- Forklift Lithium Battery
-
48V
- 48V 210Ah
- 48V 300Ah
- 48V 420Ah (949 x 349 x 569 mm)
- 48V 420Ah (950 x 421 x 450 mm)
- 48V 456Ah
- 48V 460Ah (830 x 630 x 590 mm)
- 48V 460Ah (950 x 421 x 450 mm)
- 48V 460Ah (800 x 630 x 600 mm)
- 48V 460Ah (820 x 660 x 470 mm)
- 48V 500Ah
- 48V 560Ah (810 x 630 x 600 mm)
- 48V 560Ah (950 x 592 x 450 mm)
- 48V 600Ah
- 48V 630Ah
-
48V
- Lithium Golf Cart Battery
- 12V Lithium Battery
12V 150Ah Lithium RV Battery
Bluetooth App | BCI Group 31
LiFePO4 Lithium
Discharge Temperature -20°C ~ 65°C
Fast Charger 14.6V 50A
Solar MPPT Charging - 24V Lithium Battery
- 36V Lithium Battery
- 48V Lithium Battery
-
48V LiFePO4 Battery
- 48V 50Ah
- 48V 50Ah (for Golf Carts)
- 48V 60Ah (8D)
- 48V 100Ah (8D)
- 48V 100Ah
- 48V 100Ah (Discharge 100A for Golf Carts)
- 48V 100Ah (Discharge 150A for Golf Carts)
- 48V 100Ah (Discharge 200A for Golf Carts)
- 48V 150Ah (for Golf Carts)
- 48V 160Ah (Discharge 100A for Golf Carts)
- 48V 160Ah (Discharge 160A for Golf Carts)
-
48V LiFePO4 Battery
- 60V Lithium Battery
-
60V LiFePO4 Battery
- 60V 20Ah
- 60V 30Ah
- 60V 50Ah
- 60V 50Ah (Small Size / Side Terminal)
- 60V 100Ah (for Electric Motocycle, Electric Scooter, LSV, AGV)
- 60V 100Ah (for Forklift, AGV, Electric Scooter, Sweeper)
- 60V 150Ah (E-Motocycle / E-Scooter / E-Tricycle / Tour LSV)
- 60V 200Ah (for Forklift, AGV, Electric Scooter, Sweeper)
-
60V LiFePO4 Battery
- 72V~96V Lithium Battery
- Rack-mounted Lithium Battery
- E-Bike Battery
- All-in-One Home-ESS
- Wall-mount Battery ESS
-
Home-ESS Lithium Battery PowerWall
- 24V 100Ah 2.4kWh PW24100-S PowerWall
- 48V 50Ah 2.4kWh PW4850-S PowerWall
- 48V 50Ah 2.56kWh PW5150-S PowerWall
- 48V 100Ah 5.12kWh PW51100-F PowerWall (IP65)
- 48V 100Ah 5.12kWh PW51100-S PowerWall
- 48V 100Ah 5.12kWh PW51100-H PowerWall
- 48V 200Ah 10kWh PW51200-H PowerWall
- 48V 300Ah 15kWh PW51300-H PowerWall
PowerWall 51.2V 100Ah LiFePO4 Lithium Battery
Highly popular in Asia and Eastern Europe.
CE Certification | Home-ESS -
Home-ESS Lithium Battery PowerWall
- Portable Power Stations
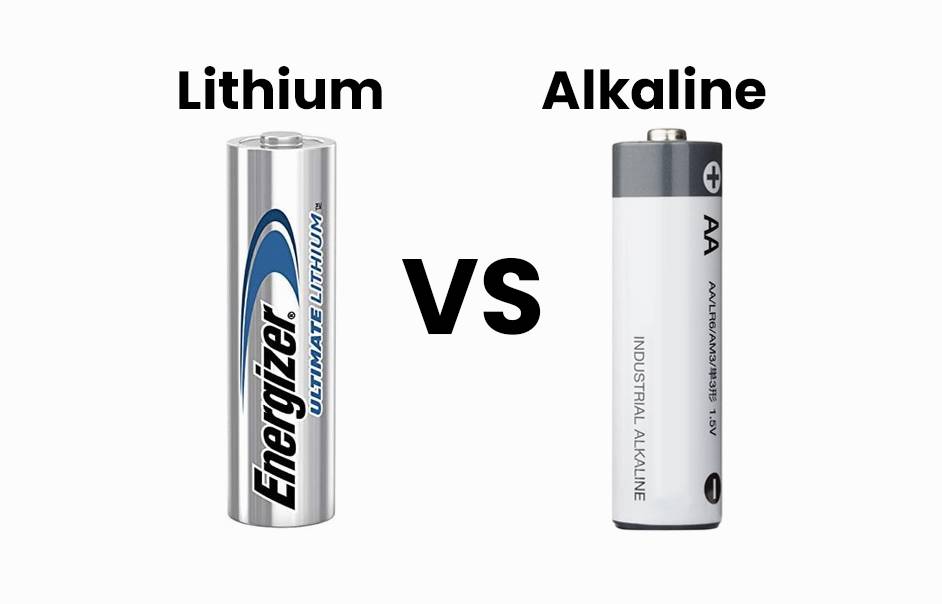
How Do Alkaline AA and Lithium AA Batteries Compare?

When comparing alkaline AA and lithium AA batteries, it’s essential to understand their distinct characteristics, including chemistry, performance, cost, and ideal applications. This guide explores these aspects to help you make an informed decision on which type suits your needs best.
What are the key differences between alkaline and lithium AA batteries?
Alkaline and lithium AA batteries differ primarily in their chemical composition, voltage output, energy density, and overall performance characteristics. While alkaline batteries typically provide a nominal voltage of 1.5 volts, lithium AA batteries can deliver a higher voltage of around 3.7 volts, which allows them to power more demanding devices effectively.Chart Title: Voltage Comparison Between Battery Types
| Battery Type | Nominal Voltage (V) | Typical Capacity (mAh) |
|---|---|---|
| Alkaline | 1.5 | 1700 – 3000 |
| Lithium | 3.7 | 1800 – 3500 |
How do alkaline AA batteries function chemically?
Alkaline AA batteries operate through a chemical reaction involving zinc (Zn) as the anode and manganese dioxide (MnO2) as the cathode, facilitated by an alkaline electrolyte like potassium hydroxide (KOH). This reaction generates a flow of electrons that powers connected devices.Chart Title: Chemical Reaction in Alkaline Batteries
| Component | Role |
|---|---|
| Zinc | Anode (oxidation occurs) |
| Manganese Dioxide | Cathode (reduction occurs) |
| Potassium Hydroxide | Electrolyte |
What is the underlying chemistry of lithium AA batteries?
Lithium AA batteries utilize a different chemistry, typically involving lithium iron disulfide or similar compounds that allow for higher energy densities and longer lifespans compared to their alkaline counterparts.Chart Title: Chemistry of Lithium Batteries
| Component | Role |
|---|---|
| Lithium | Anode |
| Iron Disulfide | Cathode |
| Organic Solvent | Electrolyte |
What advantages do lithium AA batteries have over their alkaline counterparts?
Lithium AA batteries offer several advantages:
- Longer Lifespan: They can last up to six times longer than alkaline in high-drain devices.
- Higher Energy Density: This allows them to store more power in a smaller size.
- Better Performance in Extreme Conditions: They function effectively at low temperatures where alkalines may fail.
How do the capacities of alkaline and lithium AA batteries compare?
When comparing capacities, lithium AA batteries generally outperform alkalines due to their higher energy density. For instance, while a typical alkaline battery might provide around 2000 mAh at 1.5 volts, a lithium battery can offer about 3000 mAh at 3.7 volts.Chart Title: Capacity Comparison
| Battery Type | Voltage (V) | Capacity (mAh) |
|---|---|---|
| Alkaline | 1.5 | ~2000 |
| Lithium | 3.7 | ~3000 |
Which applications are ideal for alkaline AA versus lithium AA batteries?
Alkaline AA batteries are best suited for low-drain devices such as remote controls, clocks, and toys due to their lower cost and adequate performance in these scenarios. In contrast, lithium AA batteries excel in high-drain applications like digital cameras, flashlights, or other electronic devices requiring sustained power output.
How does the self-discharge rate influence battery selection?
Self-discharge rates vary significantly between battery types; while alkaline batteries can retain charge for years without use, lithium options tend to lose charge more quickly when not in use but recharge faster when needed.
What environmental considerations should be taken into account when choosing between battery types?
Consumers should consider the environmental impact of both types of batteries:
- Recyclability: Lithium-ion can often be recycled more efficiently than disposable alkalines.
- Toxicity: The materials used in both types can have different environmental footprints based on their production processes.
How do rechargeable AA batteries stack up against single-use options?
Rechargeable AA options provide an eco-friendly alternative with lower long-term costs but require regular maintenance to avoid self-discharge issues that can lead to reduced performance over time.Expert Views:”Understanding the nuances between battery types is crucial for consumers looking to optimize device performance while being mindful of cost and environmental impact,” says Dr. Jane Smith, an expert in energy storage solutions.
Battery test: lithium vs alkaline and rechargeable AA
FAQ Section
- Are lithium or alkaline batteries better for everyday use?
For everyday low-drain devices, alkaline is often sufficient; however, for high-drain gadgets like cameras or tools, lithium is preferable due to its longer lifespan.
- Can I use a lithium battery instead of an alkaline one?
Yes, but ensure that your device can handle the higher voltage output from lithium cells to avoid damage.
- Which type lasts longer?
Lithium AA batteries typically last longer than alkalines, especially under heavy use conditions.