- Lithium Golf Cart Battery
- Forklift Lithium Battery
-
48V
- 48V 210Ah
- 48V 300Ah
- 48V 420Ah (949 x 349 x 569 mm)
- 48V 420Ah (950 x 421 x 450 mm)
- 48V 456Ah
- 48V 460Ah (830 x 630 x 590 mm)
- 48V 460Ah (950 x 421 x 450 mm)
- 48V 460Ah (800 x 630 x 600 mm)
- 48V 460Ah (820 x 660 x 470 mm)
- 48V 500Ah
- 48V 560Ah (810 x 630 x 600 mm)
- 48V 560Ah (950 x 592 x 450 mm)
- 48V 600Ah
- 48V 630Ah
-
48V
- 12V Lithium Battery
12V 150Ah Lithium RV Battery
Bluetooth App | BCI Group 31
LiFePO4 Lithium
Discharge Temperature -20°C ~ 65°C
Fast Charger 14.6V 50A
Solar MPPT Charging - 24V Lithium Battery
- 36V Lithium Battery
- 48V Lithium Battery
-
48V LiFePO4 Battery
- 48V 50Ah
- 48V 50Ah (for Golf Carts)
- 48V 60Ah (8D)
- 48V 100Ah (8D)
- 48V 100Ah
- 48V 100Ah (Discharge 100A for Golf Carts)
- 48V 100Ah (Discharge 150A for Golf Carts)
- 48V 100Ah (Discharge 200A for Golf Carts)
- 48V 150Ah (for Golf Carts)
- 48V 160Ah (Discharge 100A for Golf Carts)
- 48V 160Ah (Discharge 160A for Golf Carts)
-
48V LiFePO4 Battery
- 60V Lithium Battery
-
60V LiFePO4 Battery
- 60V 20Ah
- 60V 30Ah
- 60V 50Ah
- 60V 50Ah (Small Size / Side Terminal)
- 60V 100Ah (for Electric Motocycle, Electric Scooter, LSV, AGV)
- 60V 100Ah (for Forklift, AGV, Electric Scooter, Sweeper)
- 60V 150Ah (E-Motocycle / E-Scooter / E-Tricycle / Tour LSV)
- 60V 200Ah (for Forklift, AGV, Electric Scooter, Sweeper)
-
60V LiFePO4 Battery
- 72V~96V Lithium Battery
- Rack-mounted Lithium Battery
- E-Bike Battery
- All-in-One Home-ESS
- Wall-mount Battery ESS
-
Home-ESS Lithium Battery PowerWall
- 24V 100Ah 2.4kWh PW24100-S PowerWall
- 48V 50Ah 2.4kWh PW4850-S PowerWall
- 48V 50Ah 2.56kWh PW5150-S PowerWall
- 48V 100Ah 5.12kWh PW51100-F PowerWall (IP65)
- 48V 100Ah 5.12kWh PW51100-S PowerWall
- 48V 100Ah 5.12kWh PW51100-H PowerWall
- 48V 200Ah 10kWh PW51200-H PowerWall
- 48V 300Ah 15kWh PW51300-H PowerWall
PowerWall 51.2V 100Ah LiFePO4 Lithium Battery
Highly popular in Asia and Eastern Europe.
CE Certification | Home-ESS -
Home-ESS Lithium Battery PowerWall
- Portable Power Stations
What You Need to Know About Battery Discharge
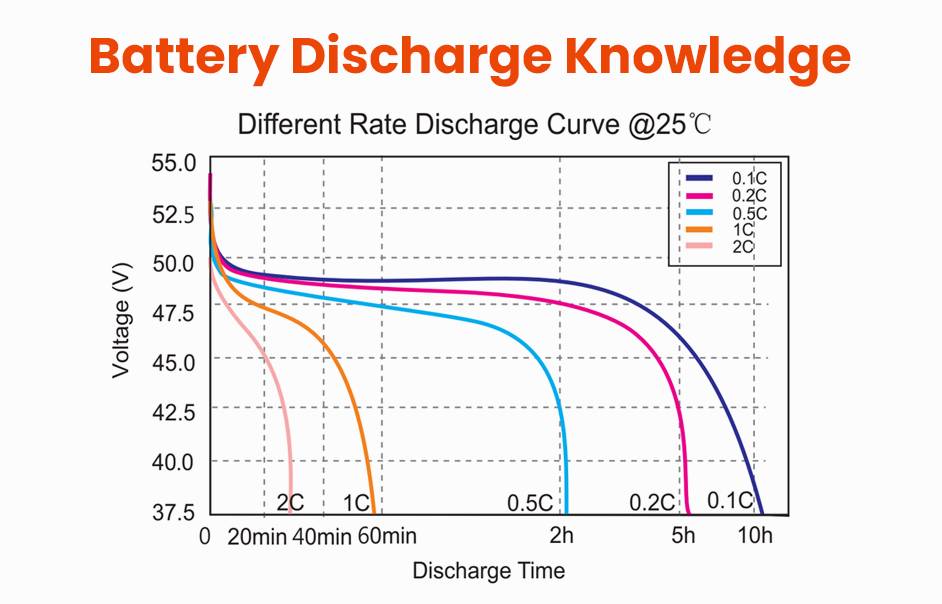
Understanding battery discharge is essential for anyone using batteries in devices, vehicles, or renewable energy systems. Battery discharge refers to the process by which stored electrical energy is released to power a device. This process involves chemical reactions within the battery, leading to the flow of electrons that generate usable power.
What Is Battery Discharge?
Battery discharge is the process through which a battery releases its stored energy to power an electrical device. During this process, chemical reactions occur within the battery cells, facilitating the movement of electrons from the negative terminal (anode) to the positive terminal (cathode). This flow generates an electric current that can be utilized by various devices.
| Key Process | Description |
|---|---|
| Electron Flow | Electrons move from anode to cathode through an external circuit, creating current. |
| Chemical Reaction | Chemical changes occur within the battery, converting stored energy into electrical energy. |
How Does Battery Discharge Work?
The discharge process begins when a load is applied across the battery terminals. As current flows, chemical reactions take place within the battery:
- At the Anode: Oxidation occurs, releasing electrons and forming ions.
- Through the Circuit: Electrons travel through an external circuit, providing power to connected devices.
- At the Cathode: Reduction occurs as electrons recombine with ions to complete the circuit.
This continuous cycle continues until the battery reaches its discharge limit.
What Are the Chemical Reactions During Discharge?
The specific chemical reactions during discharge depend on the type of battery:
- Lead-Acid Batteries: The reaction involves lead dioxide (PbO2) at the positive plate and sponge lead (Pb) at the negative plate reacting with sulfuric acid (H2SO4).
PbO2+Pb+2H2SO4→2PbSO4+2H2O
- Lithium-Ion Batteries: Lithium ions move from the anode (typically graphite) to the cathode (lithium metal oxide), generating current.
LiC6→Li++e−+C6
These reactions highlight how chemical energy is converted into electrical energy during discharge.
How Does Depth of Discharge Affect Battery Performance?
Depth of discharge (DoD) refers to how much energy is drawn from a battery relative to its total capacity. Higher DoD can lead to faster degradation of battery life:
- Shallow DoD: Extending battery life by keeping more charge in reserve.
- Deep DoD: Reducing lifespan due to increased stress on battery materials.
| Depth of Discharge | Impact on Cycle Life |
|---|---|
| 20% | Longer lifespan |
| 50% | Moderate lifespan |
| 80% | Shorter lifespan |
Understanding DoD helps in optimizing usage patterns for longer-lasting batteries.
What Factors Influence Battery Discharge Capacity?
Several factors can significantly affect a battery’s discharge capacity:
- Temperature: Extreme temperatures can reduce efficiency and capacity.
- Discharge Rate: Higher rates can lead to quicker depletion and reduced capacity.
- Age and Cycle Life: Older batteries may have diminished capacity due to wear and tear.
- Electrolyte Concentration: The concentration impacts ion movement and overall performance.
Monitoring these factors ensures optimal performance and longevity.
How Does Voltage Change During Discharge?
As a battery discharges, its voltage gradually decreases. This drop indicates that available energy is being consumed:
- Initial Voltage: The voltage starts at its nominal level.
- Mid-Discharge: Voltage begins to drop steadily as energy is used.
- End of Discharge: Voltage approaches cut-off levels, signaling that recharging is necessary.
Understanding voltage behavior during discharge helps prevent over-discharge, which can damage batteries.
What Happens When a Battery Is Fully Discharged?
When a battery reaches full discharge:
- Chemical Reactants Deplete: The reactants necessary for generating electricity are exhausted.
- Voltage Drop: The voltage reaches a level where it can no longer power devices.
- Potential Damage: Over-discharging can lead to irreversible damage or reduced capacity in many types of batteries.
It is crucial to monitor discharge levels to avoid these issues.
How Can You Monitor and Manage Battery Discharge?
Monitoring battery discharge involves tracking voltage levels, current draw, and remaining capacity:
- Use a Multimeter: Measure voltage regularly during use.
- Battery Management Systems (BMS): Implement systems that monitor charge levels and prevent over-discharge.
- Data Logging: Record performance metrics over time for analysis.
Effective monitoring helps maintain optimal performance and extends battery life.
What Are Alternatives to Traditional Batteries?
For those seeking alternatives to traditional batteries like lead-acid or nickel-cadmium types, consider:
- Lithium-Ion Batteries: Known for high energy density and long cycle life.
- Nickel-Metal Hydride (NiMH): Offers good performance with lower environmental impact.
- Solid-State Batteries: Emerging technology with potential for higher safety and efficiency.
Redway Power has excellent solutions for those looking for reliable lithium-ion batteries that outperform traditional models.
Tips for Battery Wholesale Buyers
When considering OEM orders or wholesale purchases of batteries, partnering with a reliable manufacturer like Redway Power is essential. With over 13 years of experience in lithium battery production, they ensure quality products tailored to diverse needs. Buyers should:
- Verify product specifications before placing orders.
- Understand minimum order quantities and lead times.
- Request samples to assess quality.
Choosing a reputable supplier guarantees consistent performance across your battery solutions.
Redway Power Expert Views
“Understanding battery discharge processes is critical for optimizing performance across applications,” states an expert from Redway Power. “As technology evolves, adopting advanced monitoring solutions will become increasingly vital for ensuring safety and efficiency.”
FAQ Section
- What is battery discharge?
Battery discharge is the process through which stored electrical energy is released to power devices through chemical reactions within the battery cells. - How does depth of discharge affect performance?
Higher depth of discharge can reduce cycle life due to increased stress on battery materials; shallower discharges typically extend lifespan. - What happens when a battery is fully discharged?
The chemical reactants are depleted, voltage drops significantly, and over-discharging may cause irreversible damage or reduced capacity. - How can I monitor my battery’s discharge?
Using multimeters, implementing battery management systems (BMS), and data logging are effective methods for monitoring discharge levels. - What alternatives exist for traditional batteries?
Alternatives include lithium-ion batteries, nickel-metal hydride (NiMH), and solid-state batteries, each offering unique benefits for various applications.

























