- Lithium Golf Cart Battery
- Forklift Lithium Battery
-
48V
- 48V 210Ah
- 48V 300Ah
- 48V 420Ah (949 x 349 x 569 mm)
- 48V 420Ah (950 x 421 x 450 mm)
- 48V 456Ah
- 48V 460Ah (830 x 630 x 590 mm)
- 48V 460Ah (950 x 421 x 450 mm)
- 48V 460Ah (800 x 630 x 600 mm)
- 48V 460Ah (820 x 660 x 470 mm)
- 48V 500Ah
- 48V 560Ah (810 x 630 x 600 mm)
- 48V 560Ah (950 x 592 x 450 mm)
- 48V 600Ah
- 48V 630Ah
-
48V
- 12V Lithium Battery
12V 150Ah Lithium RV Battery
Bluetooth App | BCI Group 31
LiFePO4 Lithium
Discharge Temperature -20°C ~ 65°C
Fast Charger 14.6V 50A
Solar MPPT Charging - 24V Lithium Battery
- 36V Lithium Battery
- 48V Lithium Battery
-
48V LiFePO4 Battery
- 48V 50Ah
- 48V 50Ah (for Golf Carts)
- 48V 60Ah (8D)
- 48V 100Ah (8D)
- 48V 100Ah
- 48V 100Ah (Discharge 100A for Golf Carts)
- 48V 100Ah (Discharge 150A for Golf Carts)
- 48V 100Ah (Discharge 200A for Golf Carts)
- 48V 150Ah (for Golf Carts)
- 48V 160Ah (Discharge 100A for Golf Carts)
- 48V 160Ah (Discharge 160A for Golf Carts)
-
48V LiFePO4 Battery
- 60V Lithium Battery
-
60V LiFePO4 Battery
- 60V 20Ah
- 60V 30Ah
- 60V 50Ah
- 60V 50Ah (Small Size / Side Terminal)
- 60V 100Ah (for Electric Motocycle, Electric Scooter, LSV, AGV)
- 60V 100Ah (for Forklift, AGV, Electric Scooter, Sweeper)
- 60V 150Ah (E-Motocycle / E-Scooter / E-Tricycle / Tour LSV)
- 60V 200Ah (for Forklift, AGV, Electric Scooter, Sweeper)
-
60V LiFePO4 Battery
- 72V~96V Lithium Battery
- Rack-mounted Lithium Battery
- E-Bike Battery
- All-in-One Home-ESS
- Wall-mount Battery ESS
-
Home-ESS Lithium Battery PowerWall
- 24V 100Ah 2.4kWh PW24100-S PowerWall
- 48V 50Ah 2.4kWh PW4850-S PowerWall
- 48V 50Ah 2.56kWh PW5150-S PowerWall
- 48V 100Ah 5.12kWh PW51100-F PowerWall (IP65)
- 48V 100Ah 5.12kWh PW51100-S PowerWall
- 48V 100Ah 5.12kWh PW51100-H PowerWall
- 48V 200Ah 10kWh PW51200-H PowerWall
- 48V 300Ah 15kWh PW51300-H PowerWall
PowerWall 51.2V 100Ah LiFePO4 Lithium Battery
Highly popular in Asia and Eastern Europe.
CE Certification | Home-ESS -
Home-ESS Lithium Battery PowerWall
- Portable Power Stations
What You Need to Know About Deep Cycle Batteries

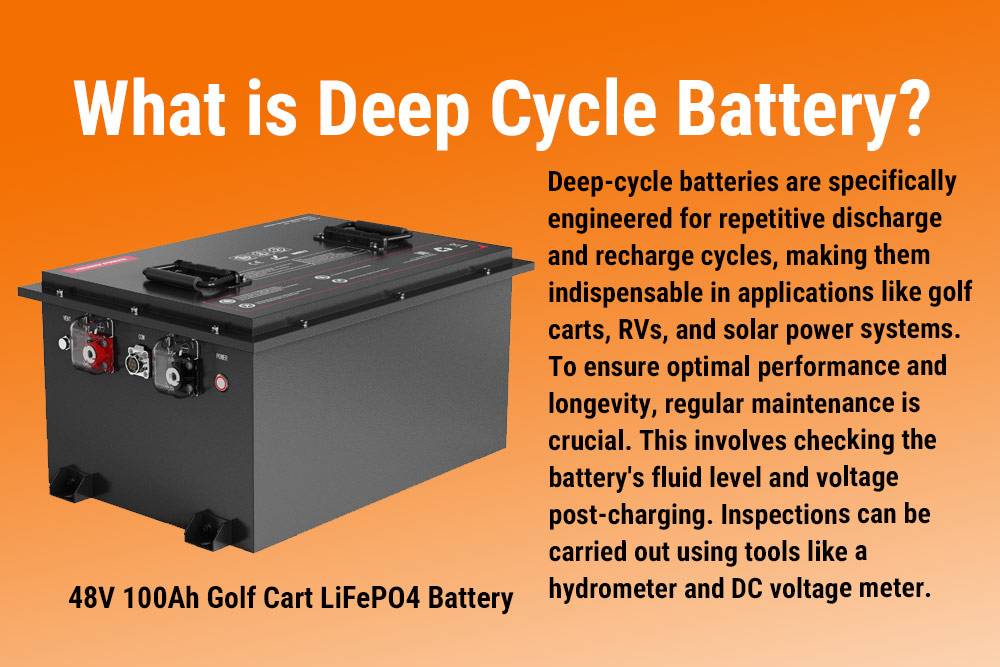
Deep cycle batteries are designed for sustained energy output over extended periods, making them ideal for applications such as RVs, boats, and golf carts. Unlike starter batteries, which provide short bursts of power, deep cycle batteries can be discharged and recharged repeatedly, offering a reliable power source for various uses.
What is Deep Cycle Battery?
How to Know A Battery is Deep Cycle or Not?
To determine if a battery is a deep cycle battery, you can look for several signs:

- Construction: Deep cycle batteries typically have thicker plates compared to regular batteries. These thick plates enable them to withstand repeated discharging and recharging cycles without getting damaged.
- Capacity: Deep cycle batteries have higher amp-hour ratings compared to regular batteries. This means they can provide power for longer periods before needing to be recharged.
- Manufacturer’s Labeling: Check the packaging or casing for keywords like “deep cycle” or “long-life” in the product description or name. Some batteries are specifically labeled as “deep-cycle” or “marine” types.
- Voltage Stability: Deep cycle batteries maintain a relatively stable voltage output throughout their discharge process. Regular batteries may experience voltage drop as they deplete their charge.
- Reserve Capacity: Deep cycle batteries usually have higher reserve capacities compared to regular batteries. Reserve capacity refers to how long the battery can run under specific conditions before dropping below its minimum voltage threshold.
By examining these factors, you can determine whether your battery is indeed a deep cycle type or not.
What are the different types of deep cycle batteries?
Deep cycle batteries come in several types, each with unique characteristics:
- Flooded Lead Acid (FLA): These are the most common and cost-effective but require regular maintenance.
- Absorbed Glass Mat (AGM): AGM batteries are sealed and maintenance-free, offering better performance in cold conditions.
- Gel Batteries: Similar to AGM but with a gelled electrolyte; they are also maintenance-free.
- Lithium-Ion Batteries: These have a longer lifespan and faster charging capabilities but come at a higher price point.
How do you maintain a deep cycle battery?
Proper maintenance is crucial for maximizing the lifespan of deep cycle batteries. Key practices include:
- Regularly checking fluid levels in flooded batteries.
- Ensuring terminals are clean and free of corrosion.
- Charging the battery promptly after use.
- Avoiding deep discharges beyond recommended levels (generally no more than 50-80%).
Chart: Maintenance Tips for Deep Cycle Batteries
| Maintenance Task | Frequency |
|---|---|
| Check fluid levels (FLA) | Monthly |
| Clean terminals | Every few months |
| Charge after use | Immediately |
| Inspect for physical damage | Quarterly |
What factors affect the lifespan of deep cycle batteries?
The lifespan of deep cycle batteries can be influenced by several factors:
- Depth of Discharge (DoD): Regularly discharging below recommended levels can significantly shorten battery life.
- Temperature: Extreme temperatures can affect performance and capacity; optimal conditions are usually between 20°C to 25°C (68°F to 77°F).
- Charging Practices: Using the correct charger and avoiding overcharging are essential for longevity.
How do you charge a deep cycle battery correctly?
Charging deep cycle batteries requires specific practices to ensure effective charging and longevity:
- Use a charger designed for deep cycle batteries.
- Avoid fast charging unless necessary; slower charges are generally better for battery health.
- Monitor the state of charge (SoC) regularly to prevent overcharging or undercharging.
What are the common applications of deep cycle batteries?
Deep cycle batteries are used in various applications, including:
- Electric Vehicles: Providing reliable power for propulsion.
- Renewable Energy Systems: Storing energy generated from solar panels or wind turbines.
- Recreational Vehicles (RVs): Powering appliances and lighting during trips.
- Marine Applications: Supplying power for boats and other watercraft.
Industrial News
The market for deep cycle batteries is evolving rapidly, with advancements in battery technology leading to improved performance and longevity. Manufacturers are increasingly focusing on lithium-ion technology due to its superior energy density and faster charging capabilities. Additionally, innovations in battery management systems are enhancing safety and efficiency across various applications.
Redway Power Expert Views
“Understanding the nuances of deep cycle batteries is essential for anyone relying on them for power,” states a Redway Power expert. “Proper maintenance and informed usage can dramatically extend their lifespan, ensuring that users get the most out of their investment.”

FAQs
How do Deep Cycle and Regular Batteries differ in charging?
Can Regular Batteries substitute for Deep Cycle Batteries?
What are Deep Cycle and Regular Batteries’ key features?
Characteristics and advantages of Lithium Iron Phosphate (LiFePO4) batteries?
How do Deep Cycle and Regular Batteries vary in recharging?
What are Deep Cycle and Regular Batteries commonly used for?
What are dual-purpose batteries, and how do they differ from deep cycle batteries?
Dual-purpose batteries are designed to provide both starting power for engines and cycling capabilities for running accessories. Deep cycle batteries, on the other hand, are specifically engineered for sustained power over extended periods without being depleted quickly.

What are the best uses for dual-purpose and deep cycle batteries?
Dual-purpose batteries are ideal for marine and RV applications where occasional bursts of energy are needed for engine starting and running accessories. Deep cycle batteries shine in renewable energy systems, golf carts, electric vehicles, and off-grid cabins, where consistent power delivery over long periods is required.
What are the pros and cons of dual-purpose batteries?
Pros: Versatility for both starting power and cycling capabilities, suitable for intermittent use. Cons: May not excel in either area compared to dedicated starter or deep cycle batteries, struggles with heavy-duty applications.
What are the pros and cons of deep cycle batteries?
Pros: Long-lasting power over extended periods, superior cycling performance and longevity. Cons: Lower cold-cranking amps, may struggle as primary starting batteries in colder climates.
How do I determine which battery type is right for me?
Consider your specific needs and usage patterns, including the capacity and lifespan of each battery type, maintenance requirements, and cost. Consult with professionals or experts for guidance based on your circumstances.
How do I maintain and replace my batteries?
Regularly inspect the battery for signs of damage or corrosion, keep it charged, avoid overcharging, and store it properly. Replace the battery when signs of reduced capacity or physical damage occur, ensuring the replacement matches your needs and requirements.
What are Group 31 deep cycle batteries?
Group 31 deep cycle batteries are specialized energy storage devices designed to provide long-lasting power for applications requiring sustained energy output, such as RVs, boats, and off-grid systems. They are known for their thick plates and robust construction, allowing them to withstand heavy usage and frequent charging cycles.
How do Group 31 deep cycle batteries differ from traditional car batteries?
Unlike traditional car batteries designed for short bursts of energy, Group 31 deep cycle batteries are built to deliver a steady and consistent flow of power over an extended period. They prioritize endurance and reliability over quick bursts of power, making them ideal for applications requiring sustained energy output.
What factors affect the lifespan of Group 31 deep cycle batteries?
Factors such as usage patterns, temperature, maintenance practices, charging habits, and brand quality can all impact the lifespan of Group 31 deep cycle batteries. Proper care and maintenance, including regular inspection, cleaning, and appropriate charging, can help extend their lifespan.
How can I extend the life of my Group 31 deep cycle battery?
To extend the life of your Group 31 deep cycle battery, ensure it is properly charged, avoid storing it in extreme temperatures, regularly maintain it, use energy-efficient appliances, and be mindful of how you discharge it. Following these tips can help maximize your battery’s lifespan.