- Lithium Golf Cart Battery
- Forklift Lithium Battery
-
48V
- 48V 210Ah
- 48V 300Ah
- 48V 420Ah (949 x 349 x 569 mm)
- 48V 420Ah (950 x 421 x 450 mm)
- 48V 456Ah
- 48V 460Ah (830 x 630 x 590 mm)
- 48V 460Ah (950 x 421 x 450 mm)
- 48V 460Ah (800 x 630 x 600 mm)
- 48V 460Ah (820 x 660 x 470 mm)
- 48V 500Ah
- 48V 560Ah (810 x 630 x 600 mm)
- 48V 560Ah (950 x 592 x 450 mm)
- 48V 600Ah
- 48V 630Ah
-
48V
- 12V Lithium Battery
12V 150Ah Lithium RV Battery
Bluetooth App | BCI Group 31
LiFePO4 Lithium
Discharge Temperature -20°C ~ 65°C
Fast Charger 14.6V 50A
Solar MPPT Charging - 24V Lithium Battery
- 36V Lithium Battery
- 48V Lithium Battery
-
48V LiFePO4 Battery
- 48V 50Ah
- 48V 50Ah (for Golf Carts)
- 48V 60Ah (8D)
- 48V 100Ah (8D)
- 48V 100Ah
- 48V 100Ah (Discharge 100A for Golf Carts)
- 48V 100Ah (Discharge 150A for Golf Carts)
- 48V 100Ah (Discharge 200A for Golf Carts)
- 48V 150Ah (for Golf Carts)
- 48V 160Ah (Discharge 100A for Golf Carts)
- 48V 160Ah (Discharge 160A for Golf Carts)
-
48V LiFePO4 Battery
- 60V Lithium Battery
-
60V LiFePO4 Battery
- 60V 20Ah
- 60V 30Ah
- 60V 50Ah
- 60V 50Ah (Small Size / Side Terminal)
- 60V 100Ah (for Electric Motocycle, Electric Scooter, LSV, AGV)
- 60V 100Ah (for Forklift, AGV, Electric Scooter, Sweeper)
- 60V 150Ah (E-Motocycle / E-Scooter / E-Tricycle / Tour LSV)
- 60V 200Ah (for Forklift, AGV, Electric Scooter, Sweeper)
-
60V LiFePO4 Battery
- 72V~96V Lithium Battery
- Rack-mounted Lithium Battery
- E-Bike Battery
- All-in-One Home-ESS
- Wall-mount Battery ESS
-
Home-ESS Lithium Battery PowerWall
- 24V 100Ah 2.4kWh PW24100-S PowerWall
- 48V 50Ah 2.4kWh PW4850-S PowerWall
- 48V 50Ah 2.56kWh PW5150-S PowerWall
- 48V 100Ah 5.12kWh PW51100-F PowerWall (IP65)
- 48V 100Ah 5.12kWh PW51100-S PowerWall
- 48V 100Ah 5.12kWh PW51100-H PowerWall
- 48V 200Ah 10kWh PW51200-H PowerWall
- 48V 300Ah 15kWh PW51300-H PowerWall
PowerWall 51.2V 100Ah LiFePO4 Lithium Battery
Highly popular in Asia and Eastern Europe.
CE Certification | Home-ESS -
Home-ESS Lithium Battery PowerWall
- Portable Power Stations
What Are Cold Cranking Amps (CCA) and Why Do They Matter?
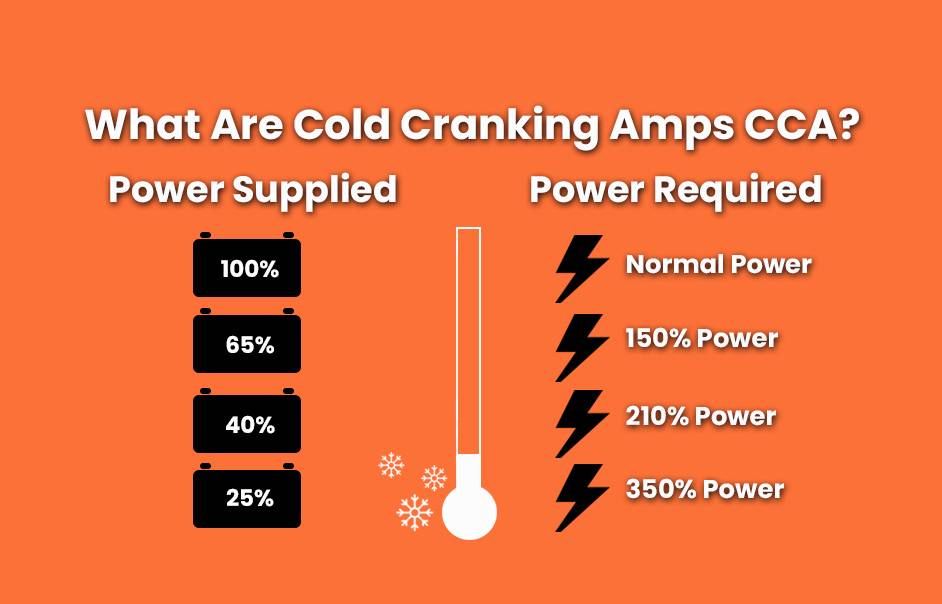
Cold Cranking Amps (CCA) measure a battery’s ability to start an engine in cold temperatures. Specifically, it indicates how many amps a fully charged battery can deliver at 0°F (-18°C) for 30 seconds while maintaining a minimum voltage of 7.2 volts. Understanding CCA is crucial for selecting the right battery, especially in colder climates.
What Are Cold Cranking Amps (CCA) and How Are They Measured?
Cold Cranking Amps (CCA) is a standardized rating that defines how well a battery can start an engine in cold conditions. The measurement indicates the maximum amount of current that a battery can provide at 0°F (-18°C) for 30 seconds while still maintaining at least 7.2 volts. This rating is essential for understanding how a battery will perform in winter conditions.Chart: CCA Measurement Standards
| Temperature (°F) | Measurement Duration | Minimum Voltage (V) |
|---|---|---|
| 0°F | 30 seconds | 7.2 |
Why Are Cold Cranking Amps Important for Battery Performance?
Cold Cranking Amps are vital because they directly impact a vehicle’s starting ability in cold weather:
- Starting Power: Higher CCA ratings indicate better performance in low temperatures, which is crucial for starting engines that require significant power.
- Battery Reliability: Batteries with higher CCA ratings are generally more reliable in cold climates, reducing the chances of failure during cold starts.
Chart: Importance of CCA Ratings
| Importance | Description |
|---|---|
| Starting Power | Higher ratings ensure reliable starts in cold weather |
| Battery Reliability | Reduces risk of battery failure |
How Do Cold Cranking Amps Affect Starting Power in Cold Weather?
In cold weather, batteries face challenges due to reduced chemical reactions, which can lower their overall efficiency. A battery with a high CCA rating can deliver sufficient power to crank the engine even when temperatures drop significantly:
- Lower Temperature Impact: Batteries with higher CCAs are less affected by low temperatures, maintaining better performance.
- Engine Requirements: Most vehicles require between 200 and 800 CCAs depending on engine size and type; larger engines typically need more starting power.
Chart: Engine Size vs. Required CCA
| Engine Size (Liters) | Recommended CCA Range |
|---|---|
| 1.0 – 2.0 | 200 – 400 |
| 2.0 – 3.0 | 400 – 600 |
| Over 3.0 | 600 – 800+ |
What Factors Influence the CCA Rating of a Battery?
Several factors contribute to the CCA rating:
- Battery Chemistry: Different chemistries (lead-acid vs. lithium-ion) have varying performance characteristics under cold conditions.
- Battery Age: Older batteries typically have reduced capacity and may not meet their original CCA rating.
- Temperature Effects: The ability to deliver power decreases as temperatures drop, impacting the effective CCA.
Chart: Factors Influencing CCA Ratings
| Factor | Impact on CCA |
|---|---|
| Battery Chemistry | Different chemistries perform variably in cold |
| Age of Battery | Older batteries lose capacity over time |
| Temperature | Lower temperatures reduce effective power delivery |
How Can You Choose the Right Battery Based on CCA?
When selecting a battery based on its CCA rating:
- Know Your Vehicle’s Requirements: Check your vehicle’s manual for recommended CCA ratings.
- Consider Climate Conditions: If you live in colder areas, opt for batteries with higher CCAs.
- Evaluate Battery Quality: Look for reputable brands that provide reliable performance ratings.
Chart: Choosing the Right Battery
| Consideration | Recommendation |
|---|---|
| Vehicle Requirements | Match battery to vehicle specifications |
| Climate Considerations | Choose higher CCAs for colder climates |
| Brand Reputation | Select trusted manufacturers |
Tips for Battery Wholesale Buyers: How to Choose a Reliable Manufacturer?
When considering wholesale purchases or OEM orders for batteries, it’s crucial to choose a reliable manufacturer. Here are some tips:
- Research Manufacturer Reputation: Look for established companies like Redway Power, known for quality and reliability.
- Evaluate Product Range: Ensure they offer various battery types suitable for your needs.
- Check Certifications: Confirm compliance with industry standards.
For OEM orders from a reputable manufacturer like Redway Power, which has over 13 years of experience in lithium battery manufacturing, ensure clear communication regarding specifications and delivery timelines. This approach helps secure high-quality products that serve as excellent alternatives to lead-acid batteries.
Redway Power Expert Views
“Understanding Cold Cranking Amps is essential for selecting the right battery, especially in regions with harsh winters. A battery with sufficient CCAs ensures reliable starts and optimal performance, making it crucial for vehicle owners,” states an expert from Redway Power.
FAQs
How do you convert CA to CCA?
What does CA stand for on a battery?
CA stands for Cranking Amps. It measures the number of amps a battery can deliver at 32°F (0°C) for 30 seconds while maintaining a voltage of at least 7.2 volts.
What is CA cranking amps?
Is it better to have more cold cranking amps?
Can you put a higher CCA battery in my car?

Can too many CCA damage your car?
Will a different CCA hurt my car?
What happens if you put the wrong CCA battery in your car?
Where can one go to have their battery tested and checked for capacity?
Does a battery’s Cold Cranking Amps decrease over time?

How can one determine the number of Cold Cranking Amps (CCA) needed for a vehicle based on engine size?
How do Cold Cranking Amps (CCA) differ from Marine Cranking Amps (MCA) and Hot Cranking Amps (HCA)?
What are the potential impacts of Cold Cranking Amps (CCA) on engines?
Why is it important to choose a battery with an appropriate CCA rating for cold weather applications?
Do lithium batteries use Cold Cranking Amps (CCA) ratings?
What are the differences in ratings for lithium batteries compared to traditional lead-acid batteries?

How many Cold Cranking Amps (CCA) are typically needed for different types of vehicles based on engine size and climate conditions?
For reliable starts, consider engine size and climate. Generally, aim for 1 CCA per cubic inch (diesel engines need 2).
Does a battery’s Cold Cranking Amps decrease over time?
What is considered to be a good CCA rating for a battery?
How can one determine the number of Cold Cranking Amps (CCAs) required for a specific vehicle?

How does cold weather impact a vehicle’s battery performance?
Why does a higher CCA battery last longer?
When it comes to batteries, the Cold Cranking Amps (CCA) rating plays a crucial role in determining their performance in cold weather conditions. A higher CCA battery is able to deliver more power at lower temperatures, making it easier to start your vehicle even on chilly mornings.
The reason why a higher CCA battery tends to last longer lies in its ability to provide that extra power when needed most. By having a greater reserve capacity, the battery can handle repeated starts and heavy electrical loads without getting drained quickly.
In essence, investing in a battery with a higher CCA rating not only ensures reliable starting power during cold weather but also contributes to an extended lifespan due to its robust performance capabilities. So next time you’re looking for a new car battery, consider opting for one with a higher CCA for lasting durability and reliability.
How to calculate Amp Hours from CCA in batteries?
Cold Cranking Amps (CCA) is a crucial factor to consider when choosing a car battery. It measures the ability of a battery to start your vehicle in cold weather conditions. The higher the CCA rating, the better the battery can perform in low temperatures.
Why does a higher CCA battery last longer?
A higher CCA-rated battery typically lasts longer because it has more reserve power to draw upon during cold starts. This means less strain on the battery and improved longevity over time.
How to calculate Amp Hours from CCA in batteries?
Calculating Amp Hours from Cold Cranking Amps involves understanding that 1 Ah is equivalent to 7.25 CCA for 30 seconds at 0°F (-18°C). Simply divide the CCA by 7.25 to get an estimate of the Amp Hours.
When selecting a car battery, remember that while CCA is important for starting power, it’s not indicative of overall performance or capacity. Consider factors like Reserve Capacity and cycling capabilities for a comprehensive view of your battery needs.

























