- Rack-mounted Lithium Battery
- Golf Cart Lithium Battery
-
Golf Cart Lithium Battery
- 36V 50Ah (for Golf Carts)
- 36V 80Ah (for Golf Carts)
- 36V 100Ah (for Golf Carts)
- 48V 50Ah (for Golf Carts)
- 48V 100Ah (Discharge 100A for Golf Carts)
- 48V 100Ah (Discharge 150A for Golf Carts)
- 48V 100Ah (Discharge 200A for Golf Carts)
- 48V 120Ah (for Golf Carts)
- 48V 150Ah (for Golf Carts)
- 48V 160Ah (Discharge 100A for Golf Carts)
- 48V 160Ah (Discharge 160A for Golf Carts)
-
Golf Cart Lithium Battery
- Forklift Lithium Battery
- 12V Lithium Battery
- 24V Lithium Battery
- 36V Lithium Battery
- 48V Lithium Battery
-
48V LiFePO4 Battery
- 48V 50Ah
- 48V 50Ah (for Golf Carts)
- 48V 60Ah (8D)
- 48V 100Ah (8D)
- 48V 100Ah
- 48V 100Ah (Discharge 100A for Golf Carts)
- 48V 100Ah (Discharge 150A for Golf Carts)
- 48V 100Ah (Discharge 200A for Golf Carts)
- 48V 150Ah (for Golf Carts)
- 48V 160Ah (Discharge 100A for Golf Carts)
- 48V 160Ah (Discharge 160A for Golf Carts)
-
48V LiFePO4 Battery
- 60V Lithium Battery
-
60V LiFePO4 Battery
- 60V 20Ah
- 60V 30Ah
- 60V 50Ah
- 60V 50Ah (Small Size / Side Terminal)
- 60V 100Ah (for Electric Motocycle, Electric Scooter, LSV, AGV)
- 60V 100Ah (for Forklift, AGV, Electric Scooter, Sweeper)
- 60V 150Ah (E-Motocycle / E-Scooter / E-Tricycle / Tour LSV)
- 60V 200Ah (for Forklift, AGV, Electric Scooter, Sweeper)
-
60V LiFePO4 Battery
- 72V~96V Lithium Battery
- E-Bike Battery
- All-in-One Home-ESS
- Wall-mount Battery ESS
-
Home-ESS Lithium Battery PowerWall
- 24V 100Ah 2.4kWh PW24100-S PowerWall
- 48V 50Ah 2.4kWh PW4850-S PowerWall
- 48V 50Ah 2.56kWh PW5150-S PowerWall
- 48V 100Ah 5.12kWh PW51100-F PowerWall (IP65)
- 48V 100Ah 5.12kWh PW51100-S PowerWall
- 48V 100Ah 5.12kWh PW51100-H PowerWall
- 48V 200Ah 10kWh PW51200-H PowerWall
- 48V 300Ah 15kWh PW51300-H PowerWall
PowerWall 51.2V 100Ah LiFePO4 Lithium Battery
Highly popular in Asia and Eastern Europe.
CE Certification | Home-ESS -
Home-ESS Lithium Battery PowerWall
- Portable Power Stations
Can I Charge My Battery At 20 Amps?

Understanding battery charging involves considering amperage, voltage, and charging processes to ensure safety and longevity. Charging at 20 amps requires assessing battery capacity, age, and temperature, with risks including overheating and accelerated wear. Alternatives like lower amperage charging or trickle chargers offer safer options. Safe charging practices involve proper equipment, monitoring, and maintenance to mitigate risks and maintain battery health.
Understanding Battery Charging
Understand battery charging basics: Higher amps mean faster charging. Match voltage for optimal results. Batteries have distinct charging stages. Stop when full to avoid damage; use chargers with safety features. Understand these for efficient, safe charging. Explore safety at 20 amps.
- Amperage Rating: Understand the rate at which electric current flows into the battery. Higher amperage means faster charging.
- Voltage Requirement: Know the specific voltage your battery needs for optimal charging. Most operate at 12 volts, but check for any variations.
- Charging Process: Different battery types have varying charging requirements. Lead-acid batteries typically undergo a three-stage process: bulk charge, absorption charge, and float charge.
- Overcharging Prevention: Stop charging once the battery reaches full capacity to prevent damage. Look for chargers with automatic shut-off features or indicator lights for safety.
By understanding these basics, you’ll make informed decisions about charging methods, ensuring efficient battery performance and longevity. Let’s explore the safety of charging at 20 amps!
Factors to Consider Before Charging at 20 Amps
Consider these factors before charging at 20 amps: Check battery capacity to prevent damage. Older batteries may struggle with high amperages; opt for lower options. Extreme temperatures affect charging efficiency. Assess if fast charging is necessary for battery longevity. By considering these, ensure smooth battery operation and longevity.
- Battery Capacity: Ensure your battery can handle the higher charge rate without overheating or damage. Check manufacturer recommendations for compatibility.
- Battery Age: Older batteries may not tolerate high amperages as well as newer ones. Consider sticking to lower amp options for aging batteries to avoid potential issues.
- Temperature Conditions: Extreme temperatures can impact charging efficiency. Optimal performance is achieved within moderate temperature ranges.
- Necessity vs. Patience: Assess whether a fast charge is truly necessary or if slower charging will suffice. Patience can preserve battery health and longevity in the long run.
By considering these factors, you’ll make an informed decision that ensures the smooth operation and longevity of your vehicle and battery.
Risks of Charging at a High Amperage
Charging at high amps poses risks: overheating can damage parts, overcharging may cause explosions, accelerating battery wear, and electrical faults can lead to hazards. Older or damaged batteries are more vulnerable. Assess battery condition and follow safety guidelines. Consider safer charging alternatives. Regular inspection is vital for battery health and risk reduction.
- Overheating: High charging rates can generate excessive heat, potentially damaging internal components.
- Overcharging: Charging at 20 amps may exceed recommended voltage levels, leading to chemical reactions that cause permanent damage or explosion.
- Accelerated Wear and Tear: High amperage charging can shorten battery lifespan and reduce performance over time.
- Electrical Faults: Increased risk of short circuits or electrical faults, posing safety hazards if not addressed.
These risks are more pronounced with older or damaged batteries. Before charging at 20 amps, assess battery age, condition, and follow manufacturer recommendations for safe charging practices. Consider alternative options for faster charging while prioritizing safety. Regular inspection and proper handling are crucial for optimal battery function and risk mitigation.
Alternatives to 20 Amp Charging
Safer charging options include lower amp chargers (10 or 5 amps) for slower but safer charging. Trickle chargers provide long-term maintenance with low current. Utilize renewable energy like solar power with a charge controller for appropriate current. Always follow guidelines or seek professional advice. Prioritize safety with batteries and electrical systems.
- Lower Amperage Charger: Opt for a 10 amp or 5 amp charger for slower but safer charging, minimizing risks associated with high amperage charging.
- Trickle Charger: Use a trickle charger for long-term maintenance, delivering low current over time to keep your battery charged without causing damage.
- Renewable Energy Sources: Utilize solar power or other renewable energy sources with a suitable charge controller to deliver appropriate current levels based on battery capacity and condition.
While these alternatives are safer, they have limitations. Always refer to manufacturer guidelines or seek professional advice for the best charging method suited to your needs. Prioritize safety when dealing with batteries and electrical systems.
How to Safely Charge Your Battery at 20 Amps
Safely charge at 20 amps by: 1. Using the right charger for your battery. 2. Checking for damage before charging. 3. Connecting positive then negative. 4. Monitoring voltage and temperature. 5. Never leaving the battery unattended. Follow these steps to minimize risks and maintain battery performance.
Follow these guidelines for safe battery charging at 20 amps:
- Choose the Right Charger: Ensure your charger matches your battery type and specifications to avoid damage.
- Inspect Battery: Check for damage or leaks before charging and ensure secure connections.
- Proper Connection: Attach the positive clamp first, then the negative to prevent sparking or short-circuits.
- Monitor Voltage and Temperature: Regularly check battery levels, stopping if they exceed safe limits.
- Stay Present: Never leave a charging battery unattended; monitor its progress closely.
By adhering to these safety measures, you can minimize risks and maintain optimal battery performance during high-amperage charging.
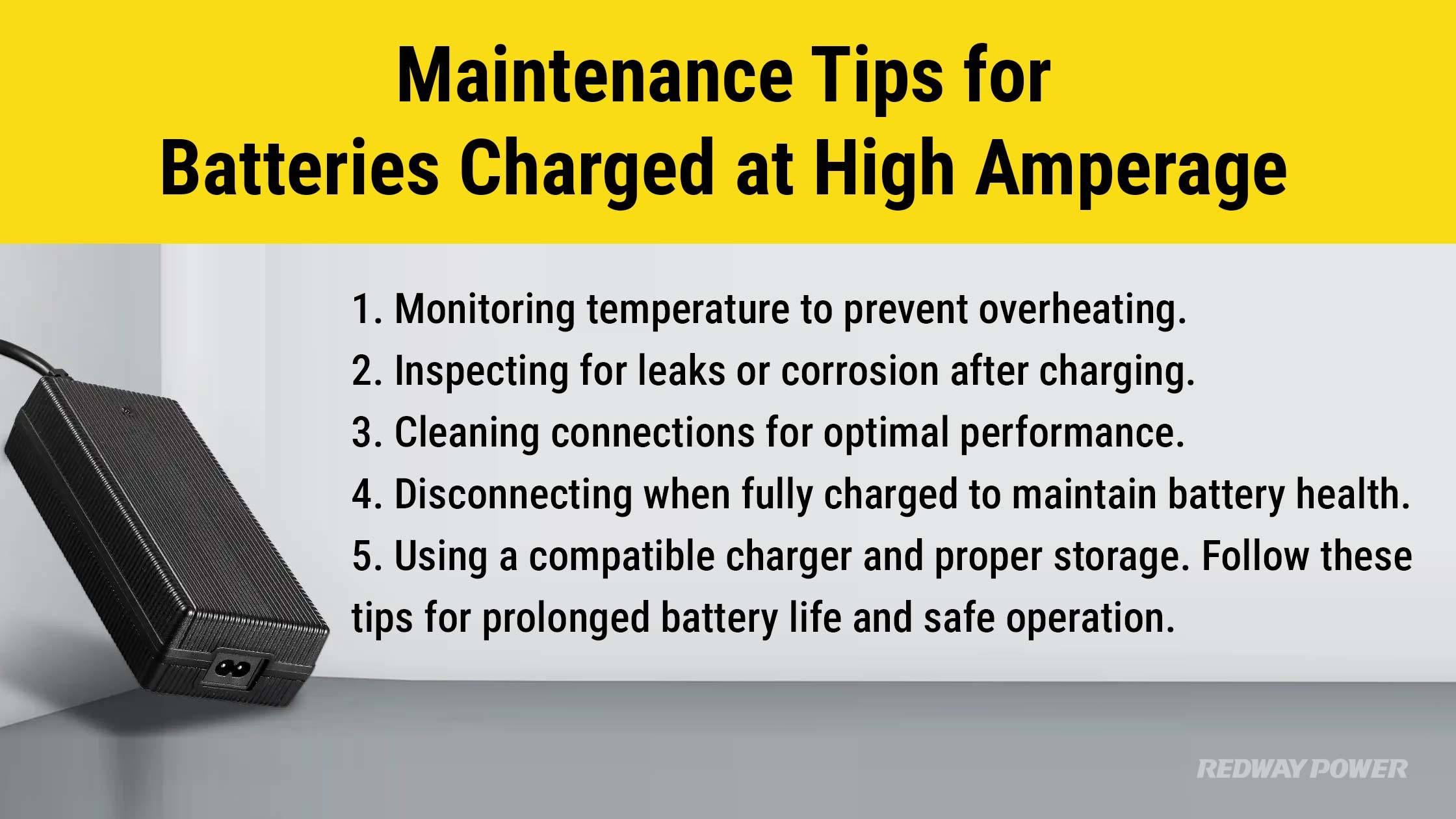
Maintenance Tips for Batteries Charged at High Amperage
Ensure safe battery care during high-amperage charging by:
1. Monitoring temperature to prevent overheating.
2. Inspecting for leaks or corrosion after charging.
3. Cleaning connections for optimal performance.
4. Disconnecting when fully charged to maintain battery health.
5. Using a compatible charger and proper storage. Follow these tips for prolonged battery life and safe operation.
Check details:
- Monitor Temperature: Check battery temperature regularly to prevent overheating; adjust charging if needed.
- Inspect for Damage: After charging, look for leaks or corrosion; address issues promptly to prevent hazards.
- Clean Connections: Ensure charger connections are clean and secure to maintain proper charging.
- Avoid Overcharging: Disconnect battery once fully charged to avoid performance decline.
- Use Compatible Charger: Always use a charger suited for your battery type and follow manufacturer guidelines.
- Proper Storage: Store batteries in a cool, dry place away from extreme temperatures when not in use.
By following these maintenance tips, you can prolong battery life and ensure safe operation during high-amperage charging. Remember to seek professional advice for any advanced charging methods.