium Batteries
Lithium batteries have gained popularity for their high energy density, lightweight design, and extended lifespan. Unlike traditional batteries, they use lithium ions for energy storage, providing features such as minimal self-discharge and voltage stability during discharge.
- Extended Charge Retention:
- Lithium batteries stand out for their ability to retain a charge for extended periods, ensuring stored energy is preserved even when not in use.
- Voltage Stability:
- Unlike other batteries, lithium batteries maintain a stable voltage throughout the discharge cycle, offering consistent power until near the end of their capacity.
- Advanced Lithium Technologies:
- Lithium battery technology has evolved with various lithium-ion chemistries like LiFePO4, LiCoO2, and LiNiMnCoO2. Each type offers specific advantages in terms of energy density, power output, safety, and cost-effectiveness.
Trickle Charging Explained
Trickle charging, a gradual and continuous method, contrasts with rapid charging by providing a low current over an extended period. This technique is particularly beneficial for lithium batteries, aiming to preserve their capacity and extend overall lifespan.
- Purpose of Trickle Charging:
- Trickle charging prevents overcharging or undercharging in lithium batteries, maintaining their health by delivering a consistent, small current over time. This method is especially useful for long-term storage and reviving deeply discharged batteries.
- Advantages and Drawbacks:
- Trickle charging ensures convenient, long-term storage without significant discharge concerns. However, it requires more time compared to rapid charging methods, potentially taking hours or days to reach full capacity.
- Considerations and Equipment:
- Before opting for trickle charging, check your lithium battery’s compatibility. Specialized chargers with safeguards, such as temperature control and voltage regulation, are essential for proper trickle charging. Alternative methods like pulse-charging or intermittent fast-charging may be considered with manufacturer recommendations or professional guidance.
Benefits and Drawbacks of Trickle Charging Lithium Batteries
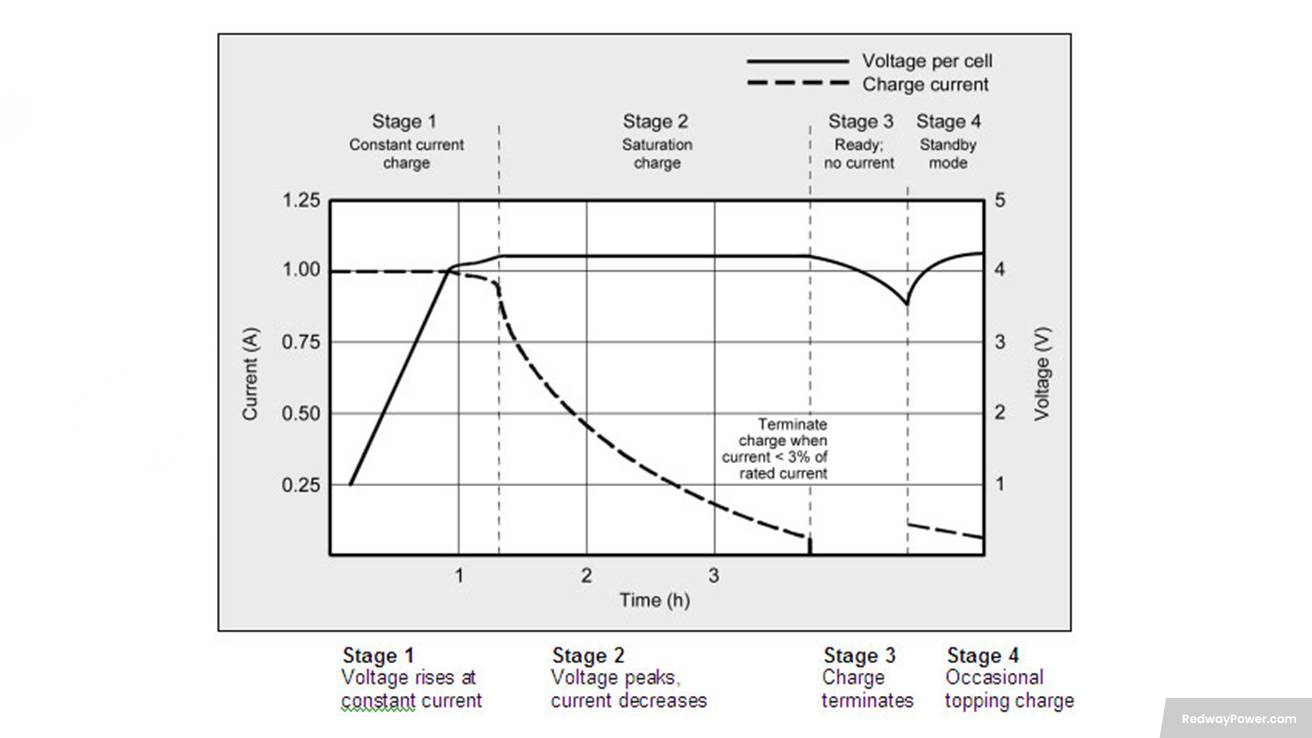
Trickle charging for lithium batteries has its pros and cons. Let’s explore the key benefits and drawbacks of this method.
- Benefits of Trickle Charging:
- Trickle charging significantly extends the overall lifespan of lithium batteries by preventing overcharging and reducing premature aging. It facilitates convenient maintenance charging for devices that are infrequently used but need a charged battery, ensuring readiness when required. Additionally, it combats self-discharge, maintaining the battery’s full capacity over time.
- Drawbacks of Trickle Charging:
- Trickle charging has longer charging times compared to faster methods, like rapid chargers. There’s a risk of overheating or damage if not done correctly or with a compatible charger designed for trickle charging. Constant exposure to small currents may increase internal resistance within the lithium battery, impacting its long-term performance.
In conclusion, while trickle charging offers benefits such as extended lifespan and convenient maintenance, users should carefully consider drawbacks like longer charge times and potential damage, ensuring proper usage and compatible equipment.
Factors to Consider Before Trickle Charging a Lithium Battery
Before opting for trickle charging your lithium battery, consider crucial factors to ensure optimal performance and safety.
- Capacity and Voltage:
- Check your lithium battery’s capacity and ensure the charger matches it. Incorrect capacity settings can lead to damage. Similarly, verify the voltage range of your battery and use a charger with appropriate settings to avoid potential harm.
- Temperature Considerations:
- Take note of the temperature during trickle charging. Extreme temperatures, whether too hot or too cold, can adversely affect battery performance and lifespan. Ensure a suitable environment for charging.
- Manufacturer Guidelines and Urgency:
- Refer to the manufacturer’s guidelines regarding trickle charging suitability for specific lithium batteries. Assess the urgency of charging – if time is not a critical factor and extending battery life is a priority, trickle charging may be suitable.
Always prioritize these factors before deciding on trickle charging to ensure the safety and longevity of your lithium battery.
How to Properly Trickle Charge a Lithium Battery
Trickle charging a lithium battery demands precision for optimal results. Follow these essential steps to ensure proper technique and safeguard your battery’s performance.
- Use Dedicated Charger:
- Employ a charger designed explicitly for lithium batteries. Using an incompatible charger can lead to overcharging and potential damage to the battery.
- Set Correct Voltage:
- Check and set the charger’s voltage to match your lithium battery’s recommended level. This precaution prevents overcharging, preserving the battery’s integrity.
- Ensure Correct Connections:
- Connect the battery’s positive and negative terminals to the corresponding charger terminals to prevent accidental short circuits. Double-check these connections for safety.
- Monitor Temperature:
- Keep a close watch on both the battery and charger temperatures during the trickle charging process. Cease charging if excessive heat is detected, signaling a potential issue.
- Patience with Time:
- Understand that trickle charging is a gradual process, taking longer than regular methods. Exercise patience, allowing sufficient time for the lithium battery to reach full charge without interruptions.
Always consult manufacturer guidelines and follow specific lithium battery instructions for a safe and effective trickle charging experience.
Alternative Charging Methods for Lithium Batteries

Conclusion and Final Thoughts
This article delves into the viability of trickle charging for lithium batteries, offering insights into their functionality and the recommended charging methods.
- Trickle Charging Risks for Lithium Batteries:
- While trickle charging is beneficial for certain battery types, it is generally not recommended for lithium batteries. The slow charge rate may lead to overcharging, degrading battery capacity, and posing safety risks.
- Considerations Before Trickle Charging:
- Before opting for trickle charging, factors such as manufacturer recommendations, charger compatibility, and overall battery health should be carefully considered. Referring to product manuals or seeking expert advice is crucial.
- Alternatives to Trickle Charging:
- Efficient alternatives like USB-C Power Delivery (PD) or Qualcomm Quick Charge provide faster and safer options for charging lithium batteries without resorting to trickle charging. These methods preserve device lifespan while delivering power effectively.
In summary, for lithium batteries, trickle charging poses risks that outweigh its benefits. Exploring alternative, manufacturer-recommended charging methods ensures optimal performance and longevity for your high-performance rechargeable cells.
FAQs
Precautions for SLA charger with lithium battery?
When it comes to charging a lithium battery with an SLA charger, caution is key. Mixing different types of batteries and chargers can lead to potential safety hazards and damage to your equipment. Always double-check that the charger’s voltage and current ratings match those recommended for your specific lithium battery model.
Avoid using an SLA charger with a lithium battery unless explicitly stated by the manufacturer. Lithium batteries have different charging requirements compared to SLA batteries, so using the wrong charger can result in overcharging or undercharging, leading to reduced battery life or even causing the battery to fail prematurely.
Before attempting to charge a lithium battery with an SLA charger, consult the user manual provided by the battery manufacturer for detailed instructions and precautions. It’s crucial to follow these guidelines carefully to ensure safe and efficient charging without risking damage to your valuable electronic devices or batteries.
Why avoid 24V charger for 12V battery?
Using a 24V charger for a 12V battery might seem like a quick fix, but it can lead to serious consequences. The voltage mismatch can damage the delicate internal components of the 12V battery, reducing its lifespan and performance over time.
These batteries are designed to operate within specific voltage ranges, and using an incorrect charger can disrupt this balance. It’s like trying to fit a square peg into a round hole – it just doesn’t work.
To avoid potential safety hazards or costly replacements, always match the voltage output of the charger with the requirements of your battery. This simple precaution ensures that your battery receives the correct amount of power without risking damage.
Remember, when it comes to charging batteries, precision is key. Stick to the recommended voltage ratings to keep your devices running smoothly and efficiently for years to come.
Recommendations for matching chargers to batteries?
When it comes to matching chargers to batteries, compatibility is key. Always check the specifications of your battery to ensure you are using the correct charger. Using a mismatched charger can result in damage to your battery and potentially pose safety risks.
For SLA batteries, opt for a charger specifically designed for use with sealed lead-acid batteries. These chargers are equipped with features that cater to the unique charging requirements of SLA batteries, ensuring optimal performance and longevity.
On the other hand, lithium batteries require chargers designed specifically for lithium chemistry. These chargers typically have built-in safeguards such as overcharge protection and balancing functions to safely charge lithium batteries without compromising their lifespan.
Avoid using a 24V charger on a 12V battery as this can lead to overcharging and potential damage. Always follow manufacturer guidelines when selecting a charger for your battery to ensure efficient and safe charging processes.
SLA vs. lithium battery self-discharge rate?
When it comes to self-discharge rate, SLA and lithium batteries have different behaviors. SLA batteries tend to self-discharge at a faster rate compared to lithium batteries. This means that if left unused for an extended period, SLA batteries will lose their charge quicker than lithium ones.
On the other hand, lithium batteries have a much lower self-discharge rate, allowing them to hold their charge for longer periods of time without needing frequent recharges. This makes lithium batteries more convenient for applications where long-term storage is required.
Understanding the self-discharge rates of these two types of batteries can help you choose the right one based on your specific needs. Whether it’s for emergency backup power or everyday use, knowing how quickly a battery loses its charge is crucial in ensuring reliable performance when you need it most.
Optimal SLA battery state for storage?
When it comes to storing SLA batteries, ensuring they are in the optimal state is crucial. The ideal storage condition for SLA batteries is around 50% charge. This level helps prevent overcharging or deep discharging during storage, which can damage the battery’s lifespan.
Avoid storing SLA batteries in extreme temperatures, as this can impact their performance and overall health. It’s best to store them in a cool, dry place away from direct sunlight and humidity.
Regularly checking the battery’s voltage during storage can help ensure it stays within the recommended range. If you plan on storing an SLA battery for an extended period, consider using a trickle charger to maintain its charge levels without overcharging it.
By following these guidelines, you can prolong the life of your SLA battery and ensure it performs optimally when you need it most.
Why different storage for SLA and lithium batteries?
When it comes to storing SLA and lithium batteries, there are key differences to keep in mind.
SLA batteries prefer a cool and dry environment with a moderate temperature range to maintain optimal performance. In contrast, lithium batteries require slightly different conditions for storage.
Lithium batteries should be stored at around 50% charge in a cool place away from direct sunlight or heat sources. This helps prevent degradation and prolongs their lifespan.
The chemistry of SLA and lithium batteries varies, leading to distinct storage requirements based on their composition and internal structure.
By understanding these differences, you can ensure that both your SLA and lithium batteries remain in top condition when not in use.
Can lead acid charger charge lithium battery?
You might be wondering if a lead acid charger can charge a lithium battery. The short answer is no, and here’s why:
Lead acid chargers are designed specifically for lead acid batteries, not lithium-ion batteries. Using the wrong type of charger can potentially damage your lithium battery or even pose safety risks. Lithium batteries require a different charging algorithm than lead acid batteries due to their unique chemistry.
Lithium batteries have specific voltage requirements that differ from lead acid batteries. Attempting to charge a lithium battery with a lead acid charger may result in overcharging, which can cause overheating and potential fire hazards.
To ensure the longevity and safety of your lithium battery, it’s crucial to use a charger specifically designed for lithium-ion batteries. This will help optimize performance and protect your investment in the long run.
Lithium vs. SLA battery float charge requirements?
Lithium batteries have different float charge requirements compared to SLA batteries. It is essential to ensure that the charger you use matches the specific type of battery you have to avoid any potential damage or safety hazards. Understanding the differences in charging protocols and storage needs between lithium and SLA batteries can help prolong their lifespan and optimize their performance. Always refer to the manufacturer’s guidelines for the recommended charging methods and storage conditions for your specific battery type. By following these recommendations, you can effectively maintain your batteries and ensure they operate efficiently when needed.
How do lithium batteries compare to lead-acid in efficiency?
Lithium batteries are more efficient than lead-acid batteries. They have higher energy density, allowing them to store more energy in a smaller size. Lithium batteries also have a higher charge/discharge efficiency, converting more stored energy into usable power. With a longer cycle life, lithium batteries maintain their efficiency over multiple charge and discharge cycles, making them a superior choice in terms of efficiency.
What are the cons of using a battery trickle charger?
Using a battery trickle charger may have some drawbacks. Improper use of a trickle charger can lead to overheating and overcharging of the battery, similar to faster chargers. It is important to follow proper usage guidelines to avoid these risks and ensure the optimal performance and longevity of the battery.
What are the benefits of a trickle charger for lead and AGM batteries?
Trickle chargers offer several benefits for lead and AGM batteries. They lower the risk of overcharging, prevent self-discharge, and combat sulfation. By providing a low and steady charge, trickle chargers ensure the optimal performance and longevity of the batteries.
What are trickle chargers and how do they work?
Trickle chargers are devices that prevent batteries from losing charge when not in use. They work by providing a low and steady current to the battery, preventing discharge and slowly recharging it. Trickle chargers help maintain the battery’s charge level and improve its long-term health.
Do large vehicle batteries need a trickle charger?
Trickle chargers are beneficial for large vehicle batteries, especially when the vehicle is not in use for an extended period. They help maintain the battery’s charge and prevent power loss over time. By providing a low and steady charge, trickle chargers ensure that the battery remains in optimal condition and ready for use when needed.
What specific lithium battery products does Ionic offer?
Ionic offers a variety of lithium battery products, including the Ionic Lithium 12V 30Ah, 50Ah, and 100Ah deep cycle batteries. These batteries come equipped with Bluetooth capabilities, allowing for convenient monitoring and control. With their high-quality construction and reliable performance, Ionic lithium batteries are ideal for marine, RV, solar, scooter, and other applications.
Why is switching to LiFePO4 lithium batteries recommended?
Switching to LiFePO4 lithium batteries is recommended due to their superior cycle life compared to lead acid batteries. While lead acid batteries offer up to 500 cycles, LiFePO4 batteries can provide up to 6,000 cycles or more. This extended cycle life is attributed to the chemical structure of LiFePO4 batteries, which minimizes thermal instability and electrode wear. By choosing LiFePO4 batteries, users can enjoy longer-lasting and more reliable power storage solutions.












