- Lithium Golf Cart Battery
- Forklift Lithium Battery
-
48V
- 48V 210Ah
- 48V 300Ah
- 48V 420Ah (949 x 349 x 569 mm)
- 48V 420Ah (950 x 421 x 450 mm)
- 48V 456Ah
- 48V 460Ah (830 x 630 x 590 mm)
- 48V 460Ah (950 x 421 x 450 mm)
- 48V 460Ah (800 x 630 x 600 mm)
- 48V 460Ah (820 x 660 x 470 mm)
- 48V 500Ah
- 48V 560Ah (810 x 630 x 600 mm)
- 48V 560Ah (950 x 592 x 450 mm)
- 48V 600Ah
- 48V 630Ah
-
48V
- 12V Lithium Battery
12V 150Ah Lithium RV Battery
Bluetooth App | BCI Group 31
LiFePO4 Lithium
Discharge Temperature -20°C ~ 65°C
Fast Charger 14.6V 50A
Solar MPPT Charging - 24V Lithium Battery
- 36V Lithium Battery
- 48V Lithium Battery
-
48V LiFePO4 Battery
- 48V 50Ah
- 48V 50Ah (for Golf Carts)
- 48V 60Ah (8D)
- 48V 100Ah (8D)
- 48V 100Ah
- 48V 100Ah (Discharge 100A for Golf Carts)
- 48V 100Ah (Discharge 150A for Golf Carts)
- 48V 100Ah (Discharge 200A for Golf Carts)
- 48V 150Ah (for Golf Carts)
- 48V 160Ah (Discharge 100A for Golf Carts)
- 48V 160Ah (Discharge 160A for Golf Carts)
-
48V LiFePO4 Battery
- 60V Lithium Battery
-
60V LiFePO4 Battery
- 60V 20Ah
- 60V 30Ah
- 60V 50Ah
- 60V 50Ah (Small Size / Side Terminal)
- 60V 100Ah (for Electric Motocycle, Electric Scooter, LSV, AGV)
- 60V 100Ah (for Forklift, AGV, Electric Scooter, Sweeper)
- 60V 150Ah (E-Motocycle / E-Scooter / E-Tricycle / Tour LSV)
- 60V 200Ah (for Forklift, AGV, Electric Scooter, Sweeper)
-
60V LiFePO4 Battery
- 72V~96V Lithium Battery
- Rack-mounted Lithium Battery
- E-Bike Battery
- All-in-One Home-ESS
- Wall-mount Battery ESS
-
Home-ESS Lithium Battery PowerWall
- 24V 100Ah 2.4kWh PW24100-S PowerWall
- 48V 50Ah 2.4kWh PW4850-S PowerWall
- 48V 50Ah 2.56kWh PW5150-S PowerWall
- 48V 100Ah 5.12kWh PW51100-F PowerWall (IP65)
- 48V 100Ah 5.12kWh PW51100-S PowerWall
- 48V 100Ah 5.12kWh PW51100-H PowerWall
- 48V 200Ah 10kWh PW51200-H PowerWall
- 48V 300Ah 15kWh PW51300-H PowerWall
PowerWall 51.2V 100Ah LiFePO4 Lithium Battery
Highly popular in Asia and Eastern Europe.
CE Certification | Home-ESS -
Home-ESS Lithium Battery PowerWall
- Portable Power Stations
Can I charge a 5v battery with a 12V charger?

Charging a 5V battery with a 12V charger poses risks like overcharging and electrical short circuits. It’s crucial to match the charger voltage with the battery’s specifications. Alternatives include voltage regulators, USB ports, or specialized lower-voltage chargers for safe and efficient charging. Prioritize safety to avoid damage and ensure longevity.
Understanding the basics of voltage and batteries
Understanding voltage and batteries is crucial. Voltage represents electron force in circuits, akin to water pressure in pipes. Batteries store and convert chemical energy into electricity, each with a specific voltage rating. Mismatched voltages can damage devices. Always check compatibility before charging to prevent hazards. Simplify the complex concept of voltage and its relation to batteries.
Let’s break it down:
- Voltage Basics:
- Voltage is the force pushing electrons in an electrical circuit, similar to water flow in a pipe.
- It represents the potential difference between two points.
- Battery Fundamentals:
- Batteries store chemical energy and convert it into electrical energy.
- They come in various sizes, each with a specific voltage rating (e.g., 5V or 12V).
- Voltage Ratings:
- Devices and chargers have different voltage requirements.
- Mismatched voltages can damage batteries or pose safety risks.
- Always double-check compatibility before charging to avoid unwanted sparks and ensure safety.
Let me know if I should continue writing
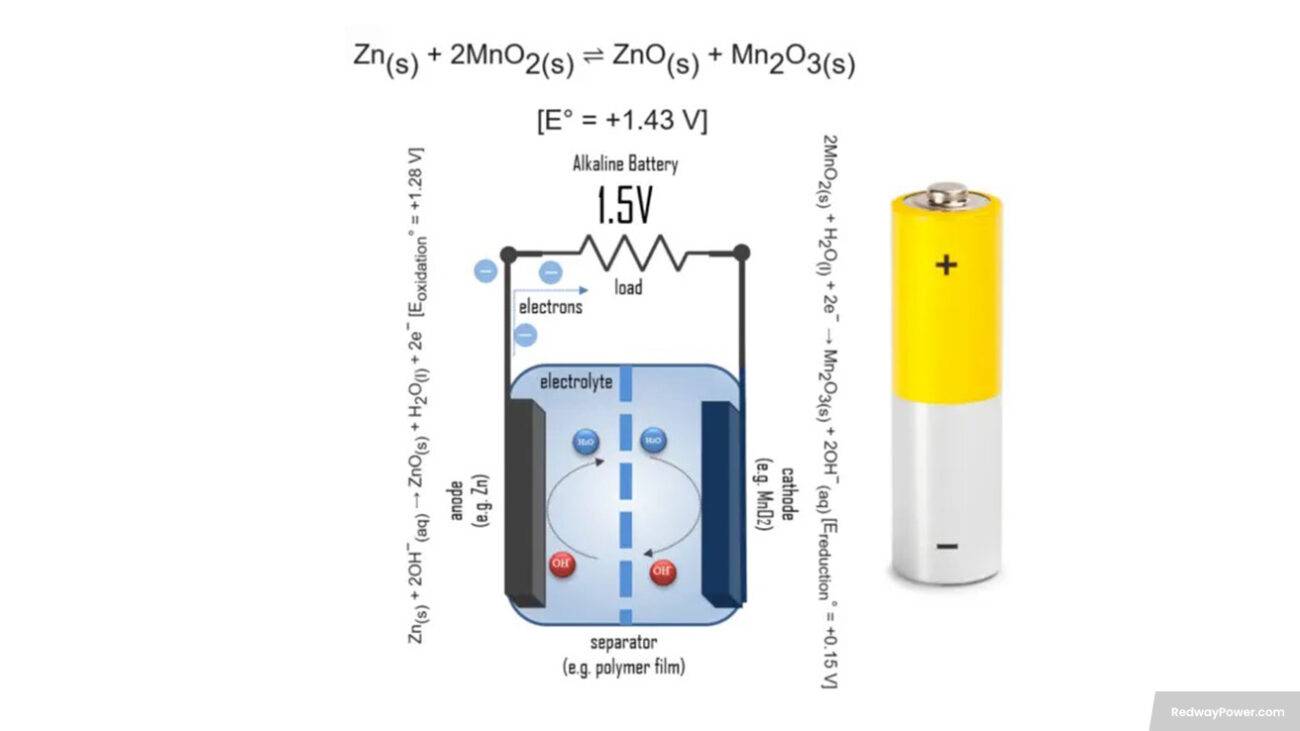
What is a 5V battery?
“5V” signifies a battery’s voltage at 5 volts, commonly used in gadgets like smartphones and tablets. Mainly associated with USB power, particularly Lithium-ion (Li-ion) types, these batteries offer high energy density and extended life. Matching voltage is vital for safe charging, highlighting the necessity of suitable chargers to prevent damage or hazards. Let’s simplify it:
- Understanding 5V Batteries:
- A 5V battery operates at a voltage level of 5 volts, measuring the electric force pushing electrons.
- Commonly found in gadgets like smartphones, tablets, and portable speakers, it powers these devices efficiently.
- Lithium-ion (Li-ion) Characteristics:
- The most popular 5V battery type is Lithium-ion (Li-ion).
- Li-ion batteries offer high energy density, longer rechargeable life, and are lightweight, making them ideal for small electronic devices.
- Importance of Voltage Matching:
- Different devices require different voltages, emphasizing the need for the right charger.
- Using an inappropriate charger can lead to damage or safety hazards, underlining the importance of matching the voltage for charging.
What is a 12V charger?
A 12V charger is tailored for batteries operating at a 12-volt level, commonly used for car batteries. It offers features like fast or trickle charging and overcharge protection. It’s crucial to match the charger’s voltage with the battery’s to avoid complications and damage, emphasizing the importance of compatibility.

Curious about 12V chargers? Let’s simplify:
- Defining a 12V Charger:
- A 12V charger is designed for batteries operating at a 12-volt voltage level.
- Commonly used for charging car batteries or larger electrical devices, it plays a vital role in maintaining power.
- Features and Capabilities:
- These chargers may offer various modes like fast or trickle charging and safety features such as overcharge protection.
- The features vary based on the charger’s intended use, providing flexibility in charging options.
- Crucial Compatibility Note:
- It’s essential to use 12V chargers only with batteries matching this voltage.
- Using them with different voltage batteries can lead to complications and potential damage, emphasizing the importance of checking battery requirements.
The potential risks of charging a 5V battery with a 12V charger
Using a 12V charger for a 5V battery risks overcharging and damage, reducing its lifespan. Short-circuiting is also possible, leading to sparks or fires. Prioritize safety by using chargers designed for the battery’s voltage. Follow manufacturer guidelines for safe usage and reliability.
- Overcharging Risks:
- Using a higher voltage charger can lead to overcharging your 5V battery.
- Overcharging causes overheating, damaging internal components and significantly reducing the battery’s lifespan.
- Electrical Short Circuiting:
- Connecting a 12V charger to a 5V battery poses a risk of electrical short circuiting.
- The higher voltage may overload the smaller battery, potentially causing sparks or fires, risking safety and device damage.
- Safety First:
- Always use chargers designed for your battery’s voltage to avoid these risks.
- Consult manufacturer guidelines or seek professional advice if uncertain. Prioritize safety over shortcuts for long-term reliability.
Alternatives to using a 12V charger for a 5V battery
Safe alternatives for charging a 5V battery with a 12V charger include using a voltage regulator or step-down converter to adjust voltage, connecting to USB ports or power banks supplying 5 volts, or choosing specialized lower-voltage chargers. Ensure compatibility and prioritize safety by adhering to your battery’s specifications for reliable charging.
- Voltage Regulator or Step-Down Converter:
- Use these devices to reduce the higher voltage from a 12V charger to the 5V needed for your battery.
- Ensures correct charging without the risk of overcharging or damage.
- USB Port or Power Bank:
- Connect your 5V battery to a USB port on devices like smartphones or power banks.
- Many USB ports provide around 5 volts, making it a safe alternative for charging.
- Specialized Lower-Voltage Chargers:
- Explore chargers designed for lower-voltage batteries with adjustable settings.
- These chargers offer a tailored solution, ensuring compatibility and safety.
Remember, safety first! Always choose alternatives that align with your battery’s specifications for a reliable and risk-free charging experience.
How to properly charge a 5V battery
Properly charging a 5V battery involves using a compatible charger, confirming voltage and current match, and monitoring progress. Check specifications, avoid overcharging, and follow recommended times. Charge within specified temperature ranges for optimal battery health. Prioritize safety and consult manufacturer guidelines when in doubt.

Charging your 5V battery correctly is key to its longevity. Follow these simple tips for safe and efficient charging:
- Use the Right Charger:
- Opt for a charger designed specifically for 5V batteries to ensure optimal voltage and current output.
- This promotes safe and efficient charging without risking damage.
- Check Specifications:
- Confirm compatibility by checking both battery and charger specifications, including voltage, current, and connector type.
- Ensure a secure connection by aligning positive and negative terminals correctly.
- Monitor Charging Progress:
- Keep an eye on the charging process using indicator lights on the charger or a reliable monitoring device.
- Avoid overcharging or undercharging to maintain overall battery performance and lifespan.
- Follow Recommended Charging Time:
- Refer to the manufacturer’s instructions for the recommended charging duration.
- Exceeding this time may lead to overheating or other safety hazards.
- Avoid Extreme Temperatures:
- Charge your 5V battery within the temperature range specified by the manufacturer.
- Extreme temperatures can negatively impact capacity and overall battery health.
By adhering to these straightforward guidelines, you can safely charge your 5V battery and maximize its lifespan. Prioritize safety, and if in doubt, seek guidance from an expert or customer support for your specific device model.
FAQs
Can I charge a 20 volt battery with a 12 volt charger?
What happens if you charge a 24 volt battery with a 12 volt charger?
What is the maximum voltage for charging a 12V battery?
Can I charge a 3.7 V battery with a 12V charger?
Can you charge a 2 volt battery with a 12-volt charger?
Can you charge batteries in series with a 12V charger?
Is it better to charge batteries in series or parallel?
Can you charge two 12V batteries in parallel with a 12V charger?
Can you charge batteries with any charger?
What are LiFePO4 (Lithium Iron Phosphate) Batteries?
LiFePO4 batteries, also known as Lithium Iron Phosphate batteries, are rechargeable batteries that use lithium iron phosphate as the cathode material. They offer advantages like long cycle life, cost-effectiveness, environmental friendliness, and safety. With at least 3000 full charge cycles, they are ideal for electric vehicles, portable electronics, and renewable energy storage systems. LiFePO4 batteries provide a greener and more reliable power solution.
What are the advantages of LiFePO4 Batteries over traditional Lithium-ion batteries?
LiFePO4 (Lithium Iron Phosphate) batteries offer several advantages over traditional lithium-ion batteries. They have a long cycle life of 3000+ full charge cycles, making them durable and cost-effective. These batteries are also safer, with superior thermal stability and reduced risk of thermal runaway. LiFePO4 batteries are environmentally friendly, containing no cobalt or nickel. Additionally, they maintain a steady voltage throughout discharge. Overall, LiFePO4 batteries excel in longevity, safety, and eco-friendliness.
What are the features and advantages of Lithium-Ion Batteries in general?
Lithium-ion batteries offer numerous advantages. They have a high energy density, meaning they can store more energy in a compact size. These batteries also have no memory effect, allowing for flexible recharging. Additionally, they have a slow rate of self-discharge when not in use and are environmentally friendly as they are rechargeable and free of harmful metals like lead or cadmium. Lithium-ion batteries are a smart and efficient power solution.
Comparing Ionic “Deep Cycle” Capacity (Ah) Rating to Lead-Acid Ah Ratings
Ionic’s “Deep Cycle” Capacity (Ah) Rating refers to its ability to provide sustained power for applications like solar energy storage, electric vehicles, and marine use. Lead-acid batteries have different Ah ratings based on their type: Flooded Lead-Acid (FLA) ranges from 50 Ah to 200 Ah, Absorbed Glass Mat (AGM) ranges from 30 Ah to 200 Ah, and Gel Cell ranges from 30 Ah to 200 Ah. Ionic’s deep cycle batteries compete favorably with lead-acid batteries in terms of capacity and performance.
Advantages of Ionic “Deep Cycle Batteries” over Other Battery Types
Ionic’s “Deep Cycle Batteries” offer several advantages over other battery types. They have a longer cycle life, higher energy density, and require no maintenance. These batteries can be charged quickly and have a safer chemistry. Overall, Ionic deep cycle batteries are a reliable choice for various applications, providing extended lifespan, efficient performance, and peace of mind.
Reasons to Choose Ionic’s Lithium-Ion “Deep Cycle” Energy Storage Battery
Ionic’s Lithium-Ion “Deep Cycle” Energy Storage Battery is a reliable choice for various applications. It offers a long cycle life, high energy density, and requires no maintenance. These batteries can be charged quickly and have a safe chemistry. With Ionic batteries, you can enjoy extended lifespan, efficient performance, and peace of mind.